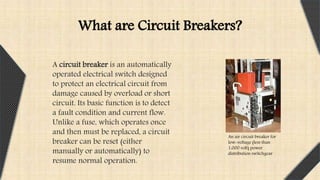
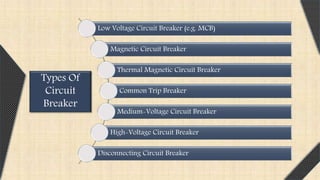
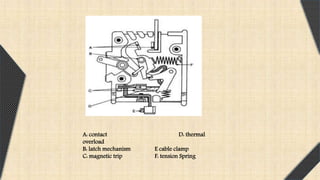
This document provides an overview of Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCBs) and Earth Leakage Circuit Breakers (ELCBs). It defines a circuit breaker and describes the types, including MCBs. It explains the construction, operation, and uses of MCBs. MCBs protect against overload and short circuits using magnetic and thermal trip units. The document also describes ELCBs, noting that they detect small stray voltages and interrupt circuits to prevent electric shock. ELCBs operate by detecting fault currents from live to earth and disconnecting power when a voltage is sensed across the sense coil.