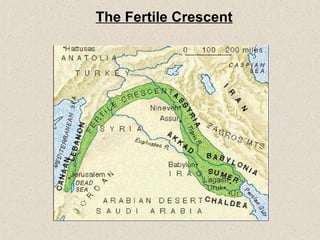
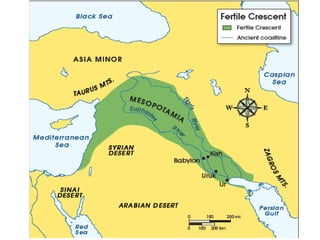
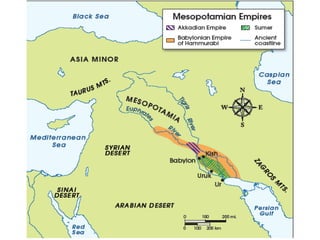
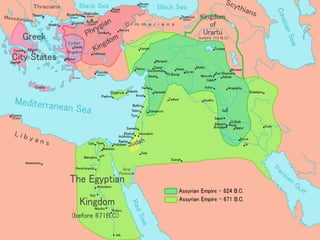
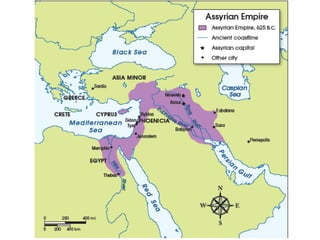
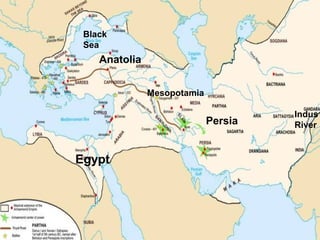
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, was home to some of the earliest civilizations including Sumer and later Akkad, Babylon, and Assyria. Sumerian cities like Ur featured ziggurats, temples dedicated to gods, and homes made of mudbricks. Around 3000 BC, Sumerians developed cuneiform writing and specialized labor led to social classes. The Epic of Gilgamesh details Sumerian beliefs. Later rulers like Hammurabi of Babylon and Cyrus of Persia expanded control over Mesopotamia.