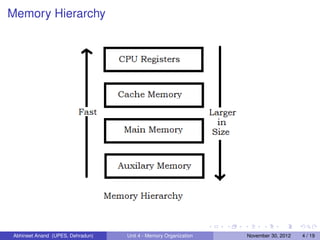
The document discusses memory organization and includes sections on main memory, auxiliary memory, associative memory, cache memory, and virtual memory. It describes the memory hierarchy from CPU registers to main memory to auxiliary storage. Main memory uses static or dynamic RAM, while auxiliary memory includes magnetic disks and tapes. Cache memory aims to reduce memory access time by keeping frequently used data close to the CPU. Mapping techniques for cache include associative, direct, and set-associative mappings. Virtual memory allows programs to access memory addresses beyond physical main memory by mapping them to auxiliary storage locations.