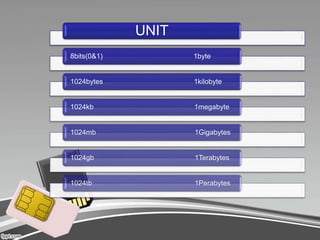
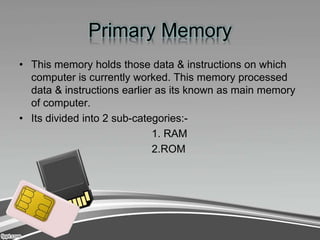
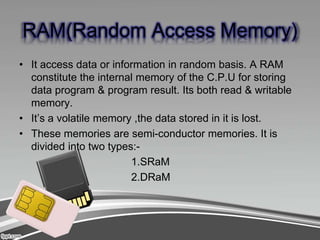
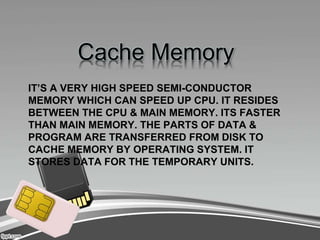
Computer memory comes in four main types: primary, secondary, cache, and register. Primary memory, also known as RAM, is the memory that holds data and instructions currently being processed by the CPU. It is volatile and divided into RAM and ROM. RAM is random access and can be written to, while ROM is read-only and helps boot the computer. Secondary memory includes storage devices like hard disks, floppy disks, and tapes, which allow permanent storage of data that can be transferred back to primary memory when needed. Cache memory resides between the CPU and primary memory to speed up access, while register memory is the smallest, fastest memory attached directly to the processor.