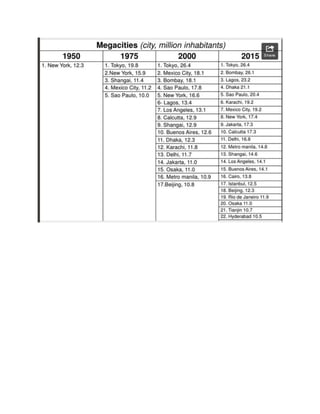
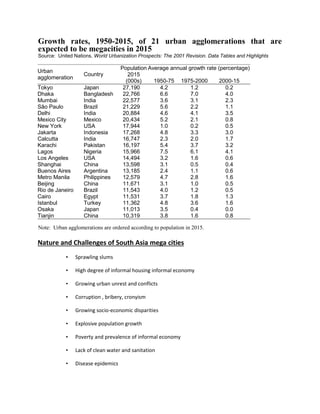
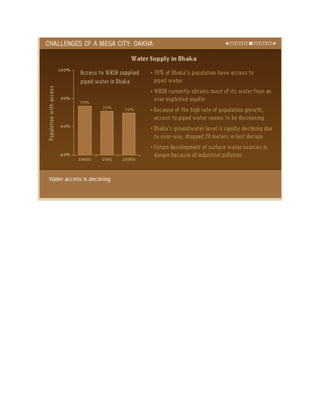
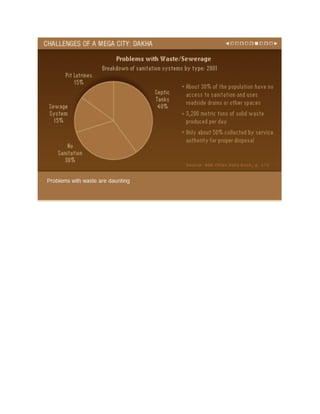
South Asia is experiencing rapid urbanization, with five of its cities projected to be among the largest in the world by 2015. This growth is driven by rural-to-urban migration as people seek economic opportunities. However, many migrants end up living in slums lacking basic services. The region's megacities face challenges like sprawling slums, poverty, disease, pollution and lack of infrastructure. Dhaka has experienced extreme population growth and now has over 12 million residents, with many living in poor conditions. Other large and growing South Asian cities discussed are Mumbai, Delhi, and Karachi. Effective solutions are needed to manage urban growth and improve living standards in a sustainable manner.