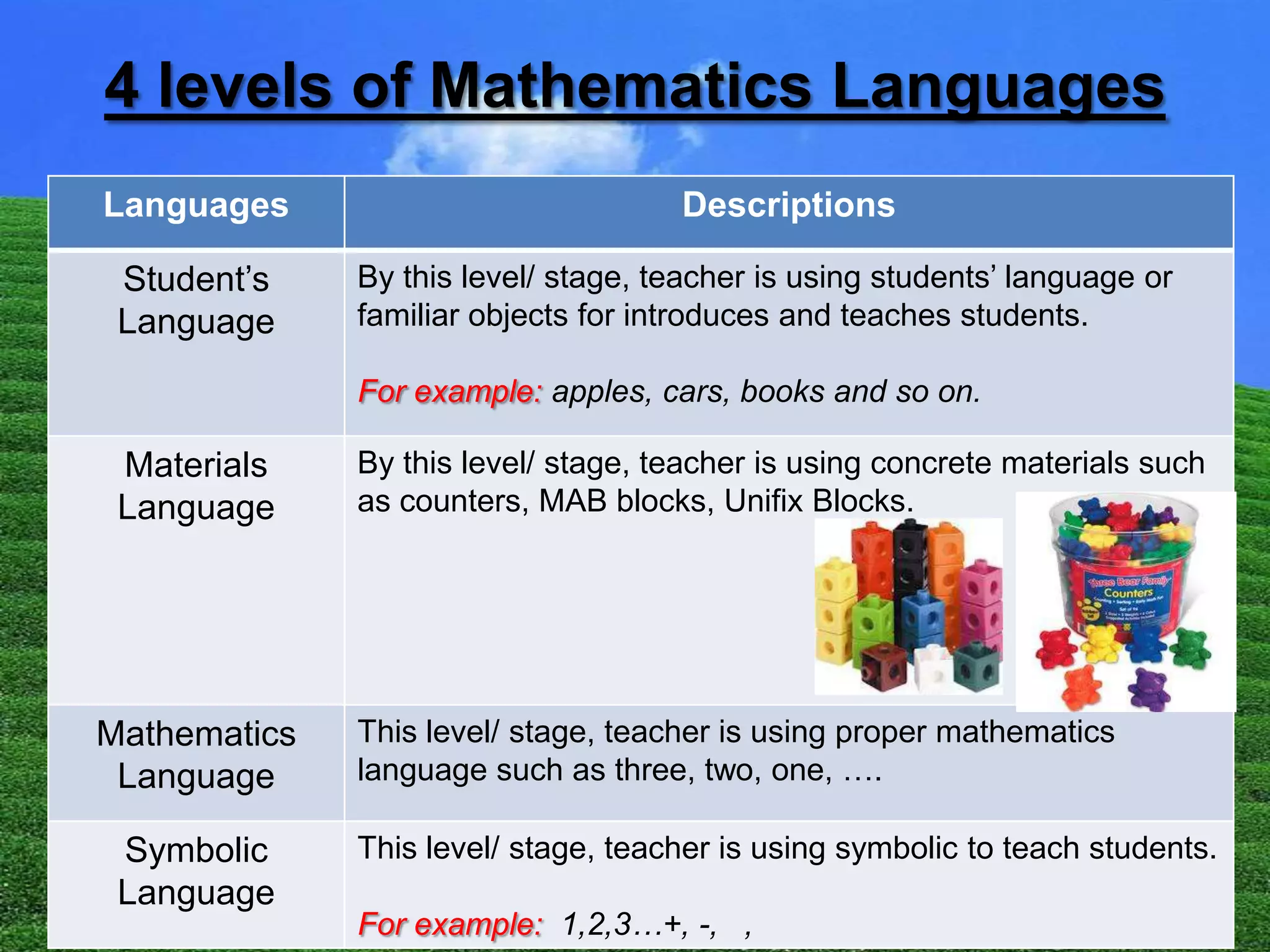
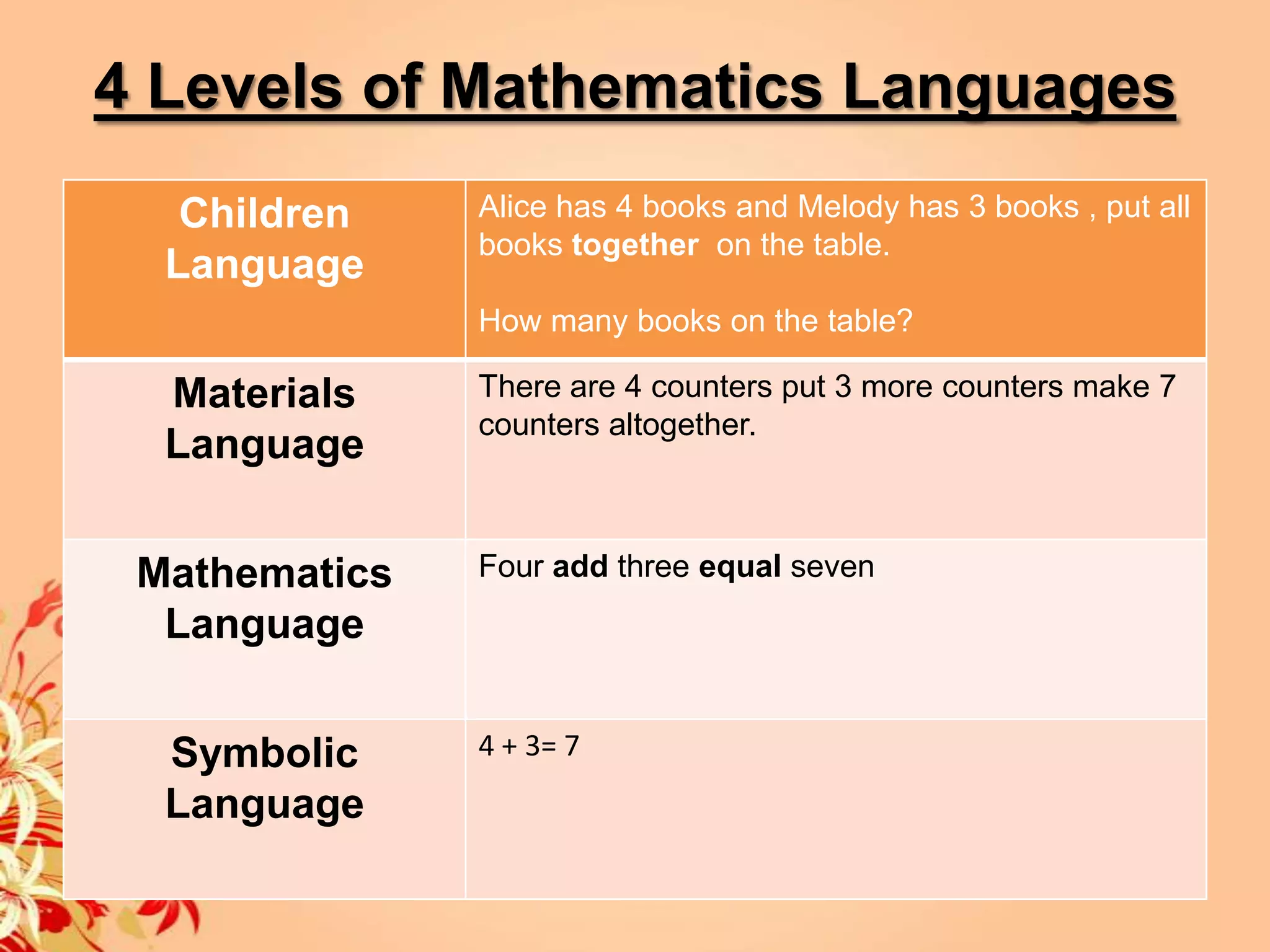
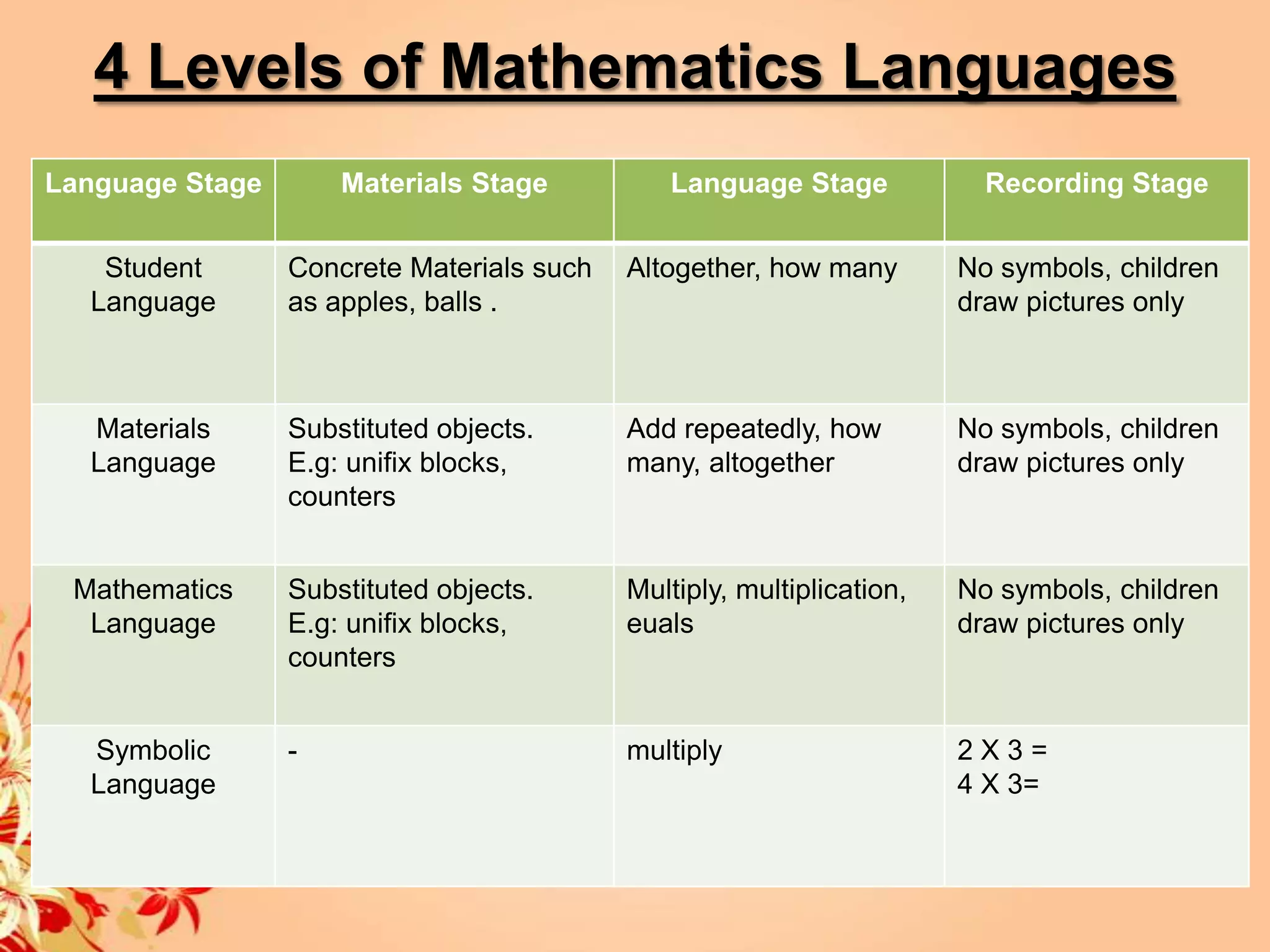
