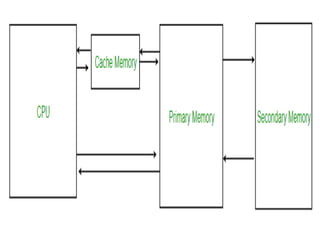
Computer memory can be divided into three types: cache memory, primary/main memory, and secondary memory. Primary memory is directly accessible by the CPU and stores active data and instructions but loses data when powered off, consisting of RAM and ROM. RAM is read-write volatile memory for active data and programs while ROM is permanent read-only memory for firmware. Secondary memory is non-volatile storage like hard disks that the CPU accesses indirectly via primary memory and is used for permanent storage. Cache memory is very fast memory between the CPU and primary memory for frequently used data and instructions.