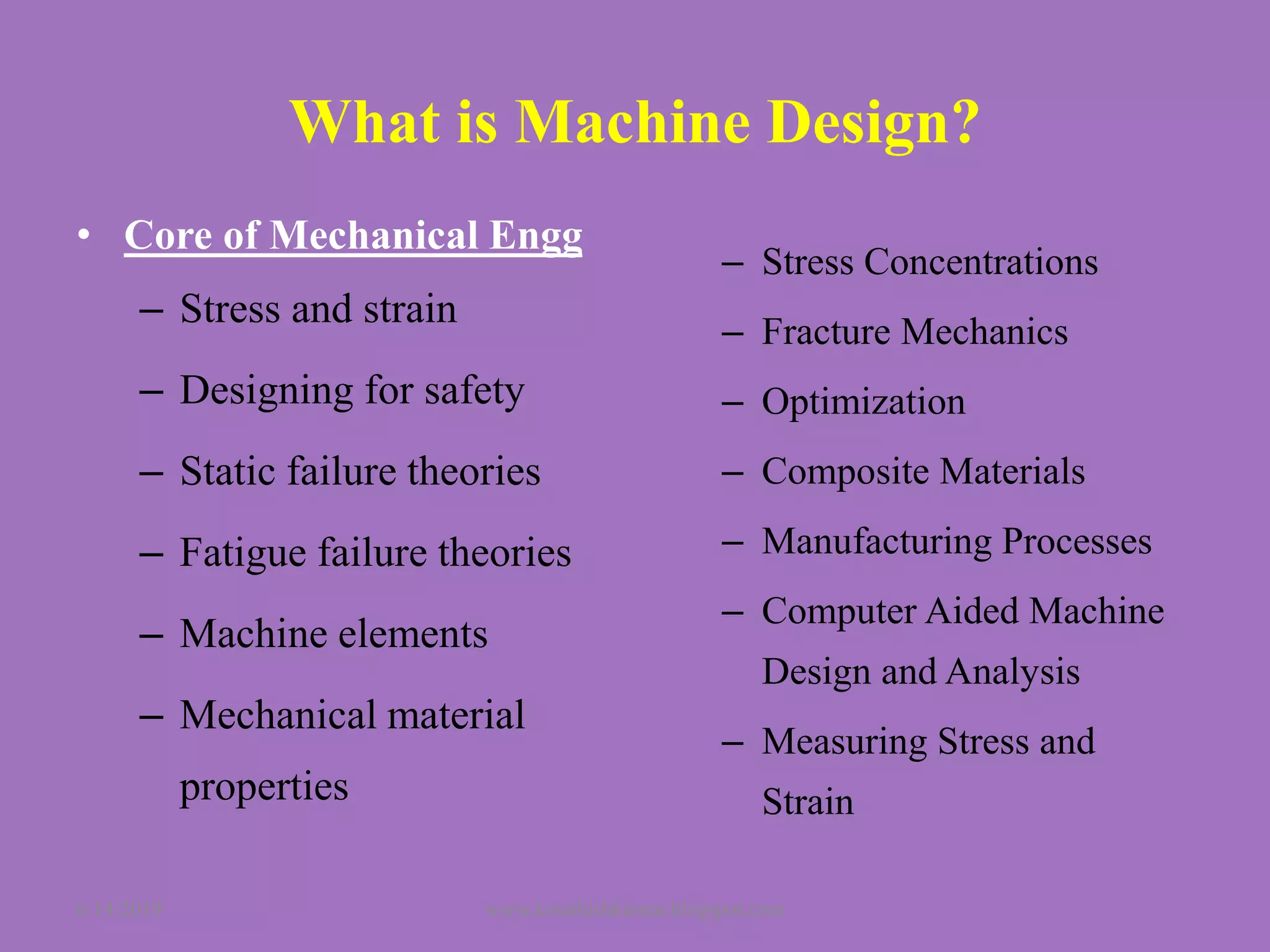
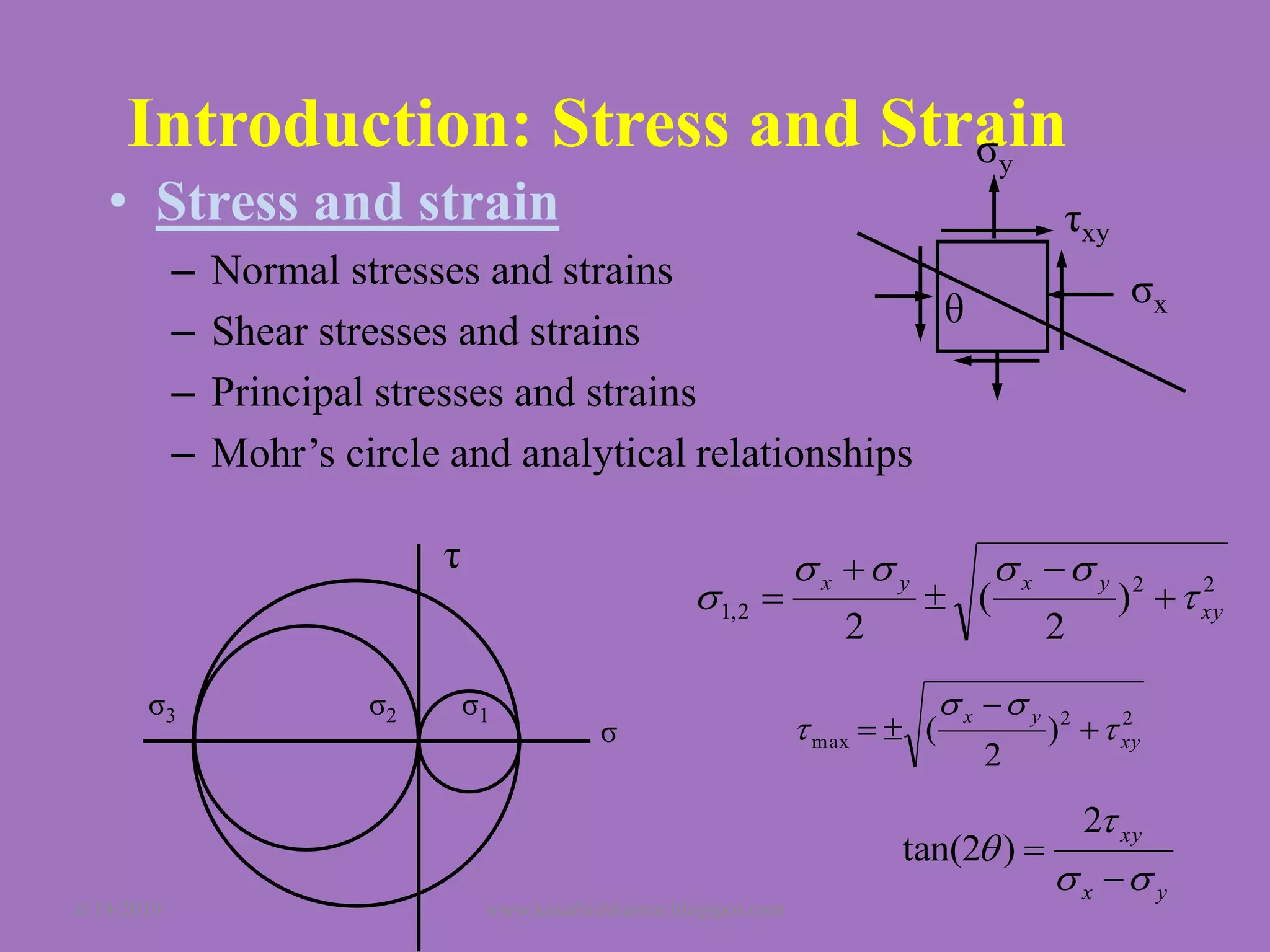
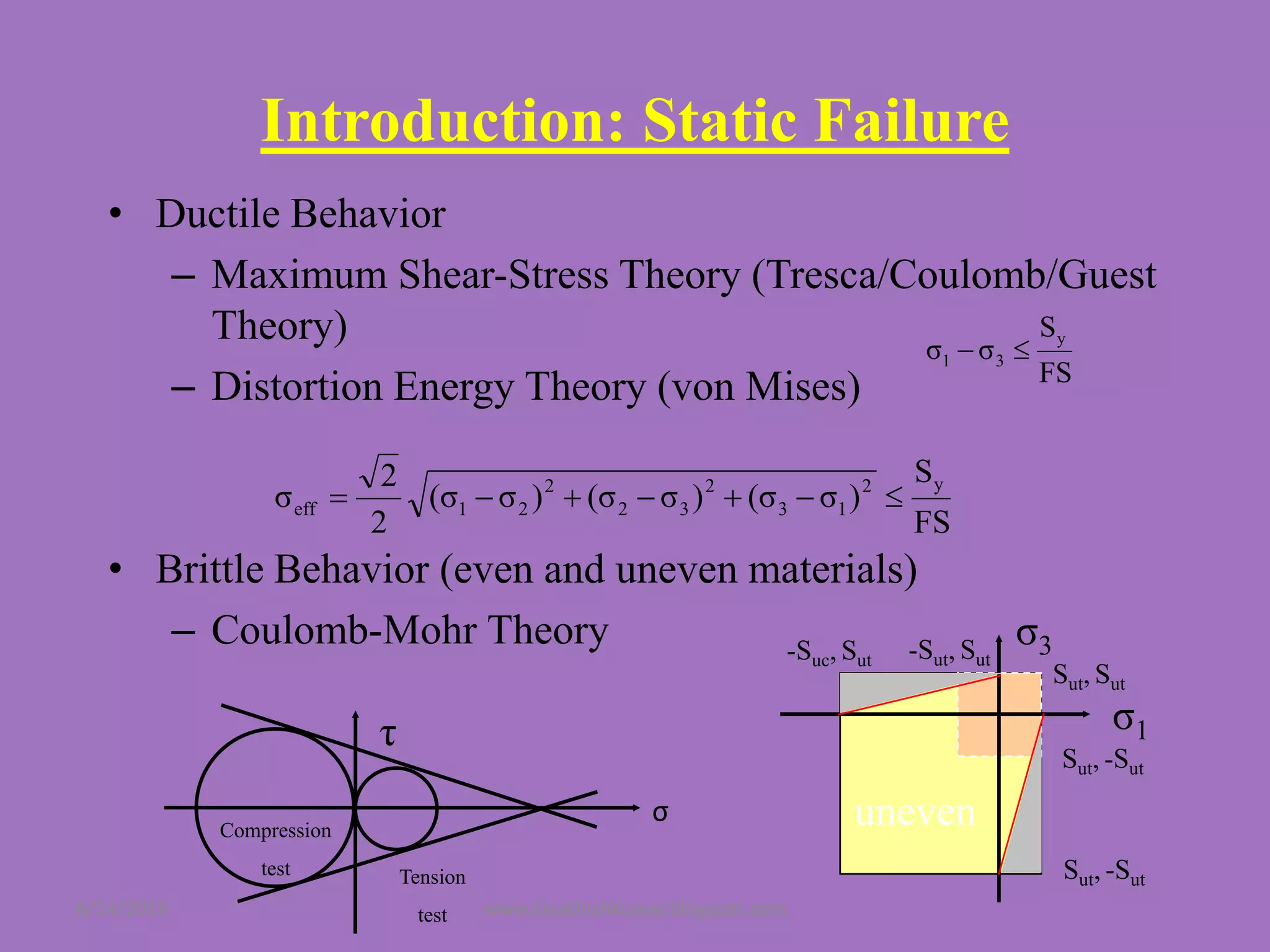