1) The document discusses 4 levels of mathematics language used in teaching: students' language using familiar objects, materials language using concrete objects, mathematics language using proper terms, and symbolic language using symbols.
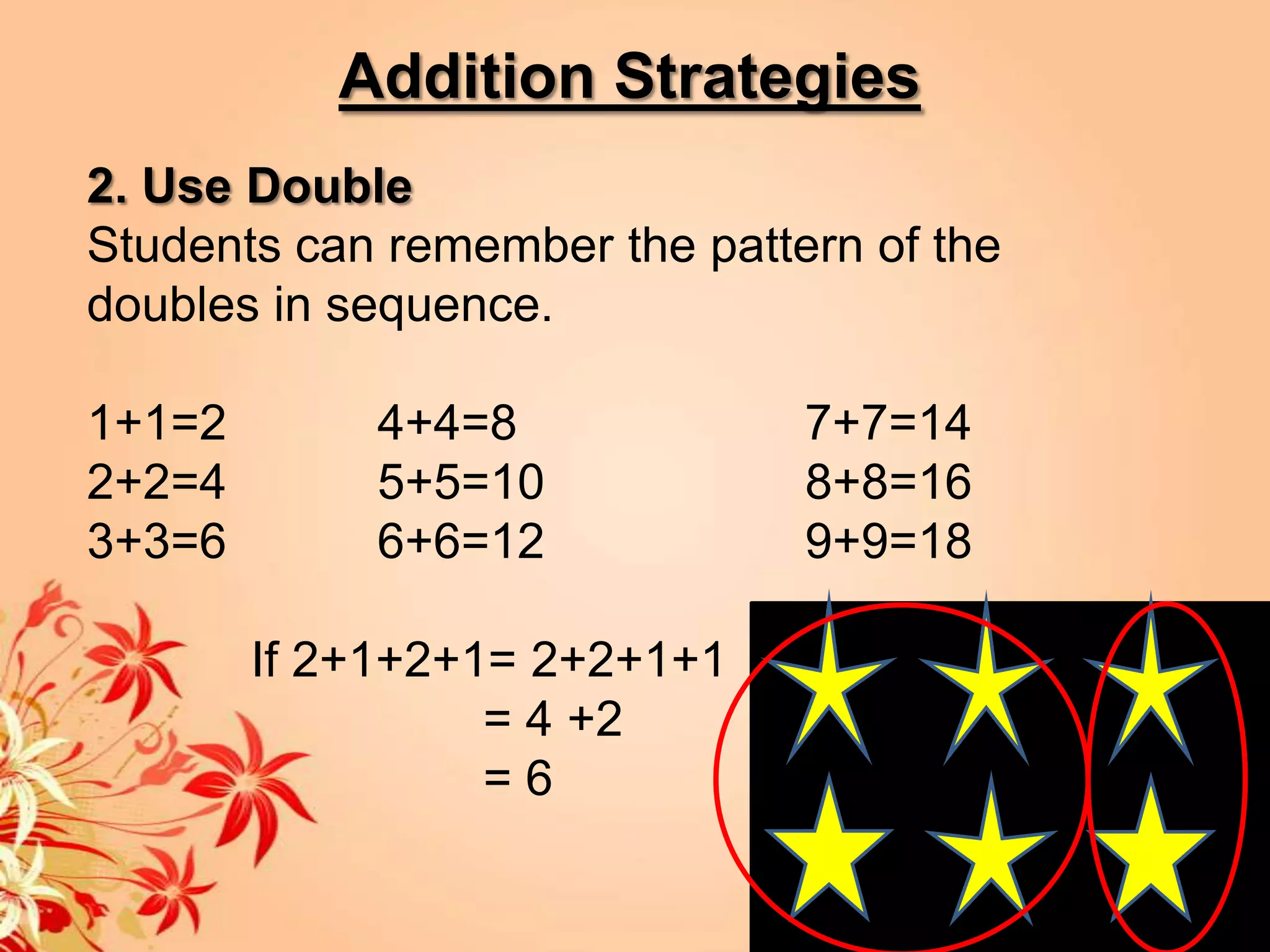
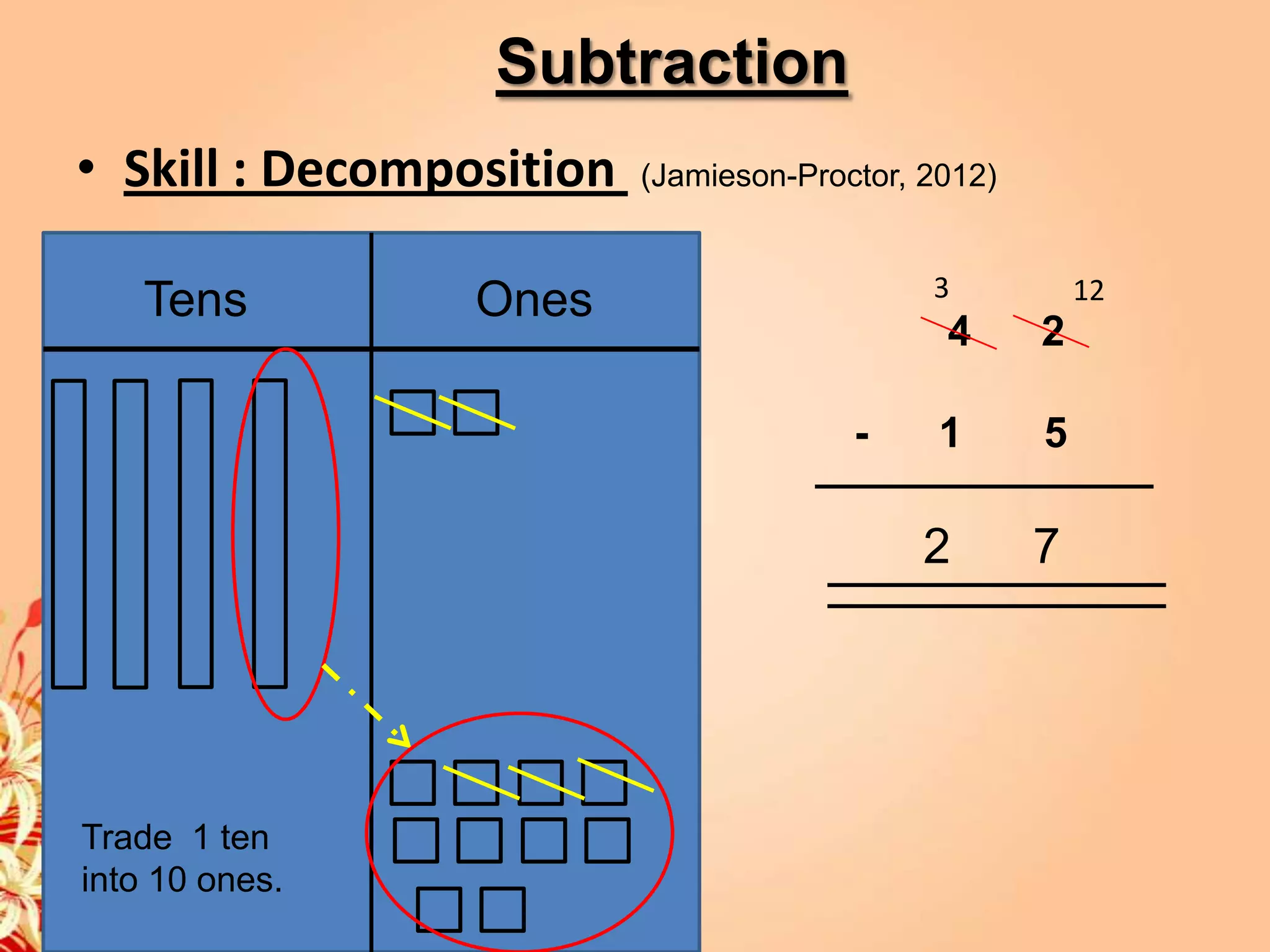
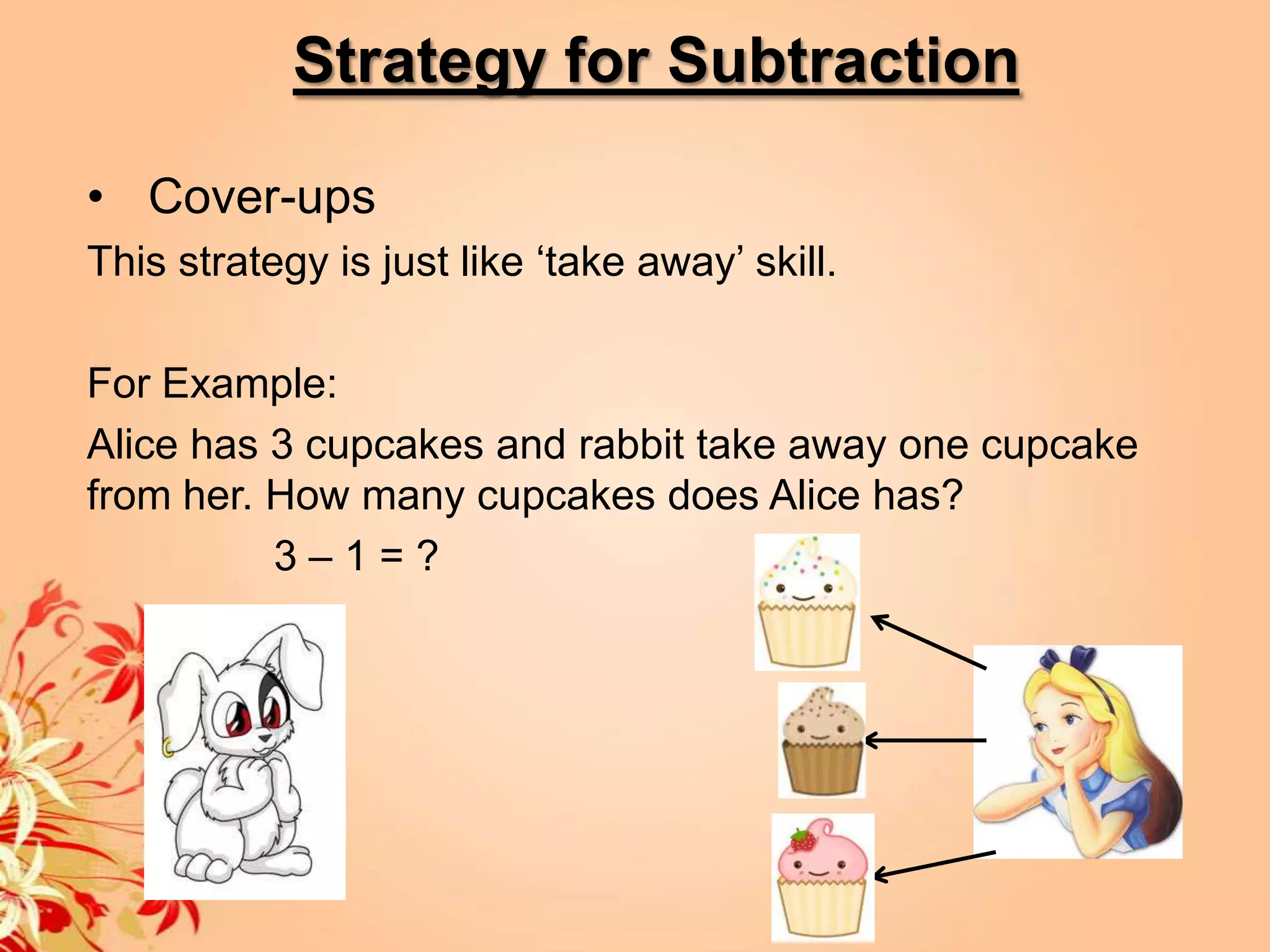
