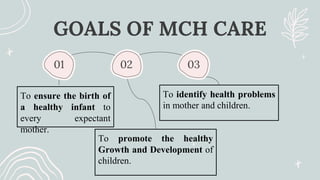
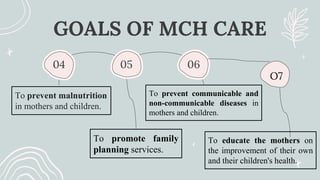
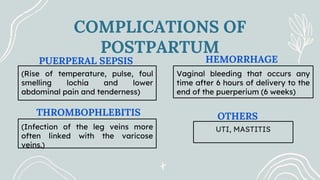
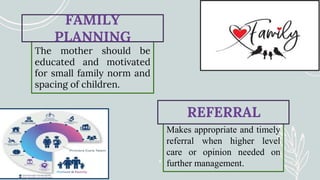
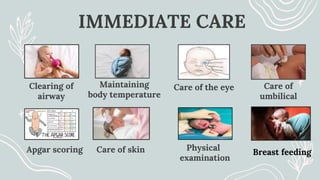
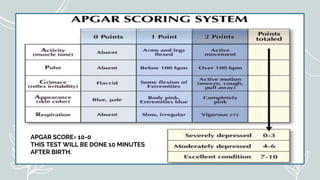
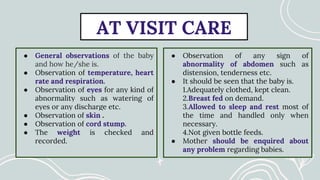
Maternal and Child Health (MCH) focuses on comprehensive healthcare services for pregnant women and children under five, aiming to reduce mortality and morbidity rates. Objectives include promoting maternal health, ensuring healthy births, preventing diseases, and providing health education. Key services encompass antenatal, intranatal, and postnatal care, alongside child health care and family planning support.