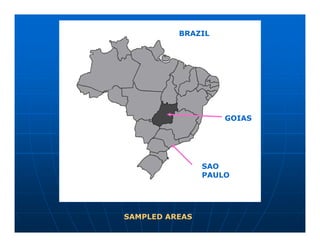
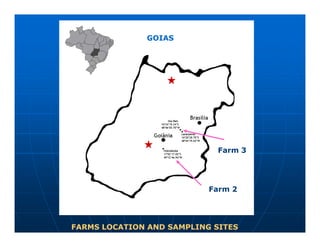
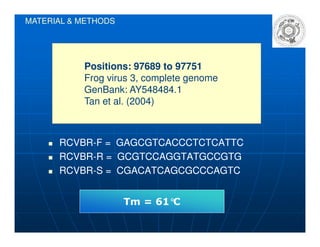
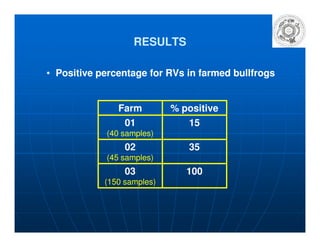
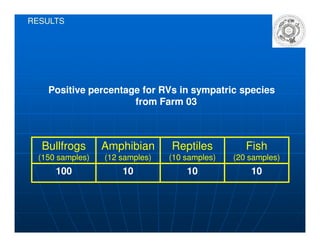
This document summarizes a study on the surveillance of ranaviruses in farmed American bullfrogs and sympatric amphibian, fish, and reptile species in Brazil. The study found high prevalence of ranaviruses in bullfrog farms with poor management practices and whole lifecycle production. Ranaviruses were detected at low levels in sympatric species near infected farms but not in other areas without bullfrog introduction. While disease was reported in farmed bullfrog tadpoles, no disease or mortality was observed in sympatric species despite some testing positive for ranaviruses. Future work is needed to further characterize the ranaviruses detected and their potential virulence.