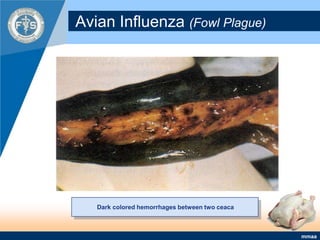
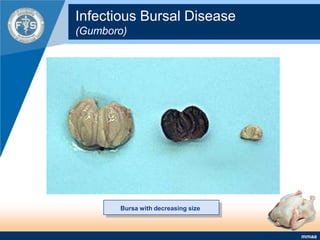
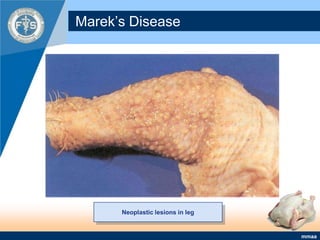
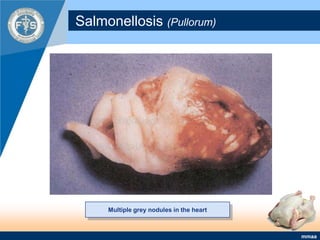
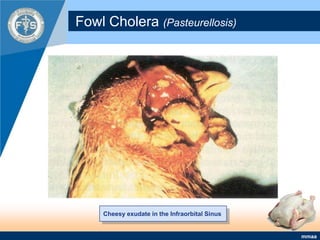
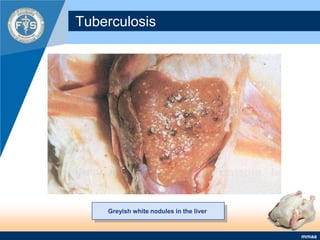
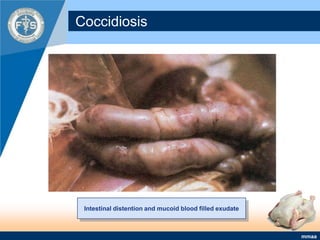
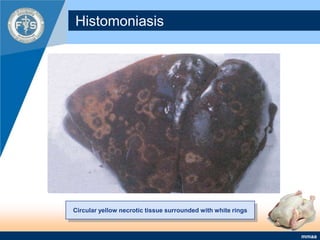
This document provides an inventory of important diseases for meat inspection in poultry. It describes several viral, bacterial, parasitic, and fungal diseases including avian influenza, Newcastle disease, infectious bursal disease, Marek's disease, salmonellosis, fowl cholera, tuberculosis, coccidiosis, and histomoniasis. For each disease, it outlines the causative organism, post-mortem lesions typically found, and decisions regarding condemnation of infected carcasses. The objective is to enable meat inspectors to properly diagnose diseases and ensure consumers receive only wholesome poultry meat.