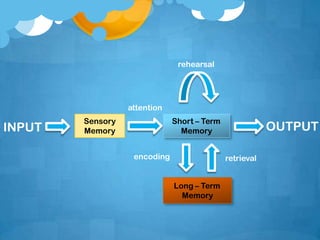
There are three types of memory: sensory memory, short-term memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory briefly stores impressions from the senses. Short-term memory acts as a temporary storage for a small amount of information. Long-term memory can store unlimited information indefinitely. Long-term memory includes explicit (declarative) memory of facts and events, and implicit (procedural) memory of skills. Encoding and retrieval are important for moving information between memories. Strategies help with encoding information into long-term memory and retrieving it.












![Retrieval involves drawing on existing knowledge. It forms the basis
for all new knowledge. Retrieval of prior knowledge during learning
directly affects the amount of new information that can be
processed. At-risk students often have low funds of previous
knowledge, hampering retrieval and, therefore, the learning
process.
A distinction between retrieval and realizing, again based on the
issue of intentionality, is made by some authors. "In an intentional
memory task, remembering is deliberately influenced by directing
attention to certain contents in the working memory. This type of
remembering is called retrieval. Retrieval may be conceived as
realizing plus emergence produced by intentional manipulations”
Herrmann, Raybeck and Gutman. Unintentional remembering is
referred to as realizing. "Retrieval is more likely to result in
[remembering] useful information than realizing since retrieval
deliberately goes after certain memories whereas realizing occurs
without a purpose” Herrmann, Raybeck and Gutman.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/memoryandforgettinginpsy-210430201204/85/Memory-and-forgetting-in-Educational-Psychology-14-320.jpg)



