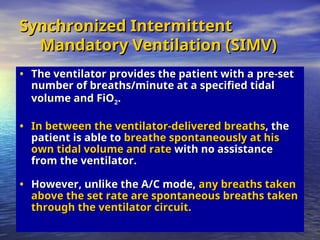
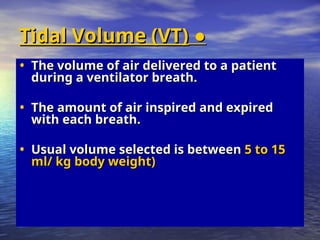
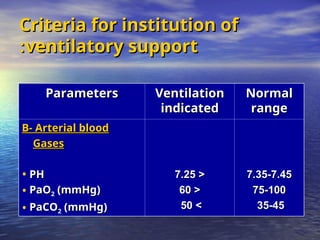
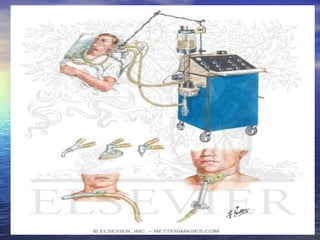
Mechanical ventilation involves the artificial ventilation of the lungs, primarily using a ventilator to maintain gas exchange and improve oxygenation, while also easing the work of breathing. Indications for mechanical ventilation include acute respiratory failure, pulmonary gas exchange abnormalities, and complications post-anesthesia or cardiac arrest. Different modes of mechanical ventilation exist, such as volume and pressure controls, which have specific clinical applications and operational parameters.












![• Although
Although pressure is consistent
pressure is consistent with these
with these
modes, volume is not.
modes, volume is not.
• Volume will change with changes in
Volume will change with changes in
resistance or compliance,
resistance or compliance,
• Therefore,
Therefore, exhaled tidal volume is the
exhaled tidal volume is the
variable to monitor closely.
variable to monitor closely.
• With pressure modes,
With pressure modes, the pressure level to
the pressure level to
be delivered is selected, and with some
be delivered is selected, and with some
mode options
mode options (i.e., pressure controlled [PC],
(i.e., pressure controlled [PC],
described later),
described later), rate and inspiratory time
rate and inspiratory time
are preset as well.
are preset as well.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanicalventilationvel-241220143754-9d0ac6f3/85/MECHANICAL-VENTILATION-anaesthesiology-ppt-17-320.jpg)