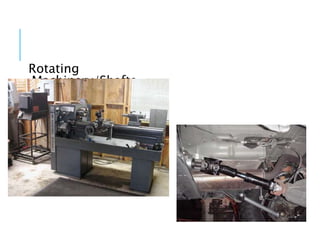
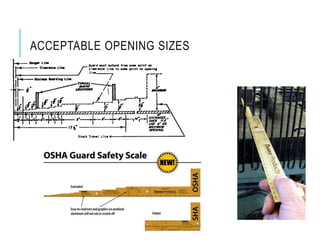
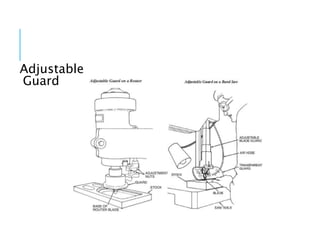
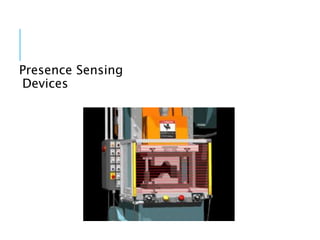
This document discusses mechanical hazards, controls for mechanical hazards, and options for guarding hazards. It identifies types of mechanical hazards like rotating machinery, compressed fluids, blades and sharp edges. It recommends eliminating hazards if possible, guarding hazards that remain, and relying on training and PPE if hazards cannot be eliminated or guarded. The document also provides examples of guards like fixed barriers, adjustable guards and interlocked guards, outlines acceptable opening sizes for guards, and lists examples of safety training and personal protective equipment.