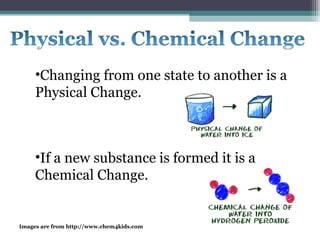
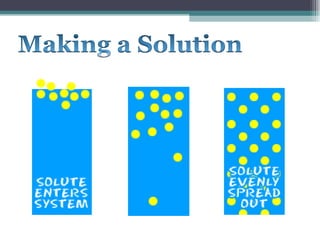
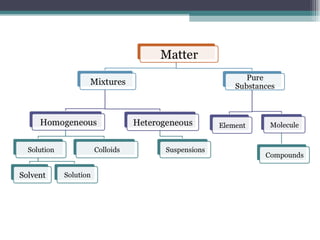
The document provides information about the key concepts of matter, including its definition as anything that has mass and volume. It describes the differences between physical and chemical changes, and explains that matter is made up of atoms that can exist as individual atoms or bonded together in molecules. Molecules can be made of two or more atoms of the same or different elements. When atoms of different elements are bonded together they form compounds. The document also defines and provides examples of solutions, suspensions, and colloids - different types of mixtures.