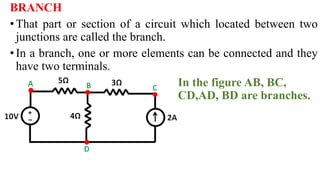
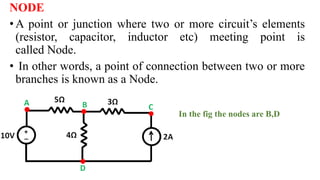
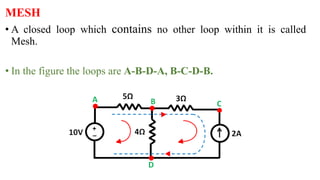
This document provides an overview of mesh and nodal analysis techniques for solving circuits. It defines key terms like branches, nodes, meshes, and loops. Mesh analysis involves identifying meshes, labeling mesh currents, writing mesh equations using KVL and Ohm's law, and solving the equations for currents. Nodal analysis involves identifying nodes, choosing a reference node, assigning voltages, writing KCL equations for each node setting the sum to zero, and solving the system. Examples of applying each technique are provided.