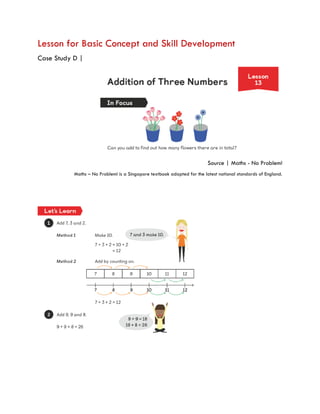
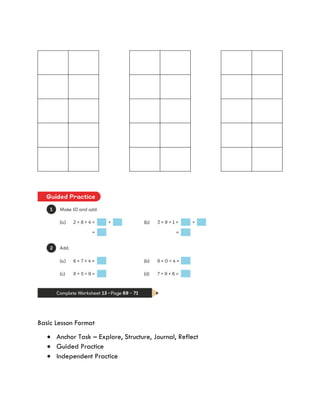
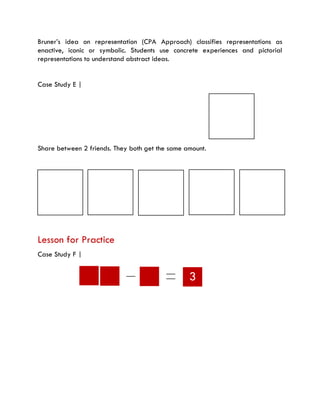
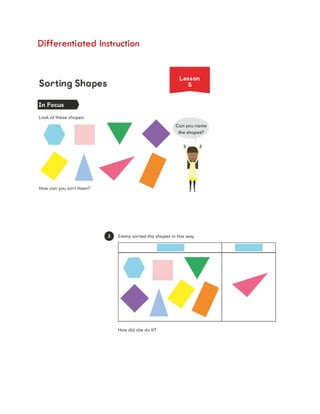
The document discusses effective teaching strategies for Grade 1 mathematics, emphasizing the importance of understanding concepts like counting through relational understanding rather than merely through memorization. It presents case studies and a structured lesson format that incorporates various mathematical concepts and the CPA (Concrete, Pictorial, Abstract) approach to enhance student learning. Key educational theories by Piaget, Bruner, Dienes, Vygotsky, and Skemp are highlighted as foundational to differentiated instruction in mathematics.