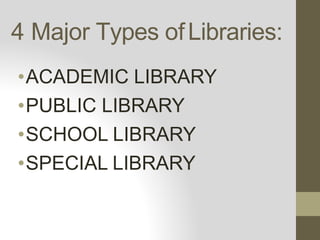
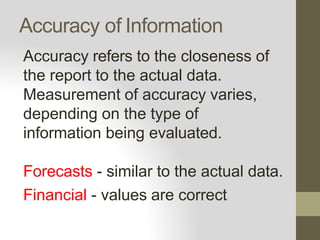
This document discusses different sources of information and how to evaluate information found online. It describes libraries, indigenous media, and the internet as key information sources. For libraries, it outlines the four major types: academic, public, school, and special. Indigenous media is defined as forms of media created and shared within indigenous communities, often orally. When evaluating online information, factors like authorship, accuracy, value, authority, and timeliness should be considered to assess reliability. Skills for analyzing reliability include checking the author, date, citations, and domain or owner of the information source.