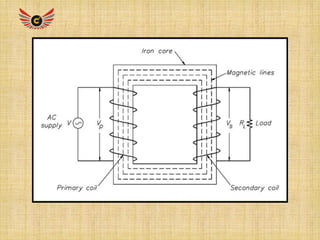
1) A transformer is a static electrical device that transfers energy from one circuit to another through common magnetic fields without changing frequency. It works by using Faraday's laws of induction to induce voltage in a secondary coil when voltage is applied to a primary coil.
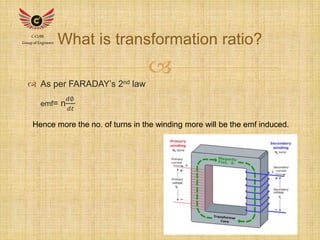
2) Transformers use the principle of mutual inductance between two coils separated by an iron core to increase or decrease voltage levels. An alternating current in the primary coil creates a changing magnetic field that induces voltage in the secondary coil.
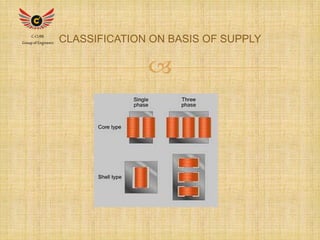
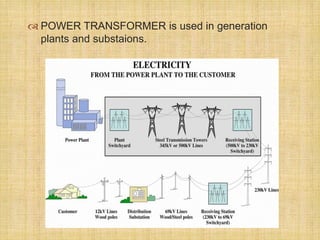
3) Transformers have various applications including power generation, transmission, and distribution as well as applications in electronics like mobile phone chargers and induction motors. They allow efficient transmission of electrical power over long distances and adaptation of voltages for end