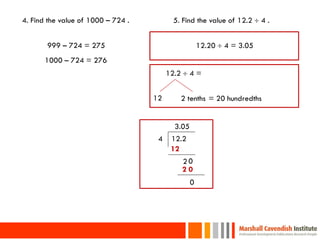
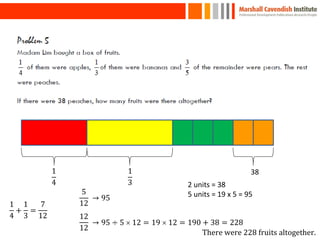
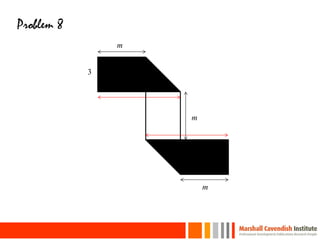
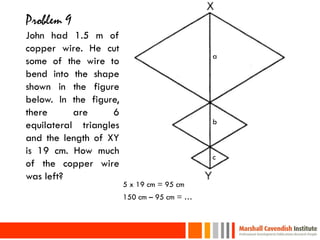
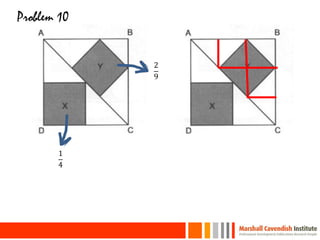
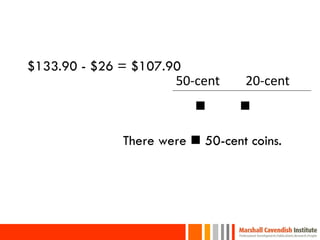
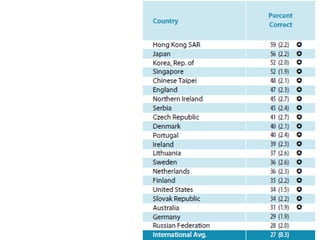
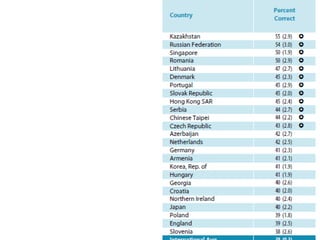
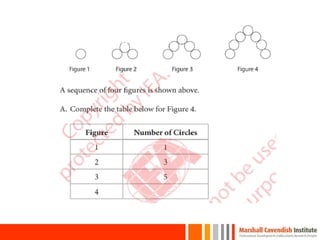
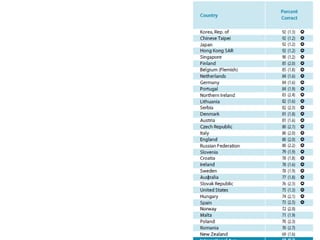
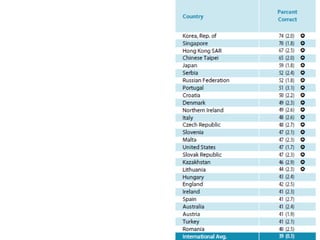
This document provides a summary of a presentation on surviving math given by Dr. Yeap Ban Har from the Marshall Cavendish Institute in Singapore. The presentation included slides available on Facebook and discussed shifts in math test questions over time towards requiring more conceptual understanding. It also showed sample math problems and performance data from Primary 4 students in Singapore on TIMSS tests. The document lists the speaker, location, contact information and source of additional slides.