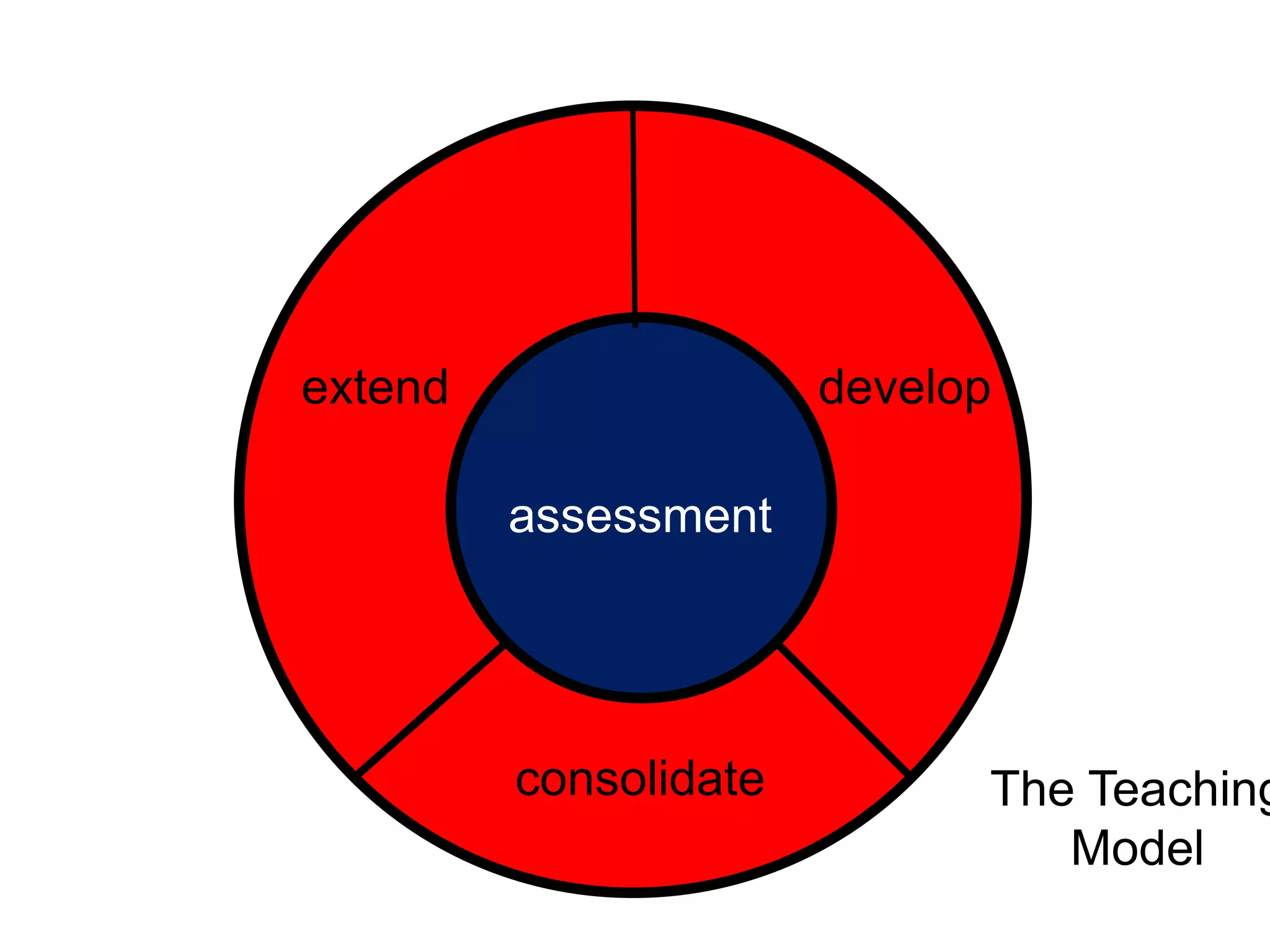
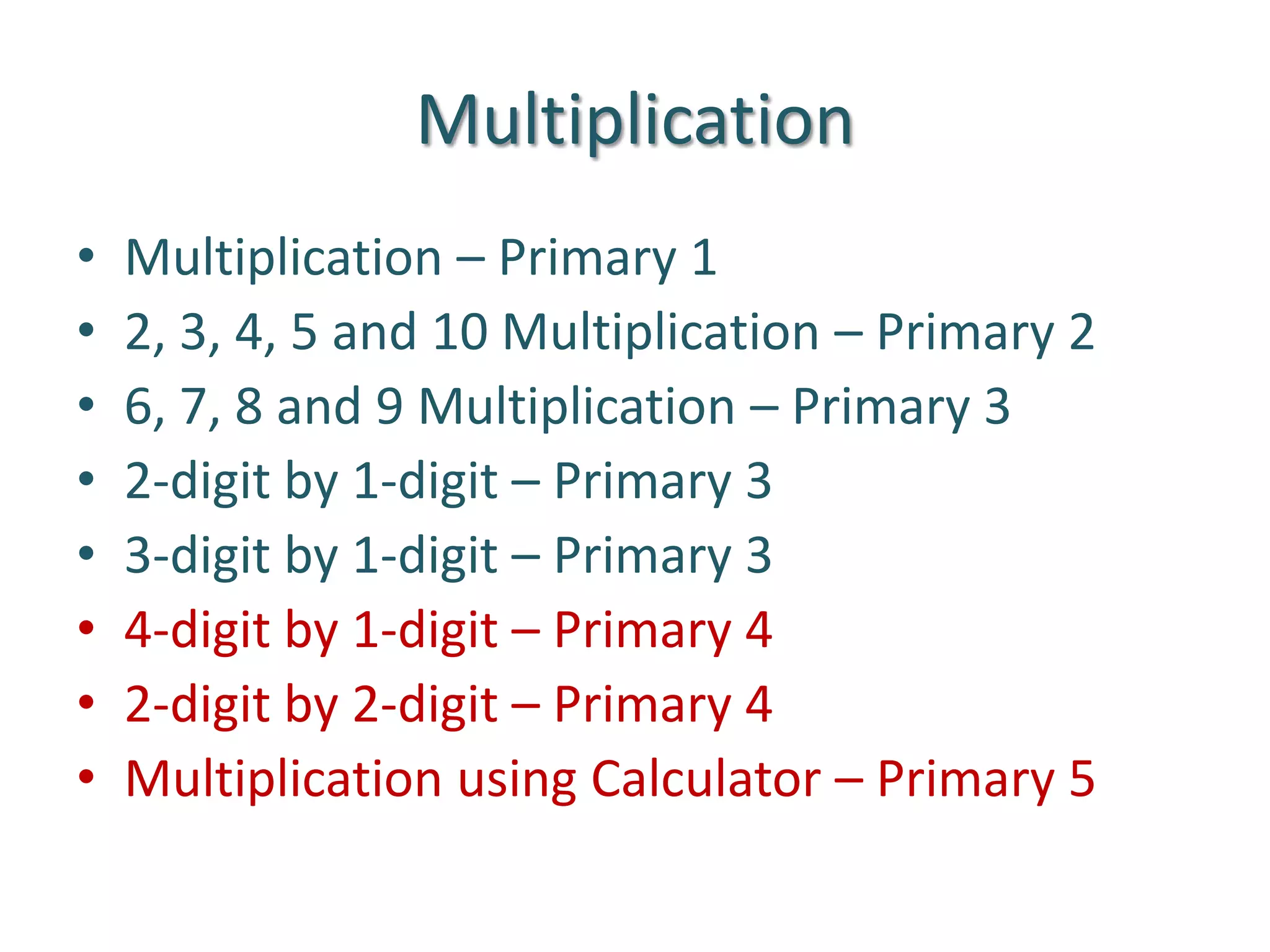
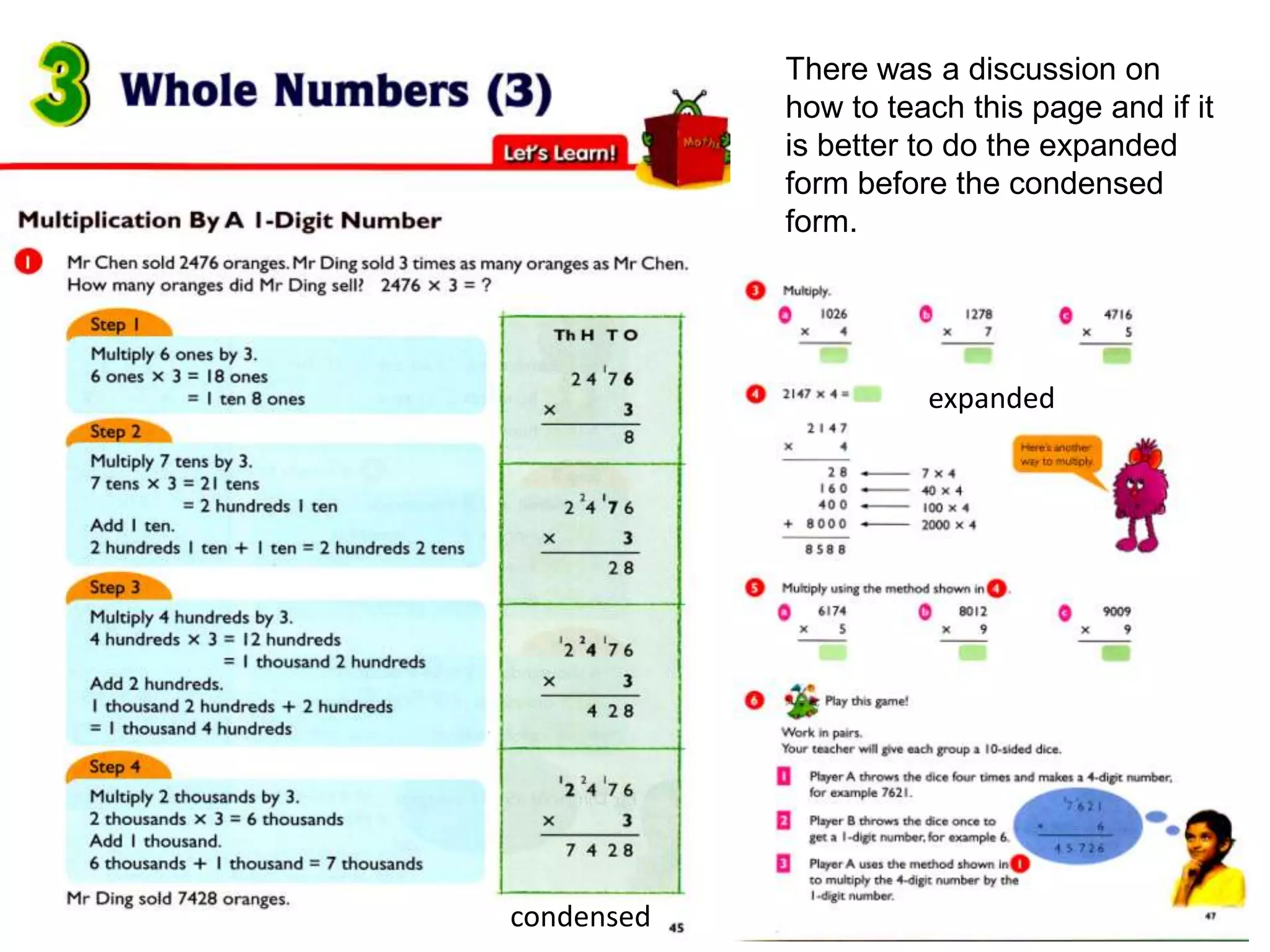
