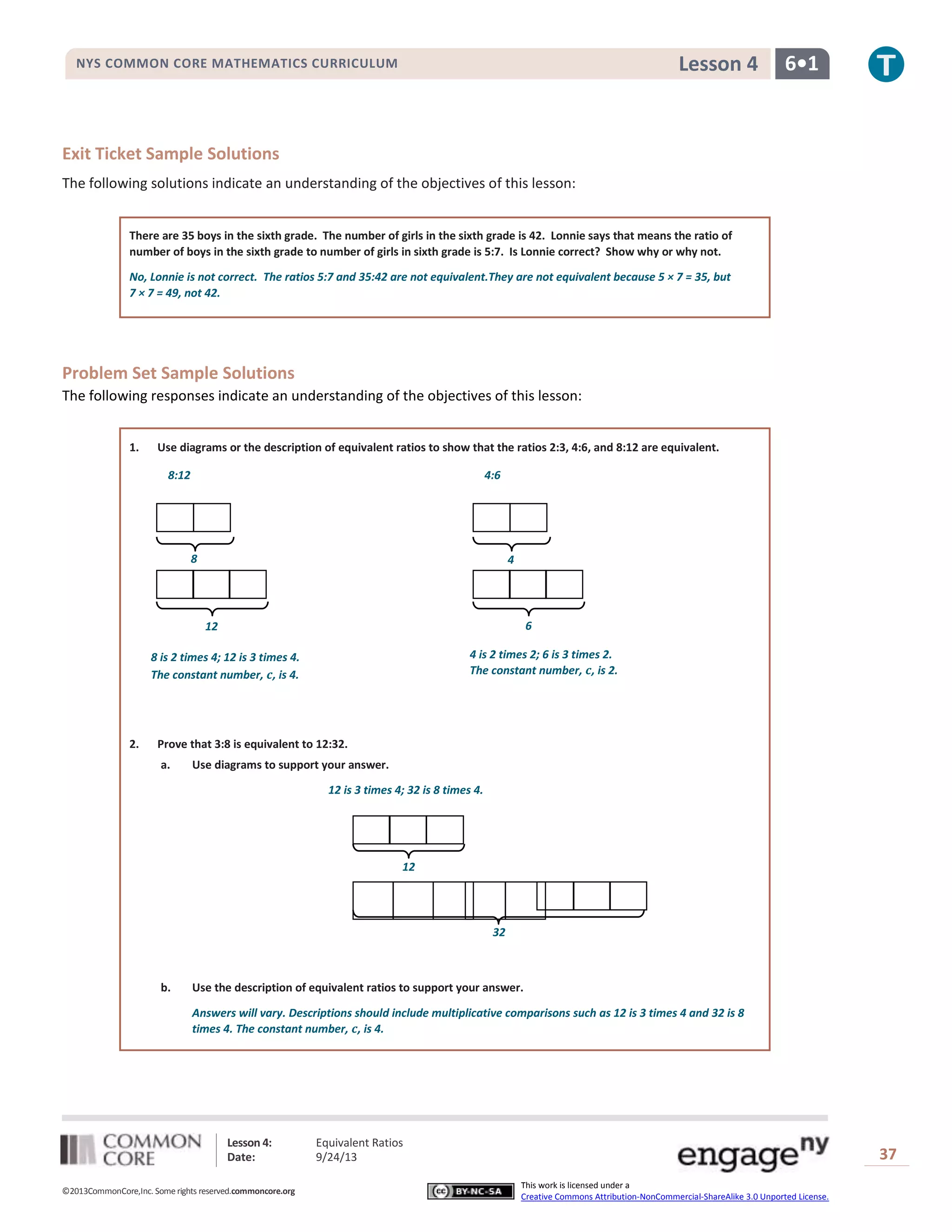
This document provides a lesson on equivalent ratios for 6th grade students. It includes examples and exercises for students to practice determining if two ratios are equivalent. The key points are:
- Ratios are equivalent if there is a positive number that can be multiplied to each part of one ratio to equal the corresponding parts of the second ratio.
- Tape diagrams can be used to represent ratios and determine if the diagrams have a consistent unit value, showing the ratios are equivalent.
- Students work through sample problems applying the definition of equivalent ratios and using tape diagrams to justify their answers.