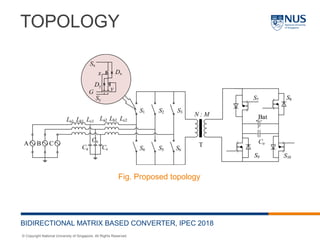
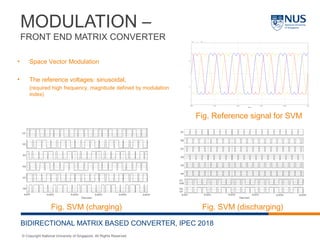
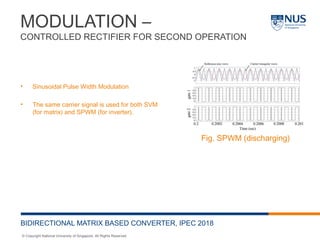
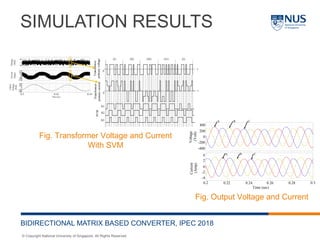
This document describes a bidirectional AC-DC converter with an LCL input filter for energy storage applications. It proposes a matrix-based topology that uses space vector modulation for the front-end matrix converter and sinusoidal pulse width modulation for the controlled rectifier. The converter allows bidirectional power flow between the grid and an energy storage device. It was simulated in MATLAB and results showed total harmonic distortion below 2% for both charging and discharging operations. Future work includes hardware implementation and improving the LCL filter design to further reduce harmonic distortion.