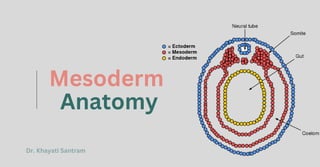
The mesoderm is a vital germ layer formed during embryonic development, located between the ectoderm and endoderm, and is crucial for organ and tissue formation. It differentiates into three types: paraxial mesoderm (muscles, bones), intermediate mesoderm (urogenital system), and lateral plate mesoderm (heart, blood vessels). Understanding the mesoderm's development and functions is essential for diagnosing and treating congenital disorders related to its abnormalities.