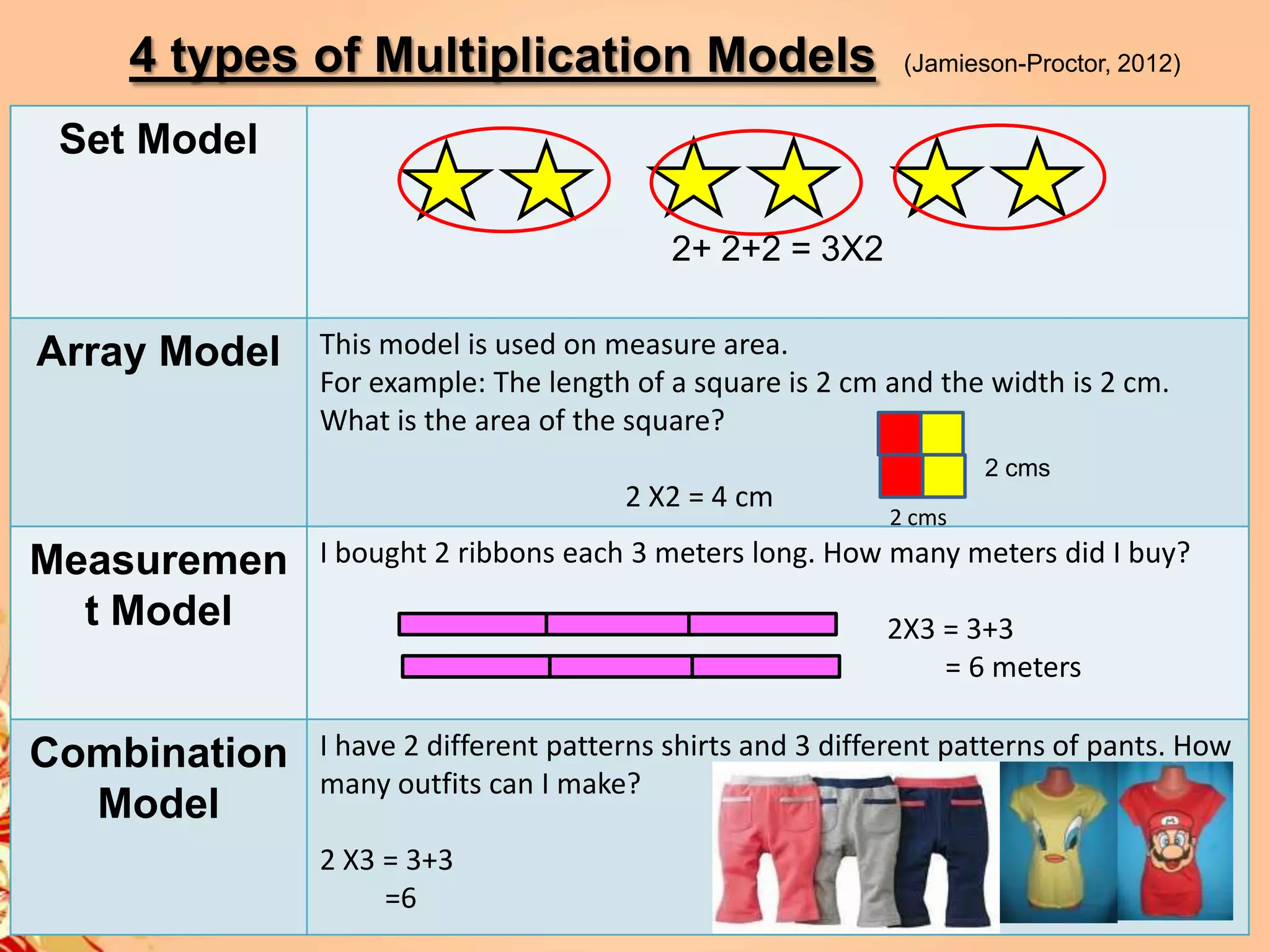
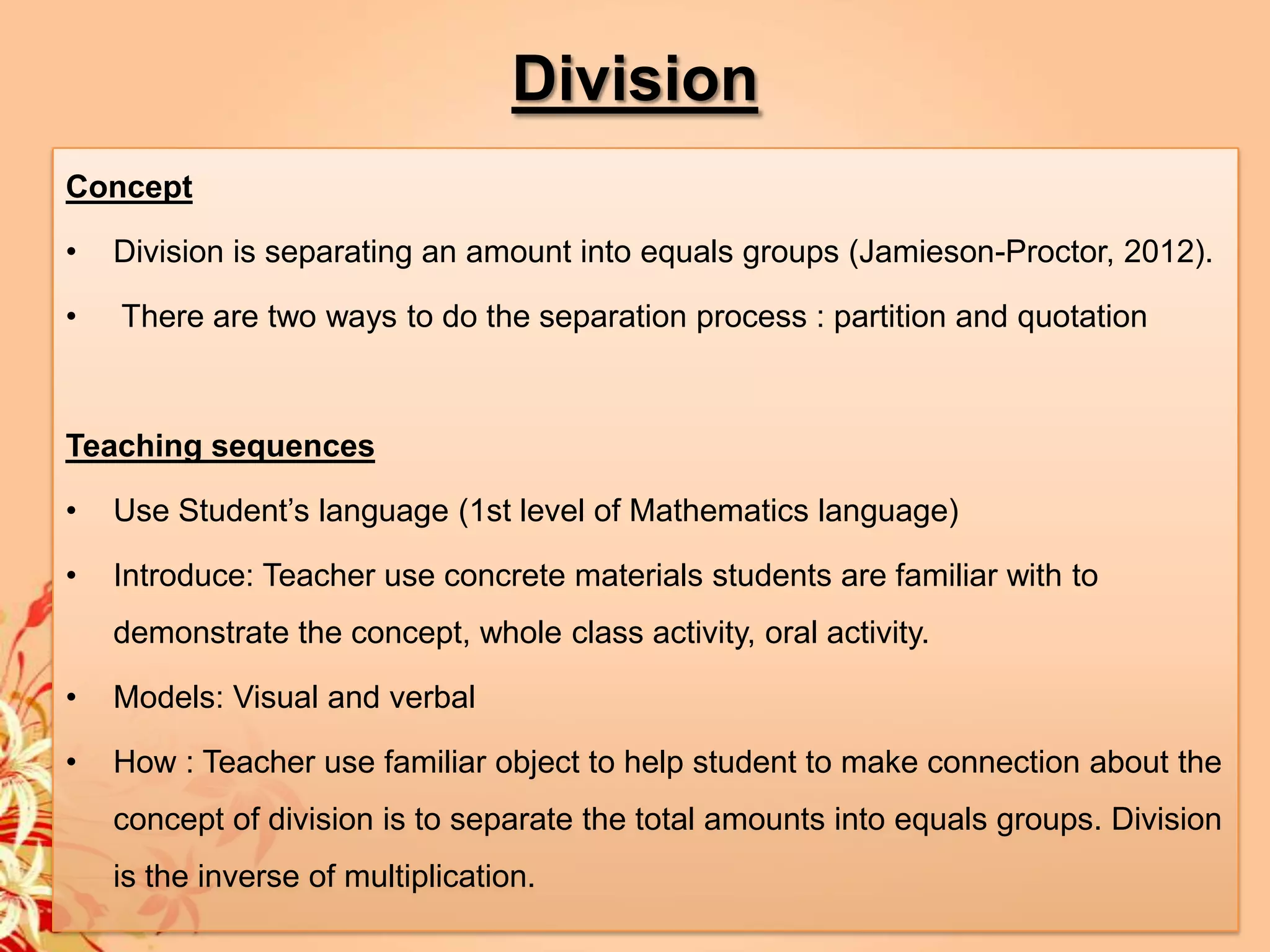
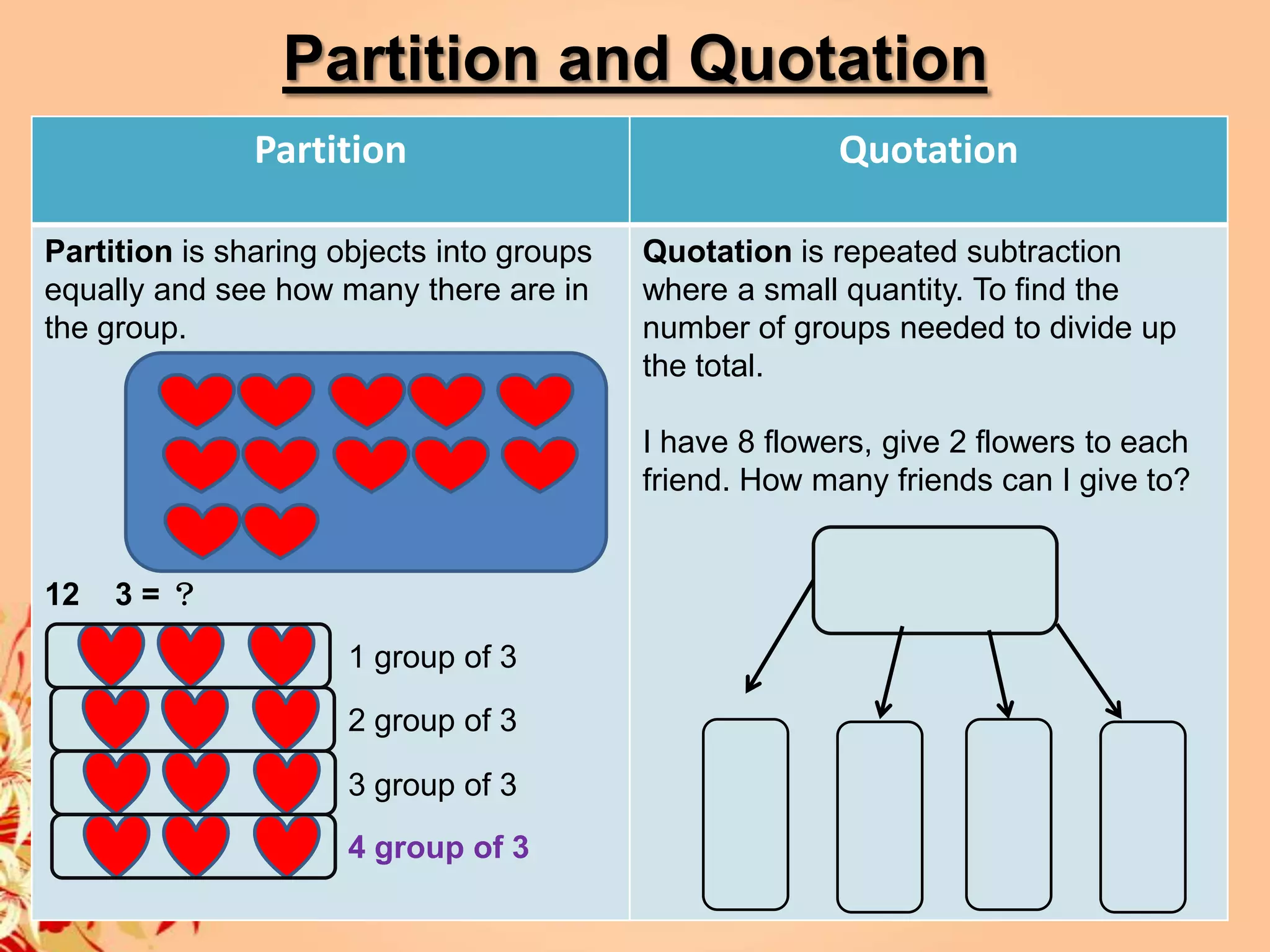
2) It provides strategies and concepts for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, including counting on, doubles, decomposition, cover-ups, repeated addition, arrays, measurements, combinations, partitioning and quoting.
3) Visual and verbal models are recommended for introducing new concepts along with using familiar objects and materials to help students make connections.