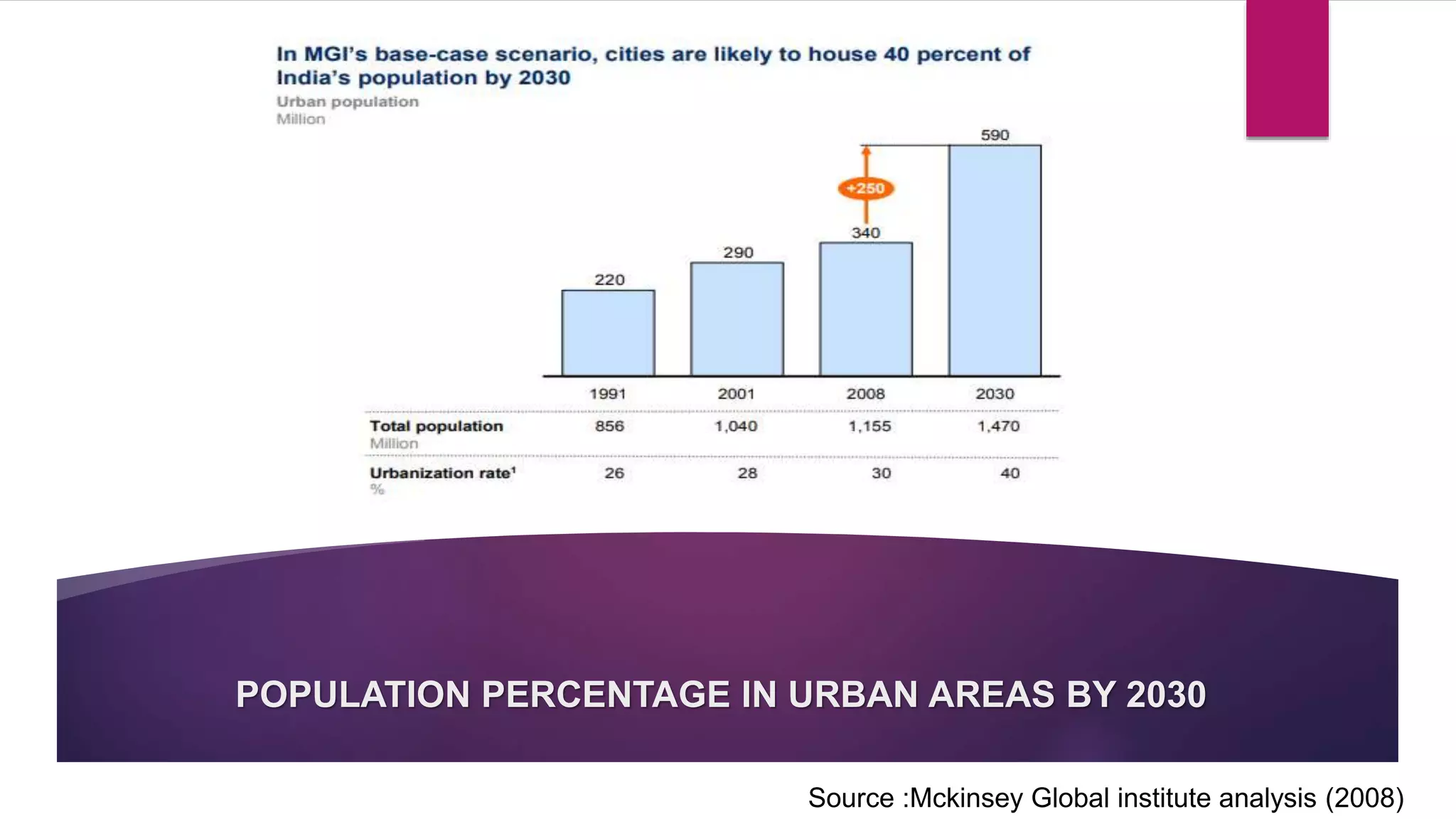
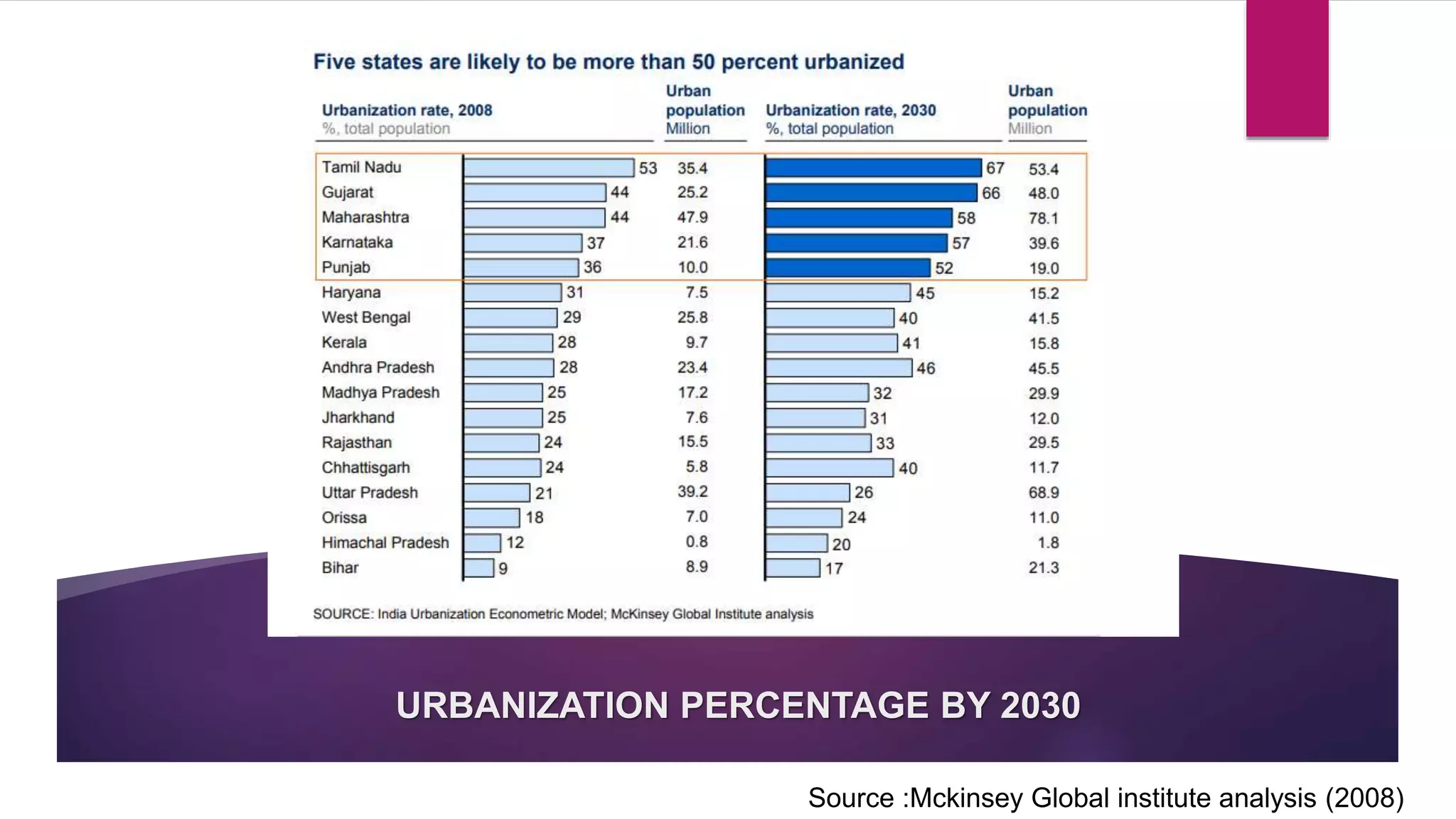
This document discusses urban growth and urbanization in India. It defines urban growth as the rate at which a city's population increases, and urbanization as the process by which there is an increase in the proportion of people living in urban areas. The major causes of urbanization in India are industrialization, which provides more jobs, as well as opportunities for better education, healthcare, and standards of living that attract people to cities. However, rapid urbanization can also lead to issues like overcrowding, poverty, and pollution. The document provides statistics on India's past and projected urbanization rates and their economic and social impacts.