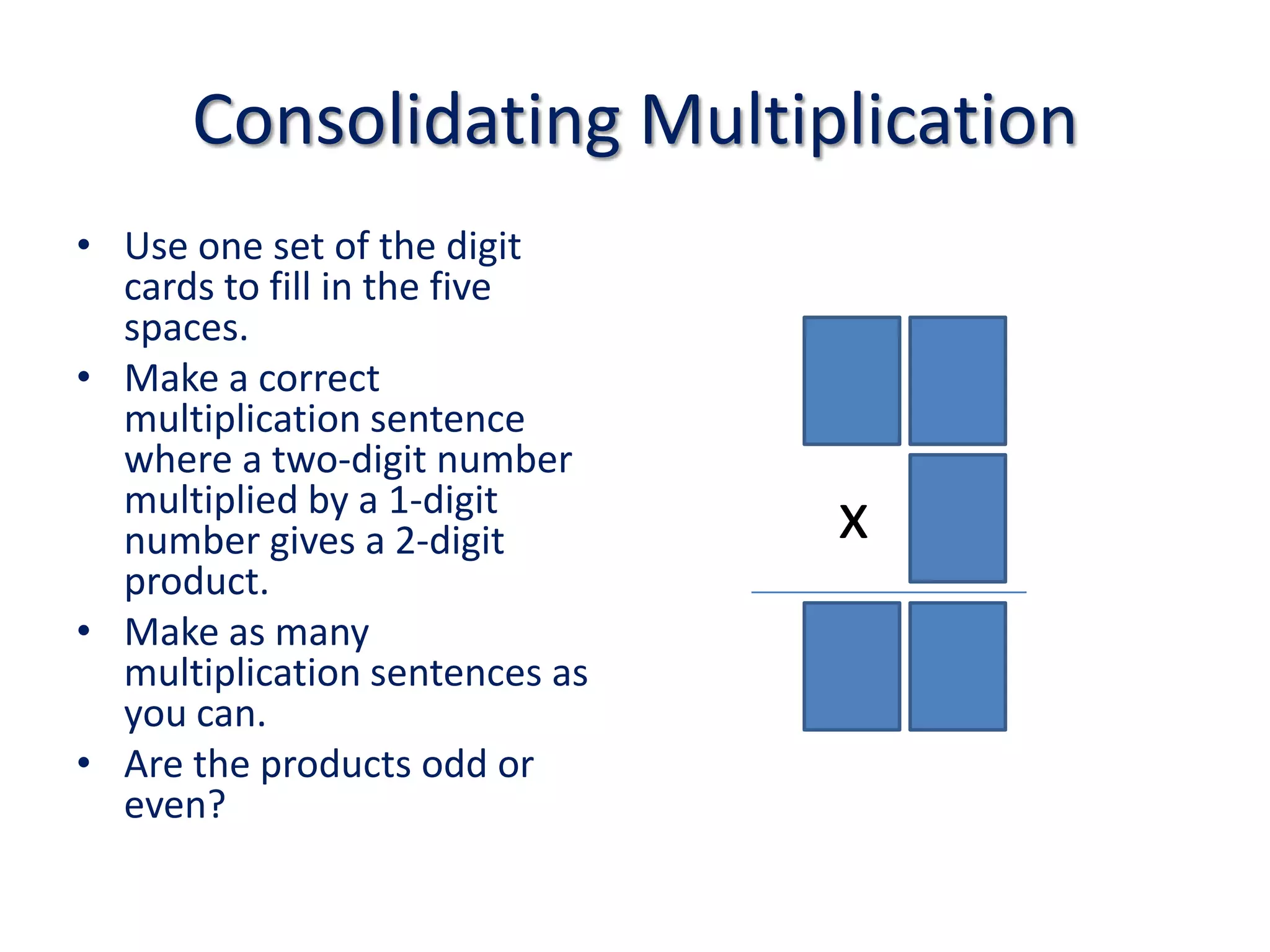
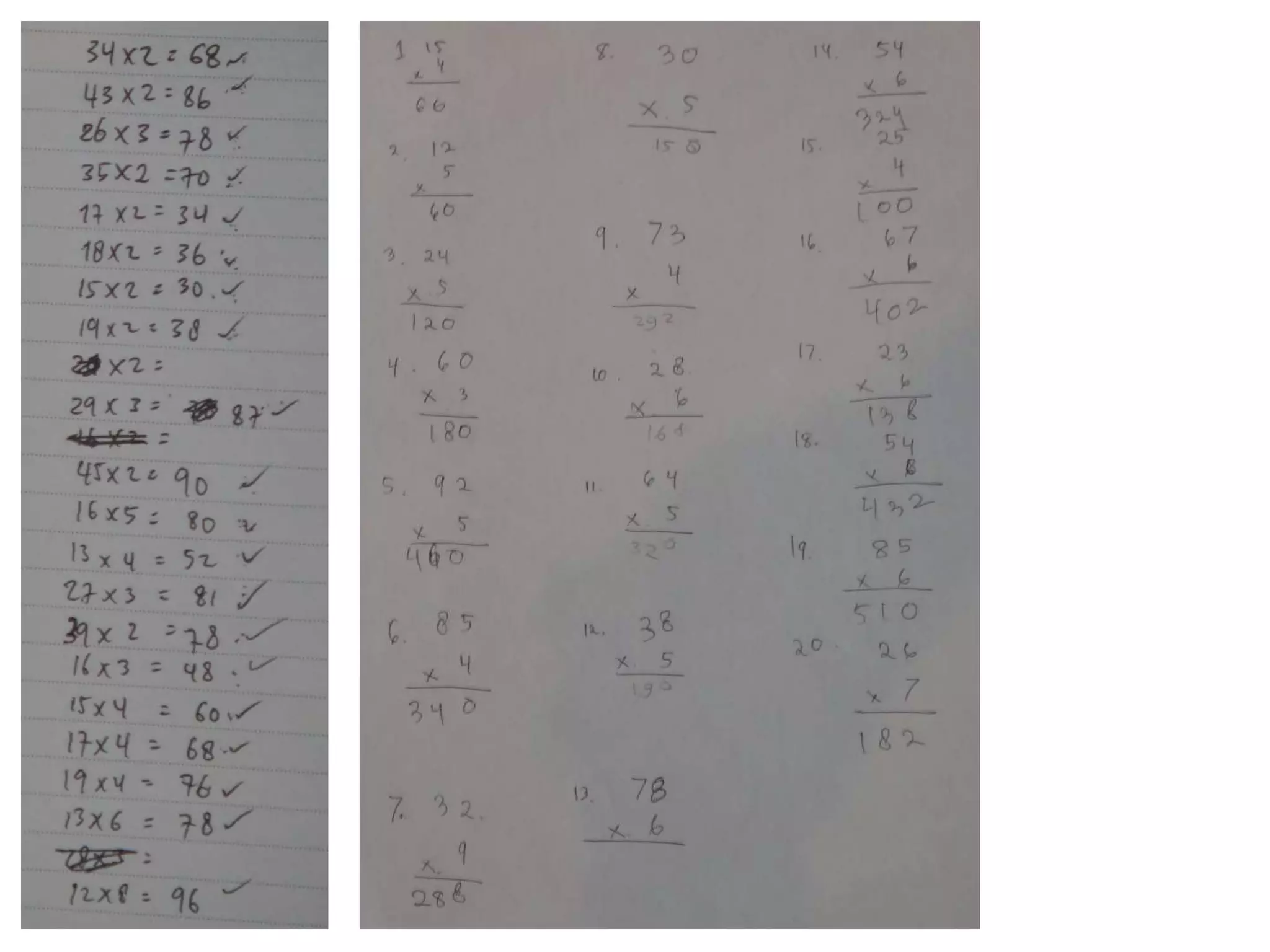
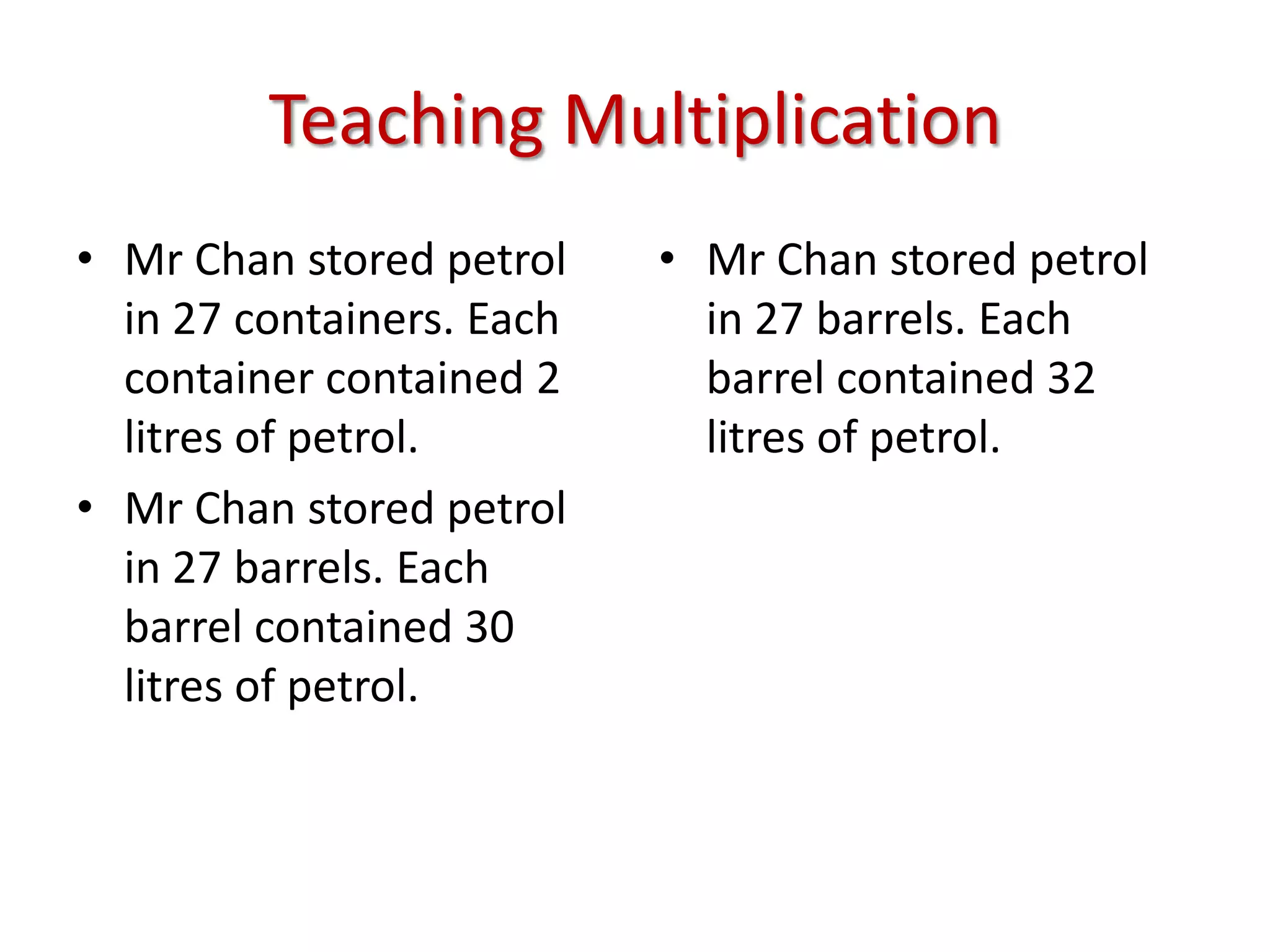
