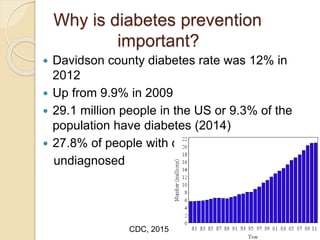
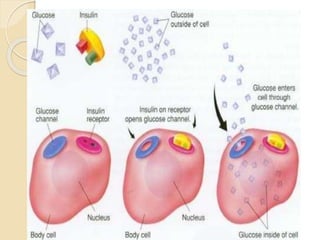
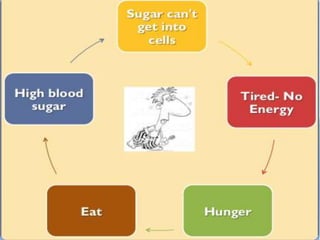
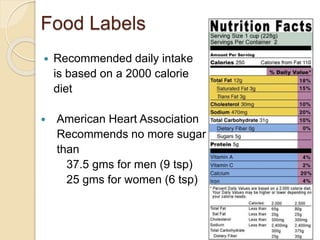
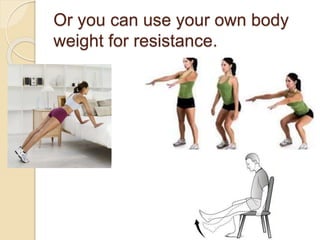
The document discusses the importance of diabetes prevention through lifestyle changes like healthy eating and regular physical activity. It notes that diabetes rates have risen significantly in recent years and poses serious health risks. Maintaining a healthy weight, diet low in sugar and high in fiber, and getting 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week can lower one's risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The document provides tips and resources for making these lifestyle changes.