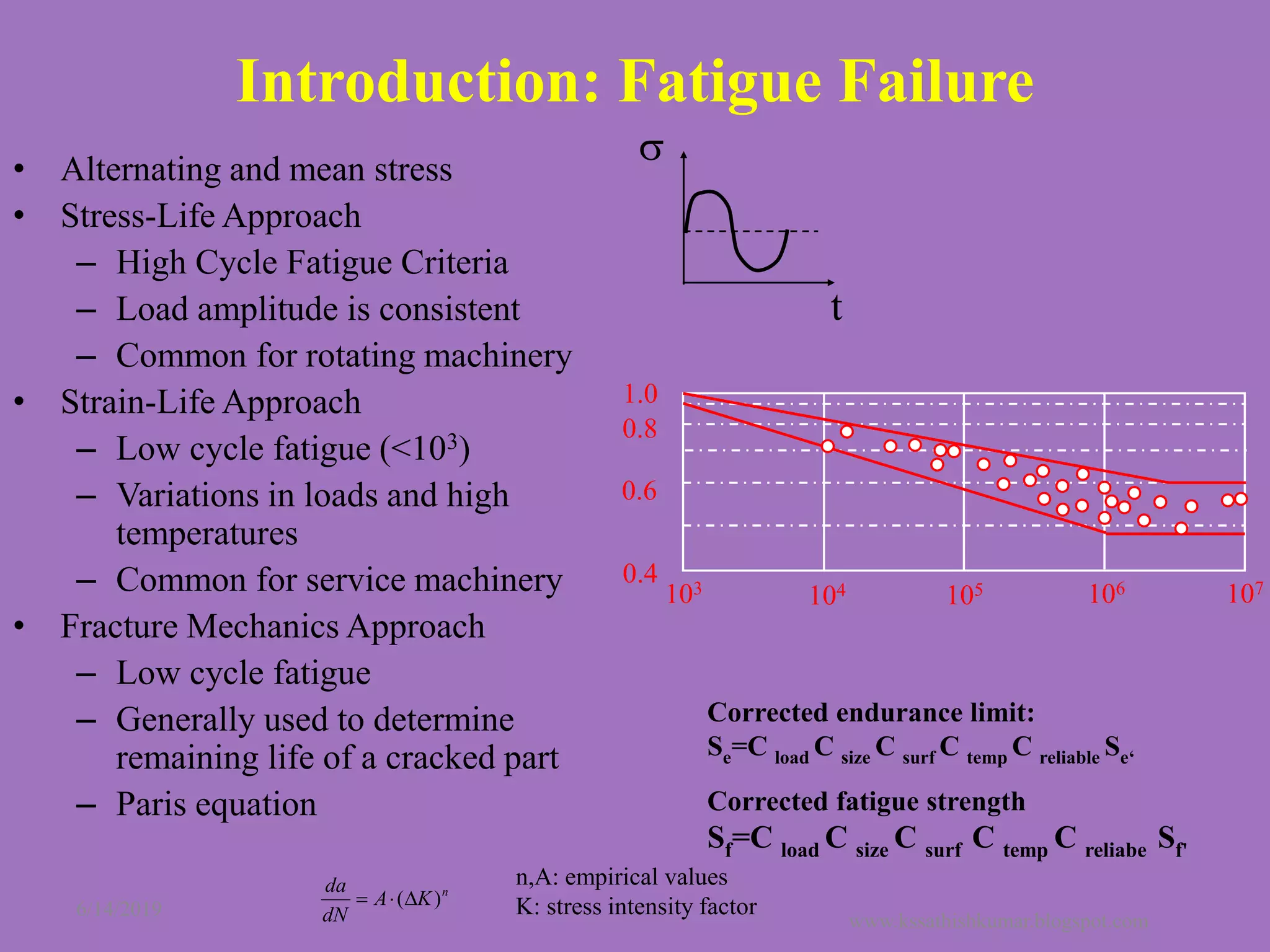
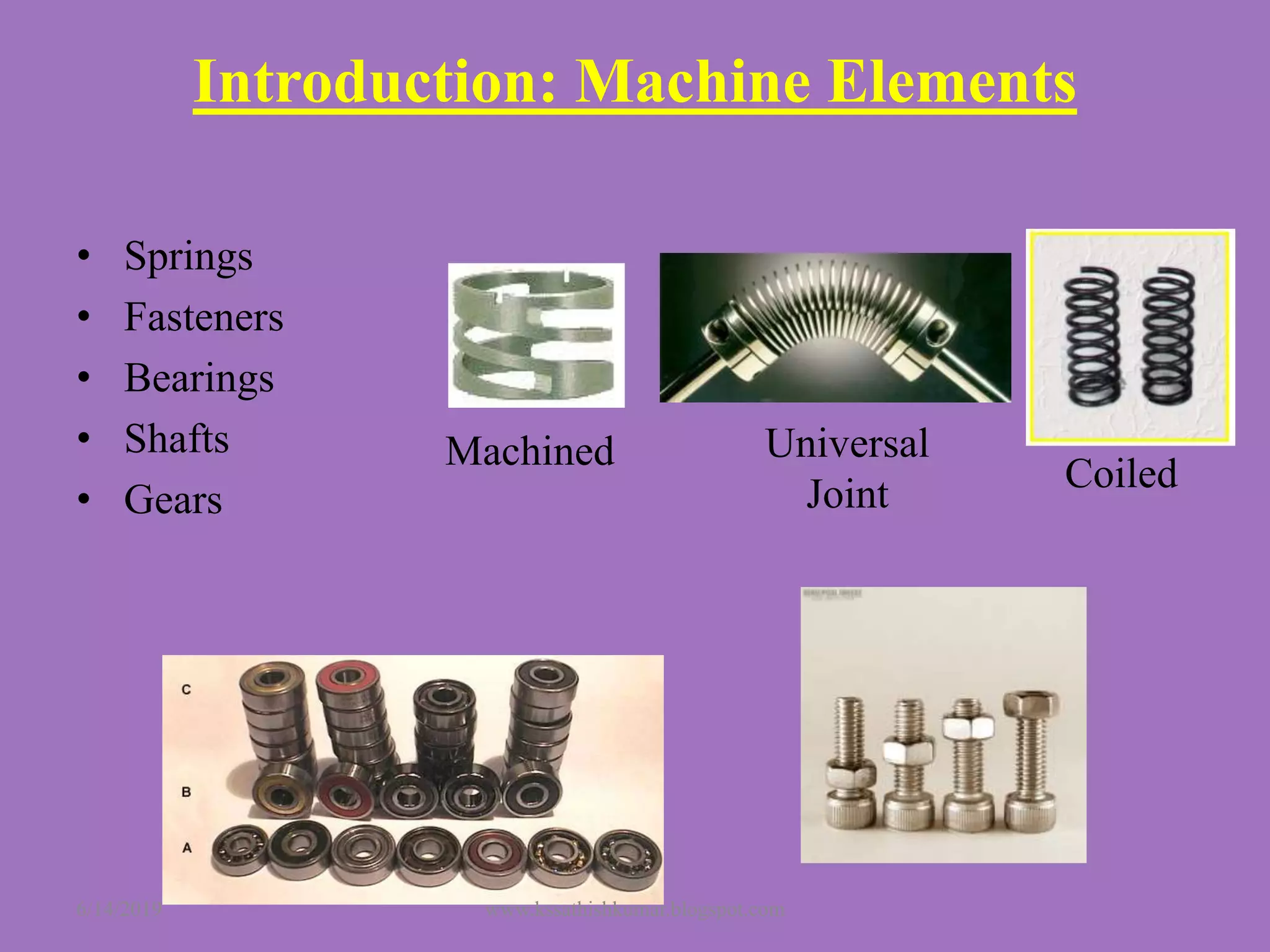
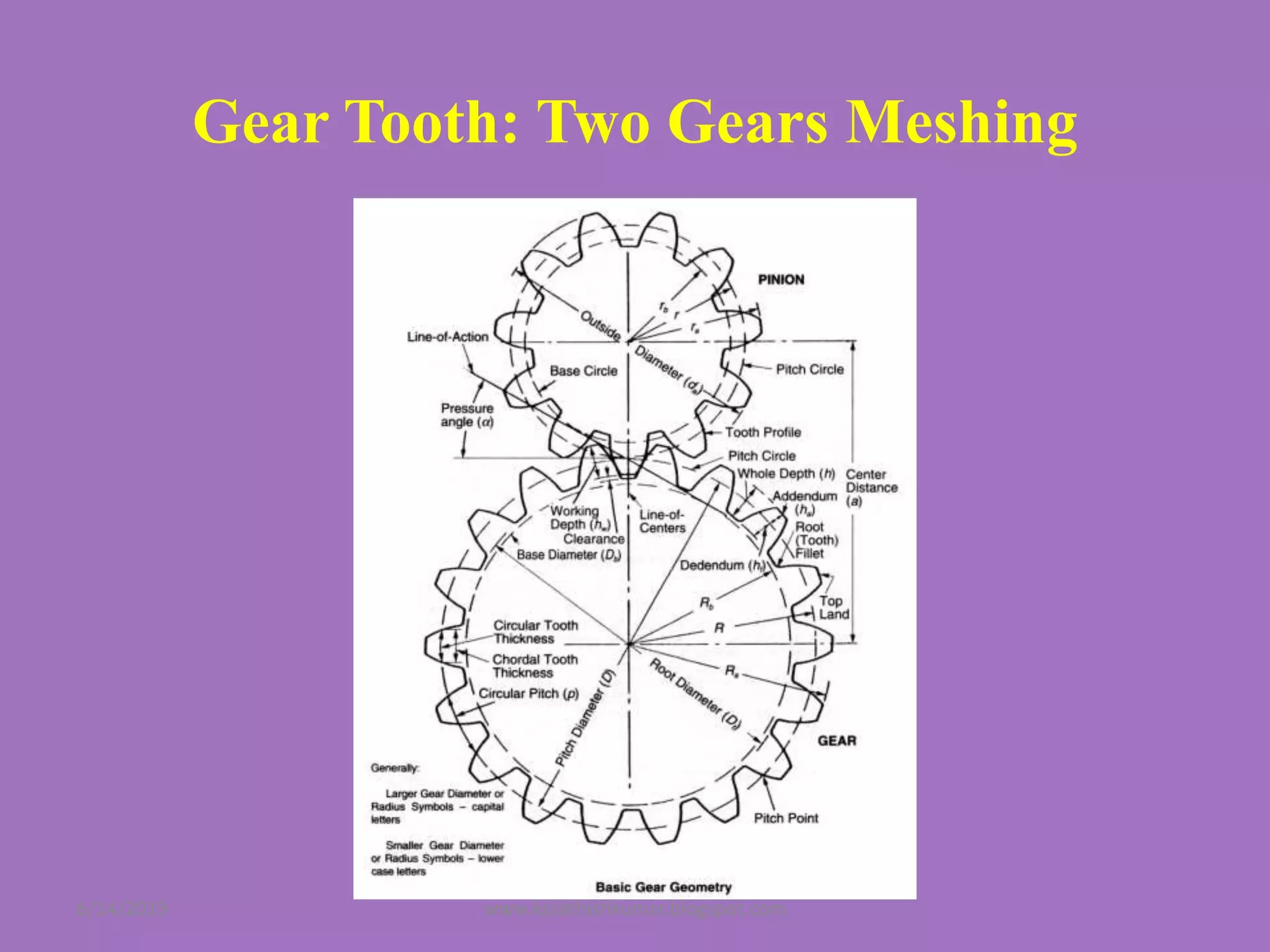
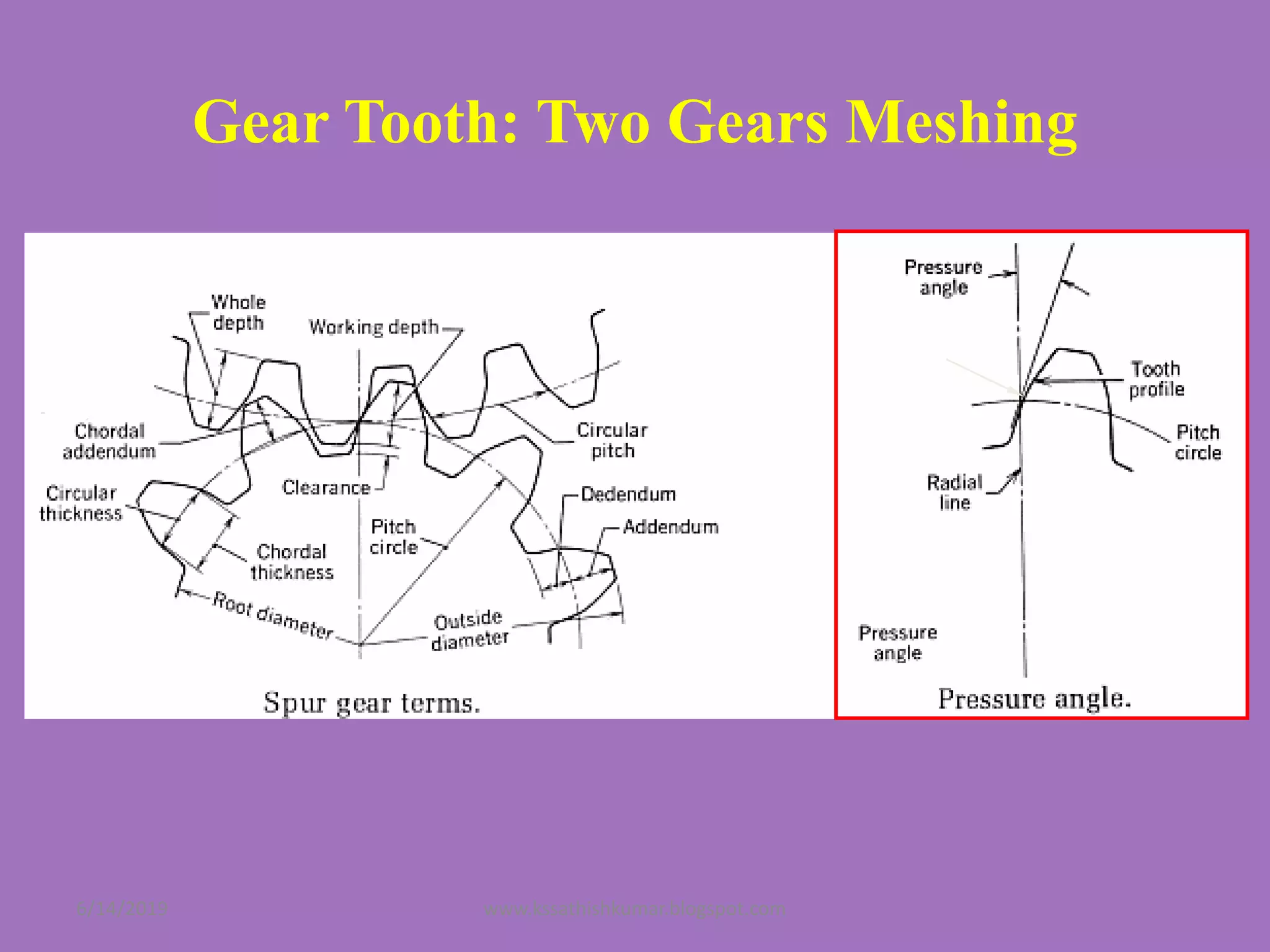