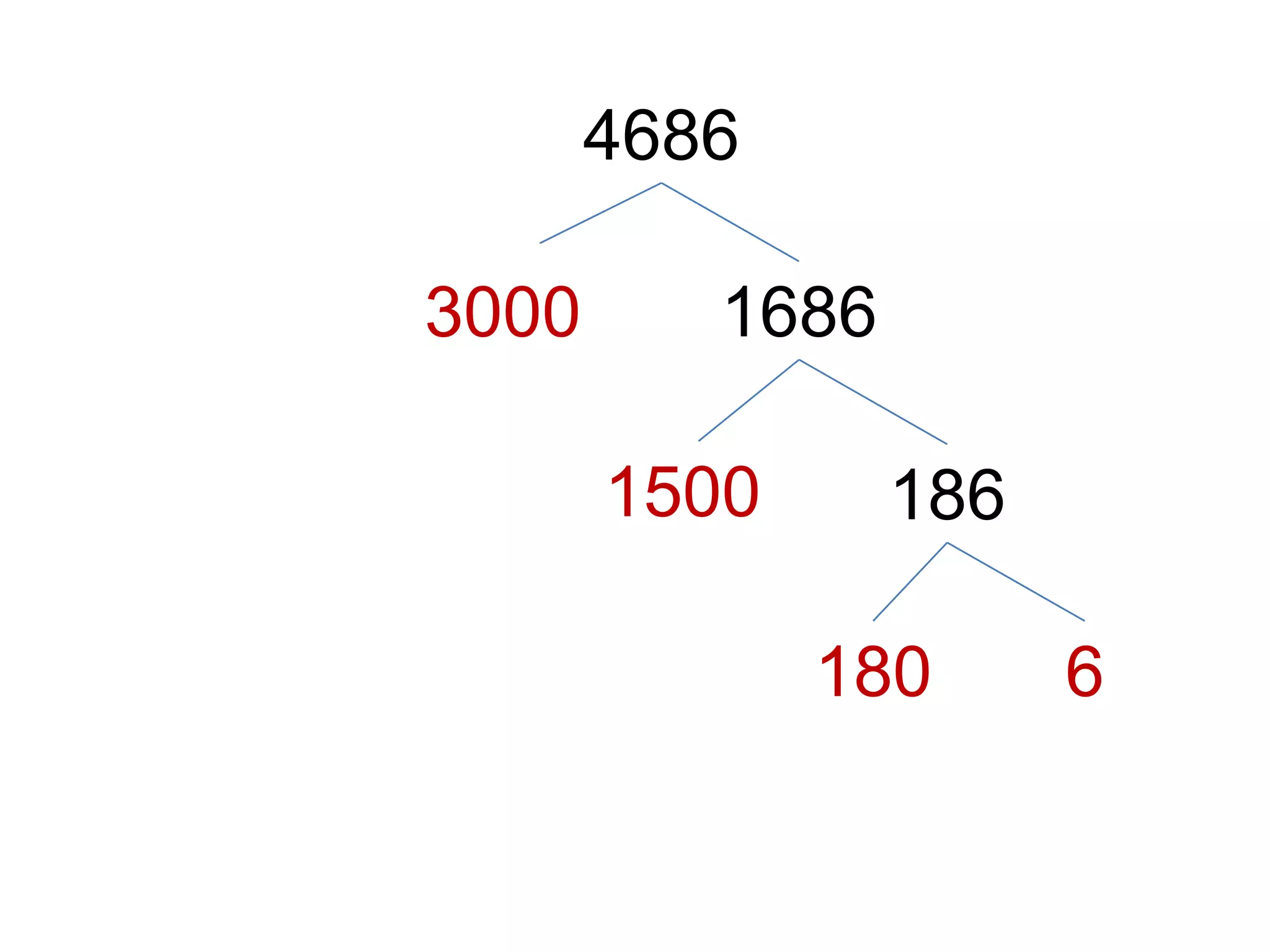
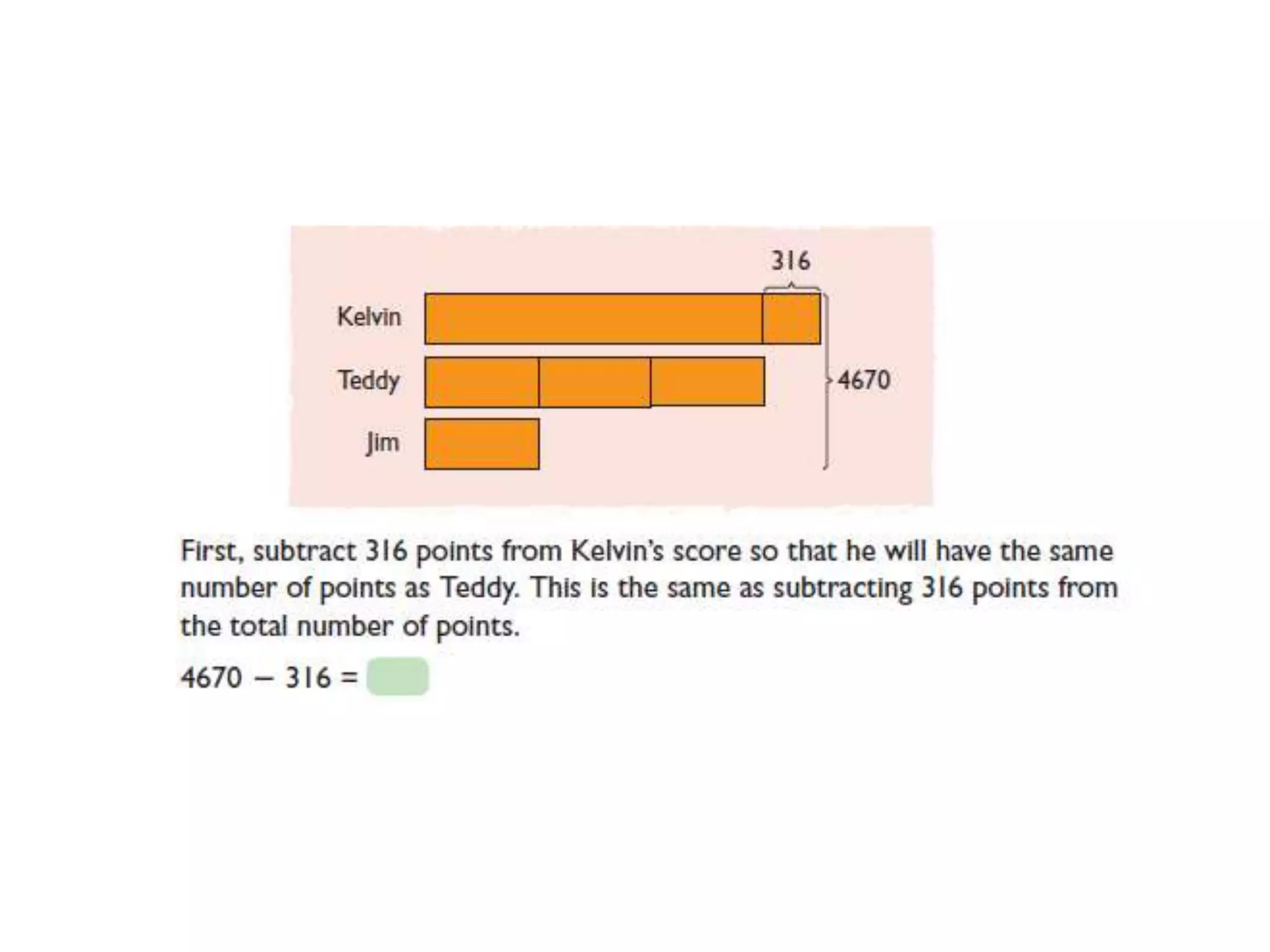
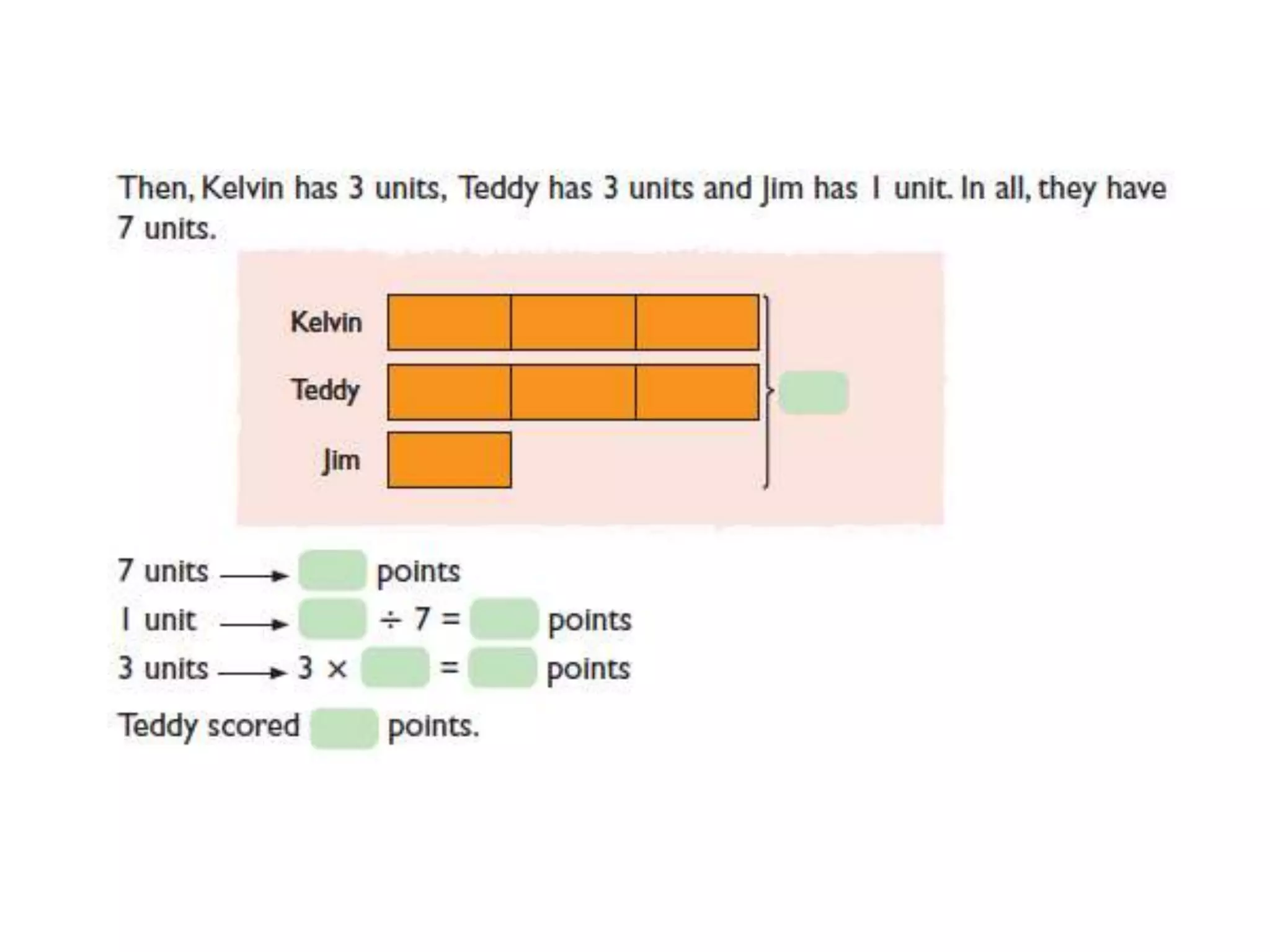
