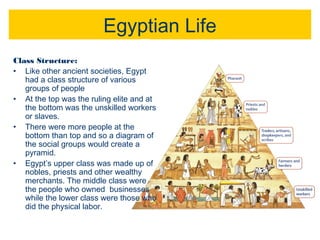
Ancient Egyptian society was divided into classes in a pyramid structure. The pharaoh and nobles made up the ruling class at the top as the religious and political leaders. Priests, scribes, merchants and artisans comprised the middle class of educated professionals and skilled workers. Farmers and laborers formed the largest lower class, which included slaves at the very bottom who worked for the pharaoh and nobles.