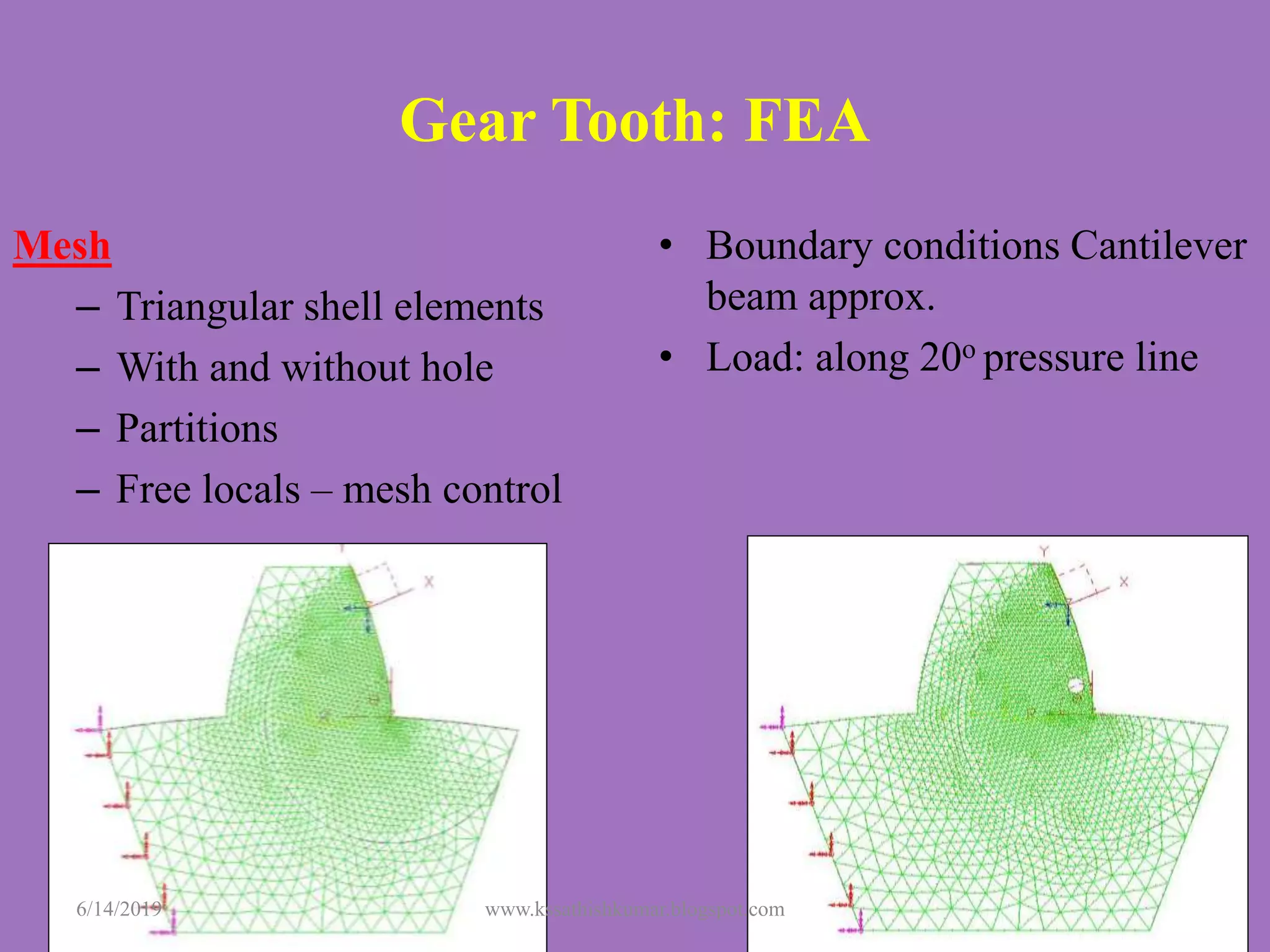
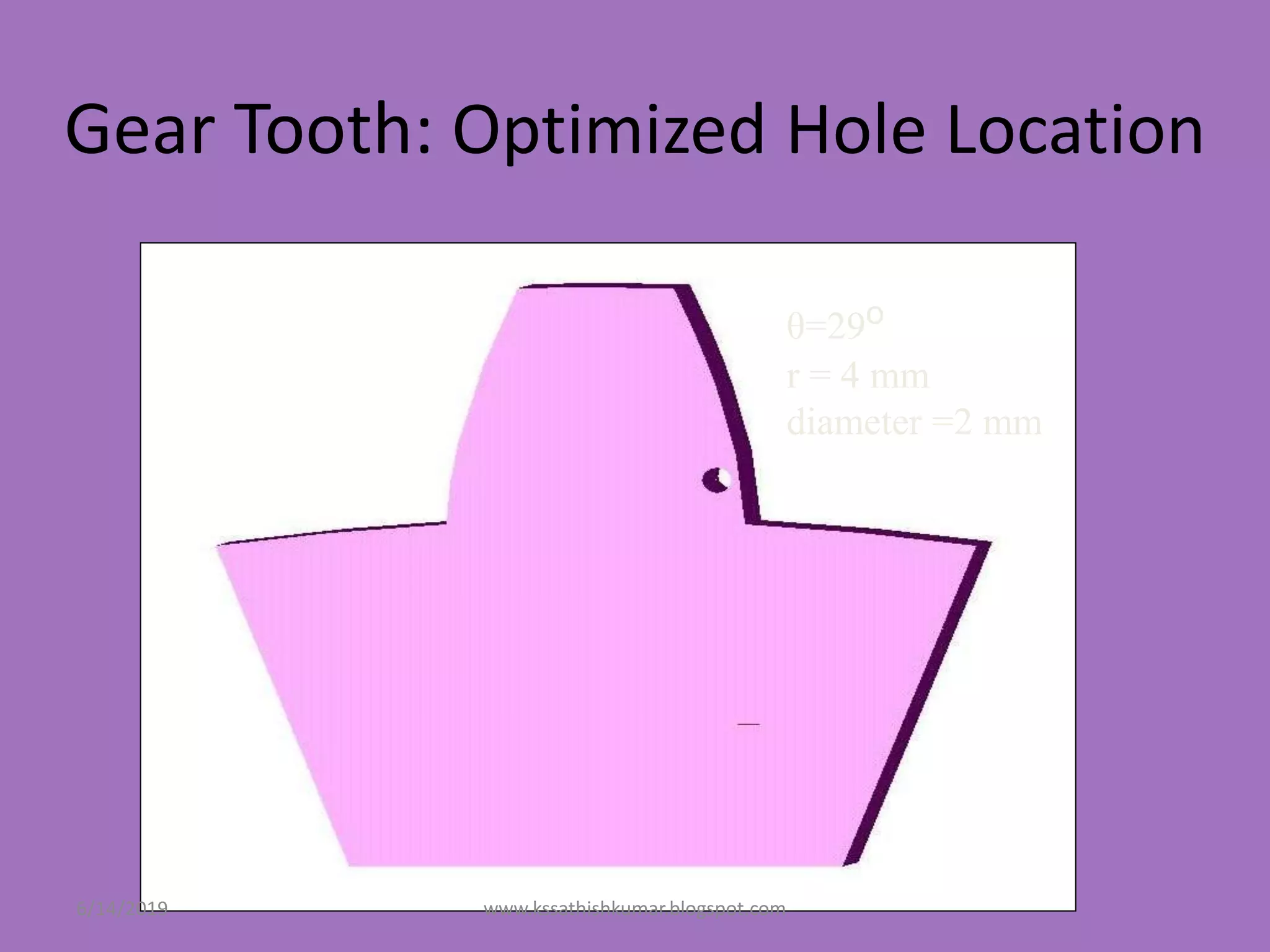
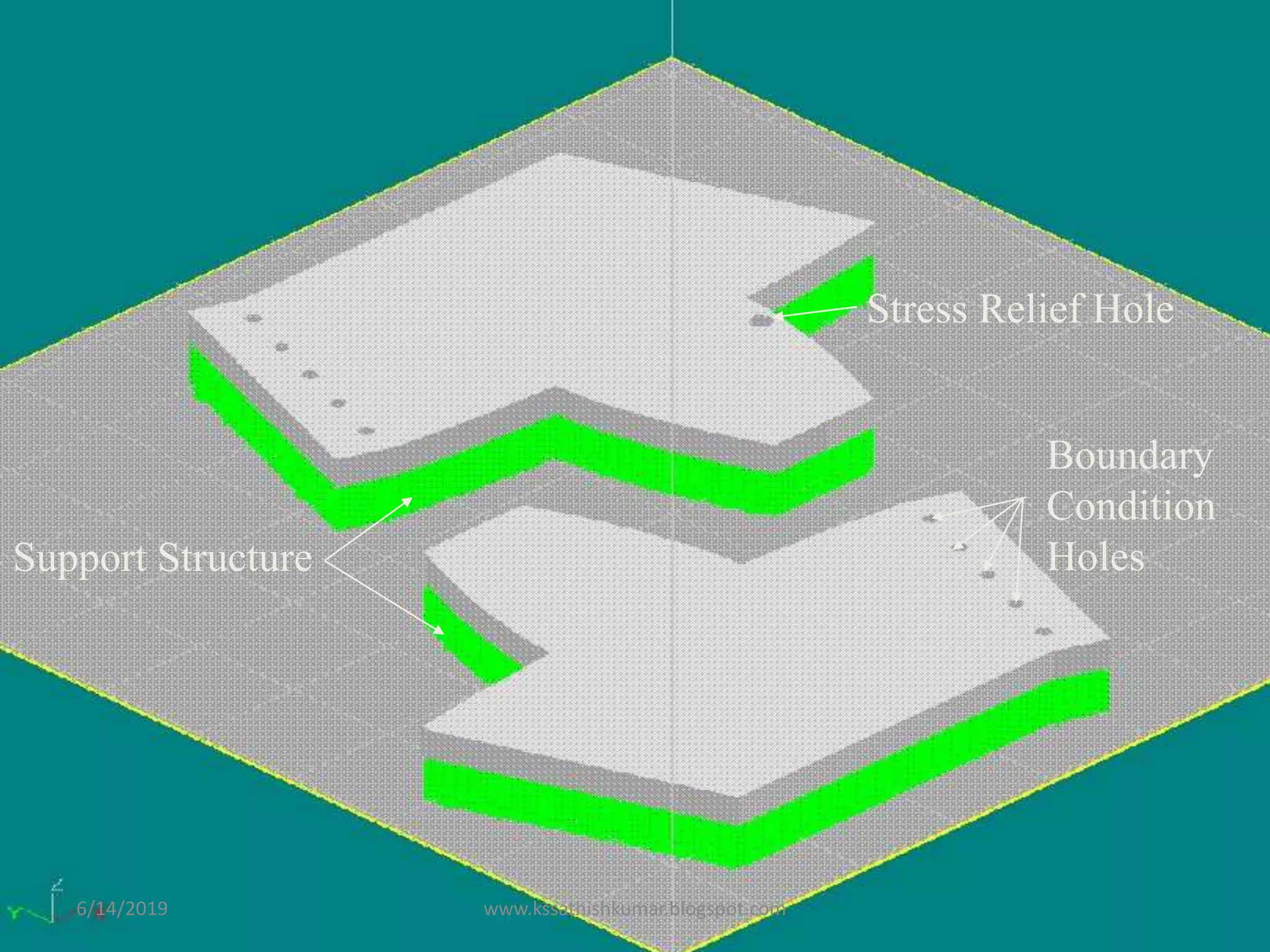
