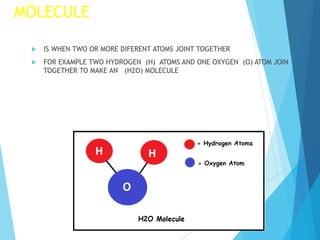
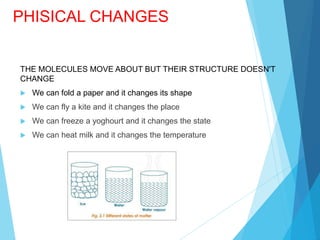
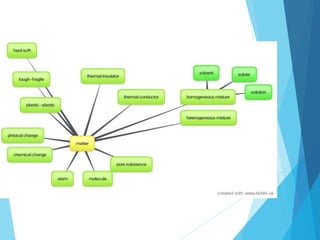
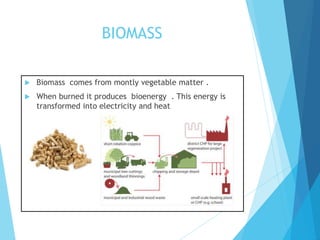
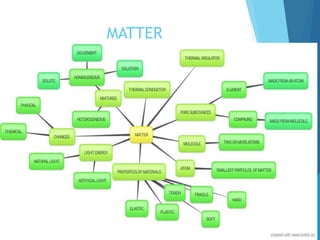
The document discusses the distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures, along with basic concepts of atoms, molecules, and physical and chemical changes. It also covers properties of materials, types of energy such as light and sound, and methods for harnessing energy from sources like solar panels and wind turbines. Finally, it mentions the transformation of biomass into bioenergy.