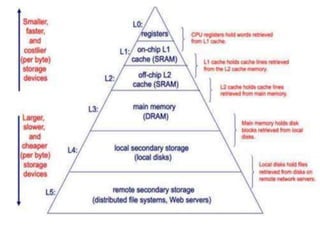
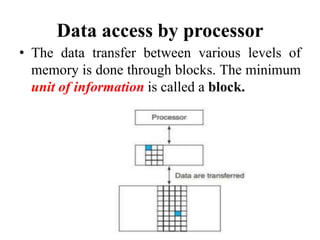
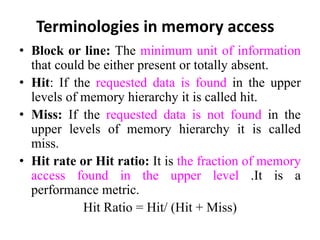
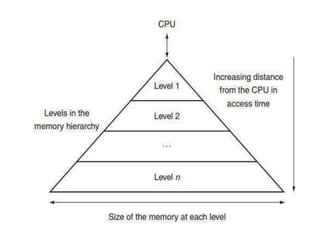
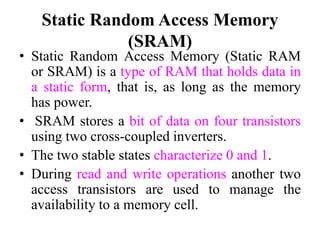
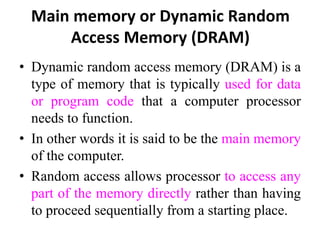
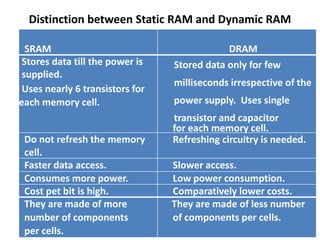
The document discusses computer memory hierarchy and input/output organization. It explains that memory is organized in a hierarchy with different levels that have varying speeds and sizes. The faster but smaller and more expensive memories (like CPU registers and cache) sit at the top, while the slower but larger and cheaper memories (like hard disks) sit at the bottom. This organization exploits the principle of locality, where data accessed recently is likely to be accessed again. It provides details on each level of memory and concepts like hit rate, miss rate, hit time and miss penalty in memory access.