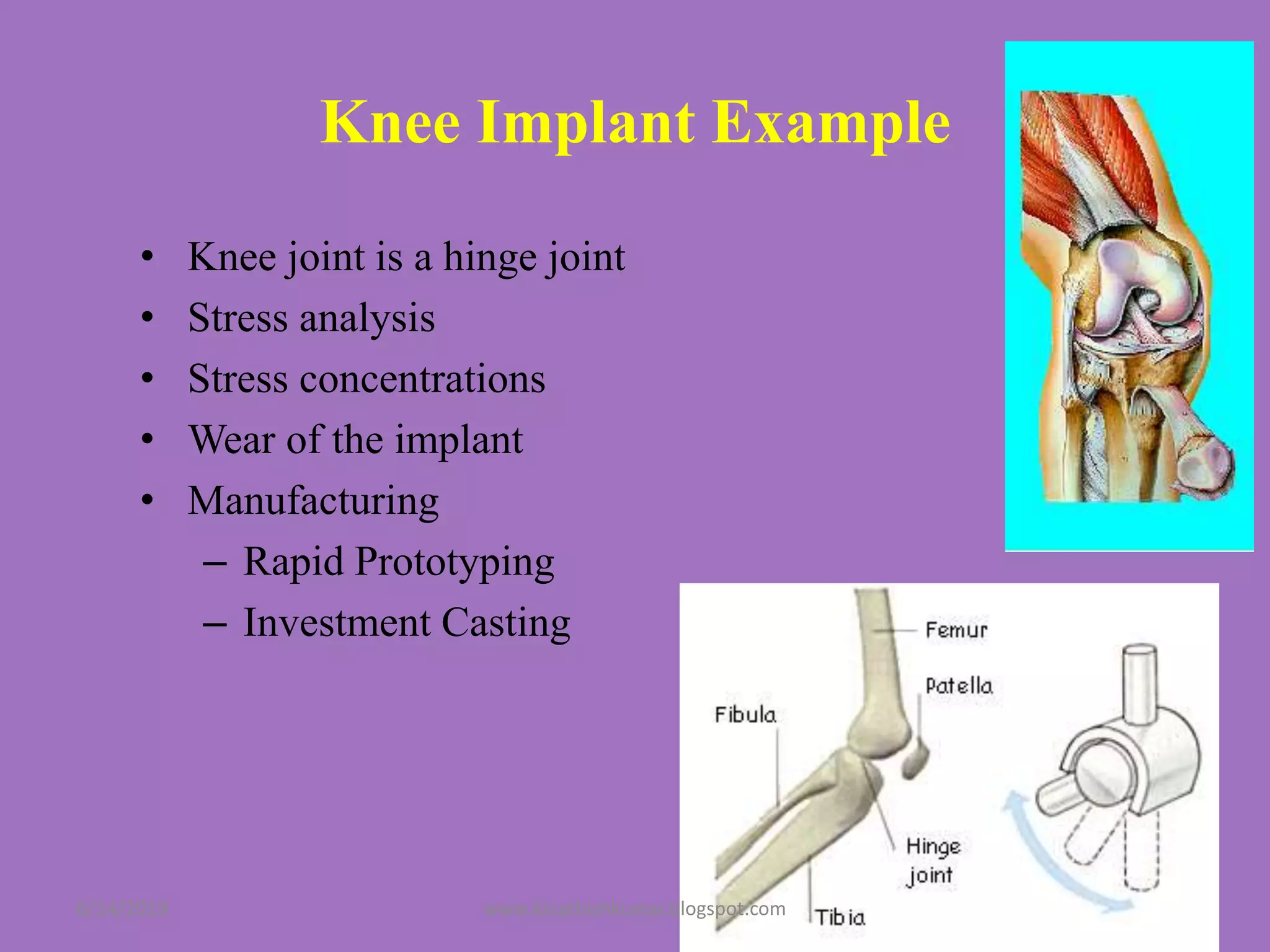
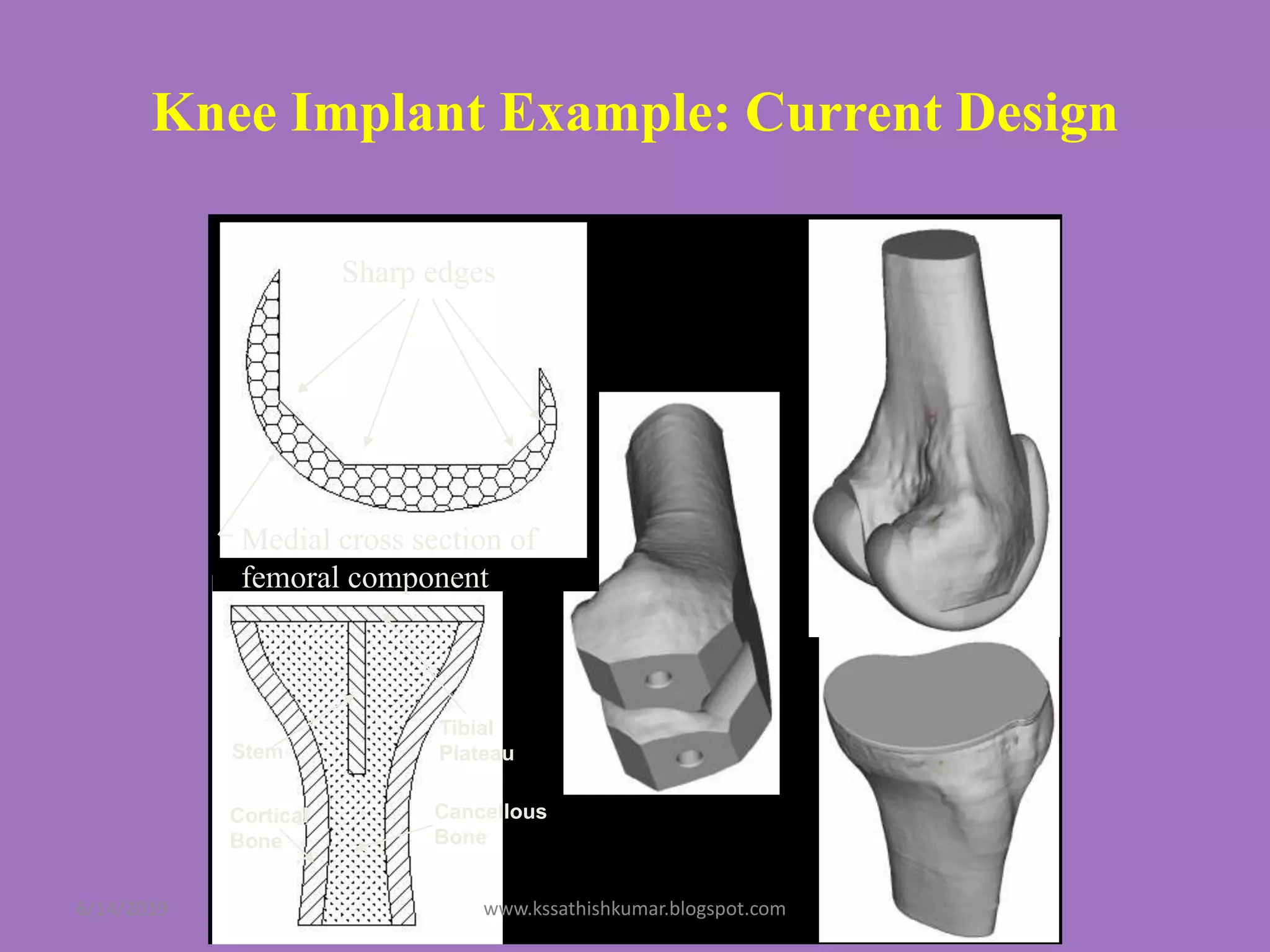
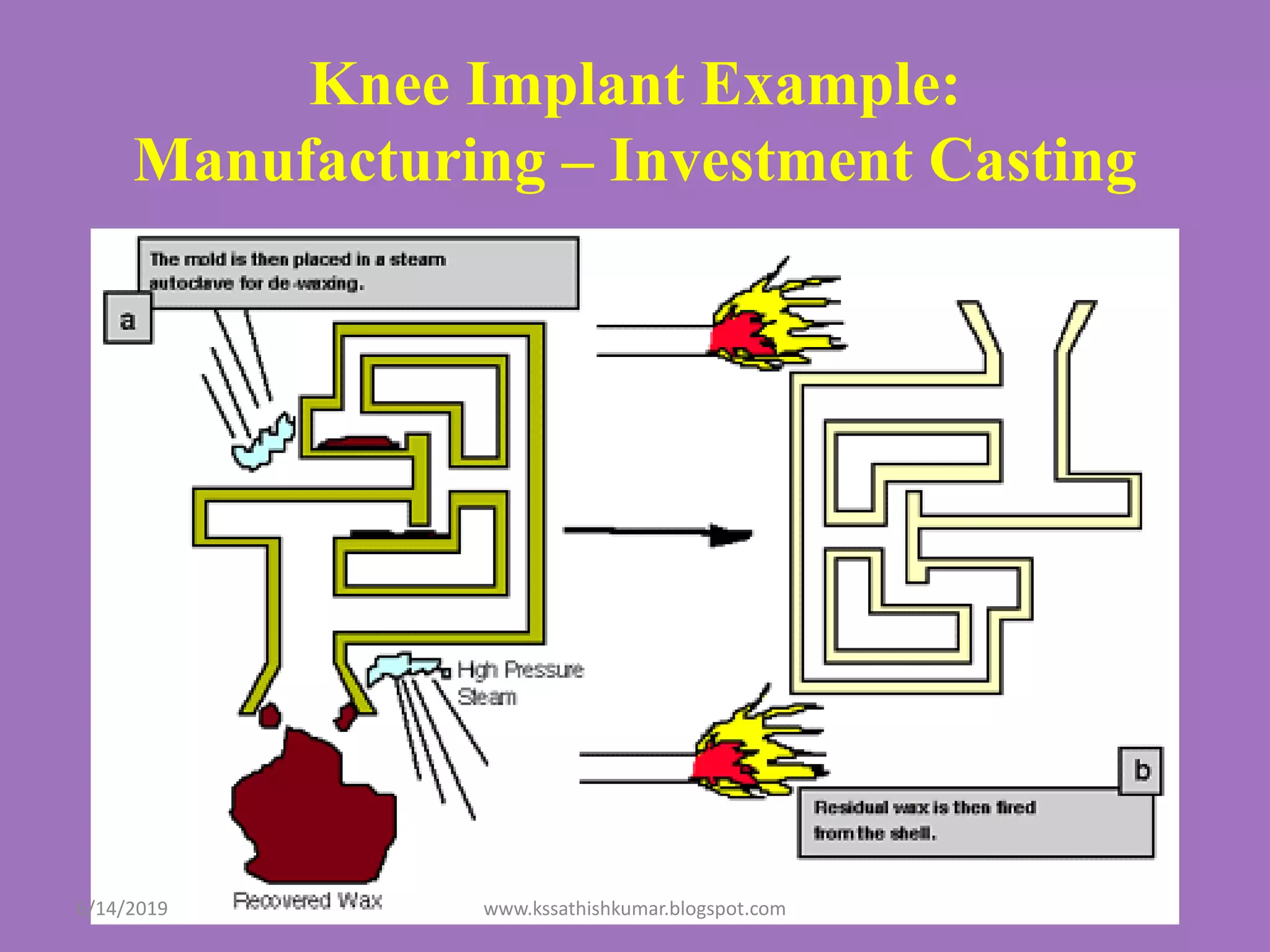
The document summarizes a presentation on machine design given by Prof. S. Sathishkumar. The presentation covers an introduction to machine design, research areas in machine design like finite element analysis and optimization, and applications involving gear tooth stress analysis, machine design optimization for a missile, and design of a customized knee implant. Specific examples on stress analysis of a gear tooth using FEA and experiments, and optimization of the gear tooth design by introducing a stress relief hole are discussed in detail.