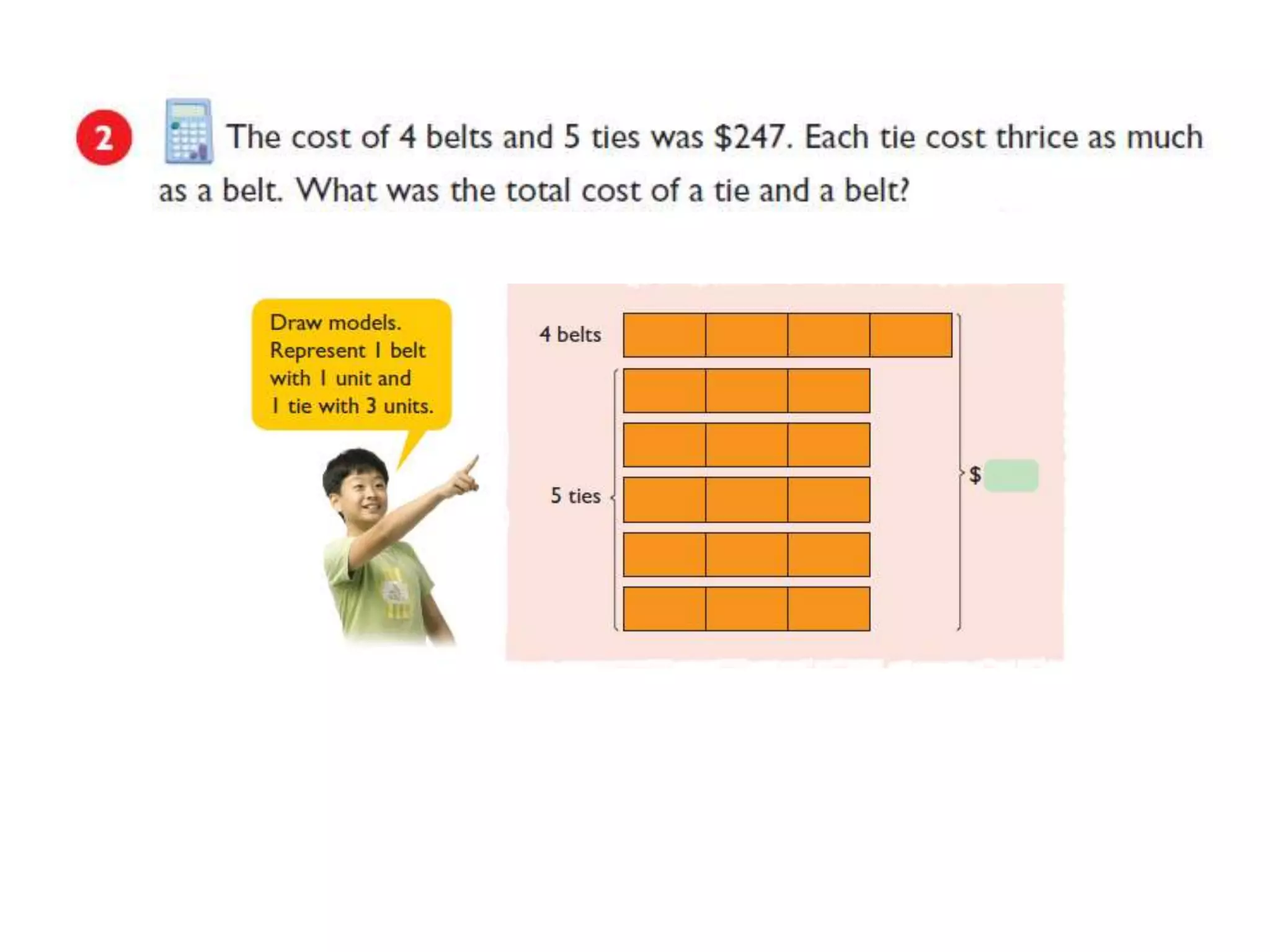
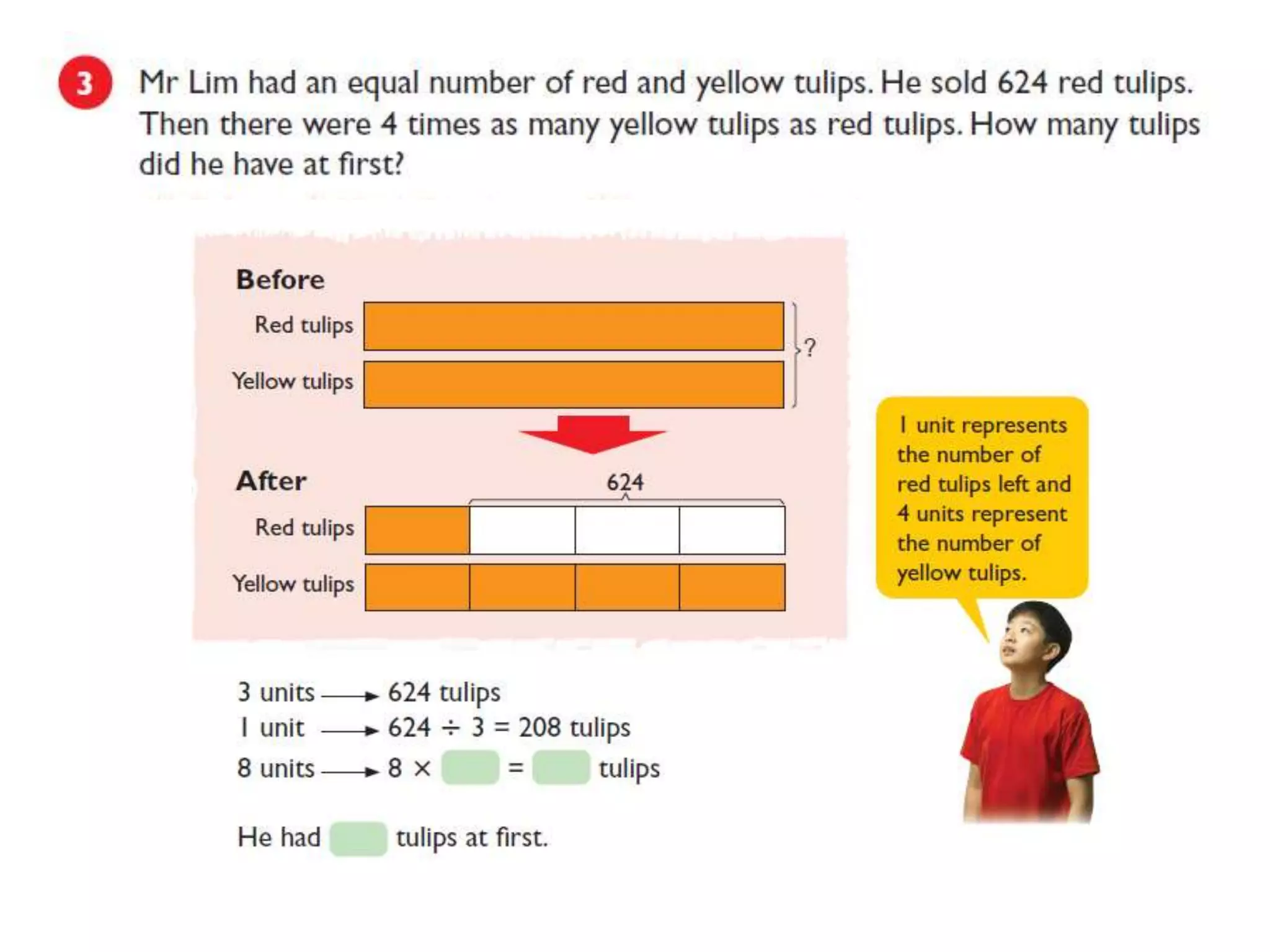
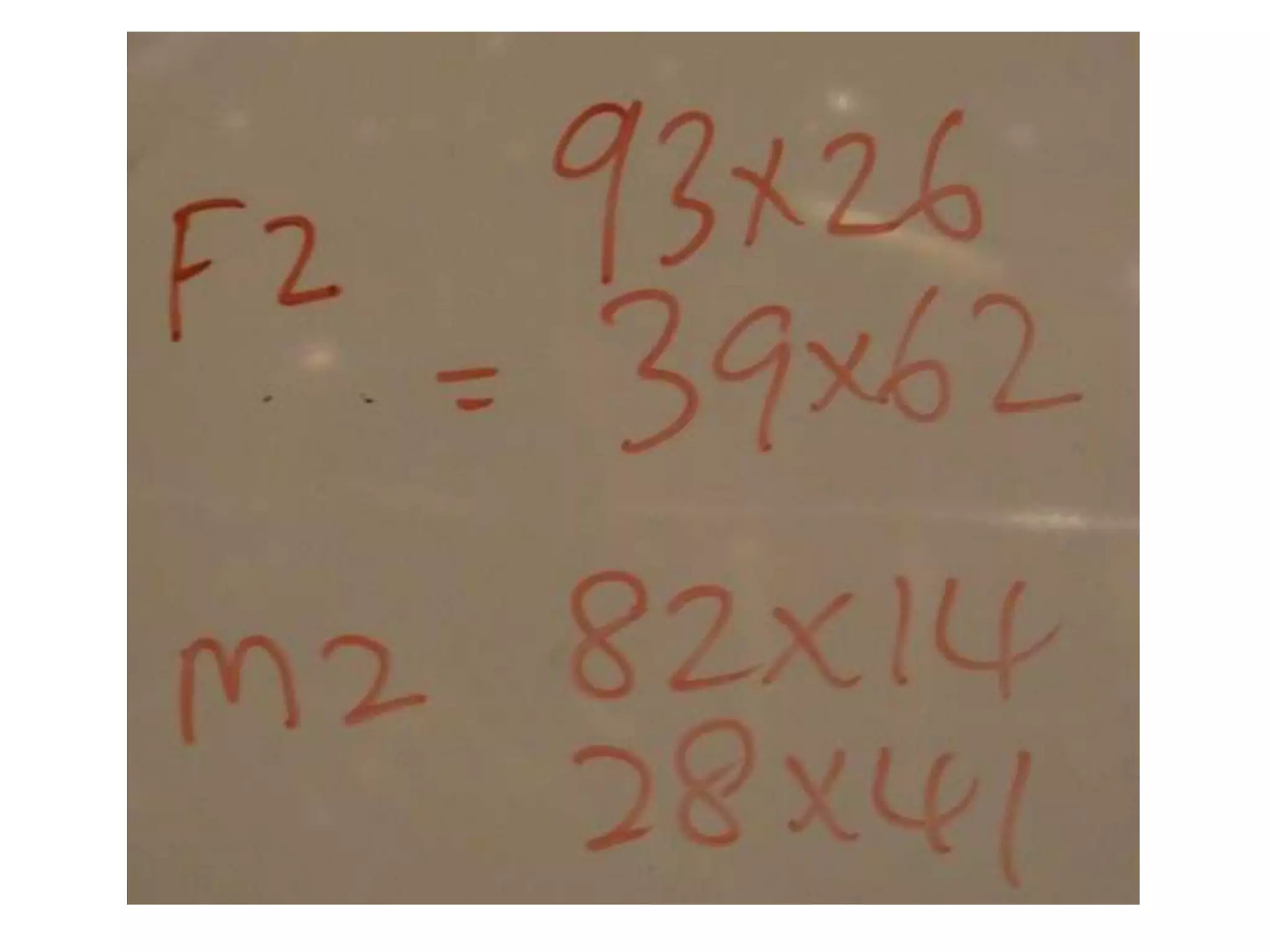The document is a teaching guide from the National Institute of Education focusing on mathematics instruction for primary students, covering key concepts such as place value, multiplication, and division. It includes teaching methodologies, example problems, and activities to enhance students' understanding of numbers and operations. The guide emphasizes the importance of regrouping in multiplication and problem-solving strategies across various mathematical scenarios.