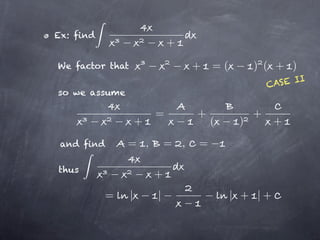Rational functions can be decomposed into the sum of partial fractions. This involves three main steps:
1. Use long division to decompose any improper rational functions into a polynomial plus a proper rational function.
2. Factor the denominator of the proper rational function into linear and irreducible quadratic factors.
3. Decompose the proper rational function into a sum of partial fractions with undetermined coefficients that are solved for.
There are four cases to consider depending on whether the factors of the denominator are distinct, repeated, distinct quadratics, or repeated quadratics.