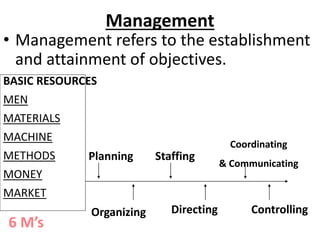
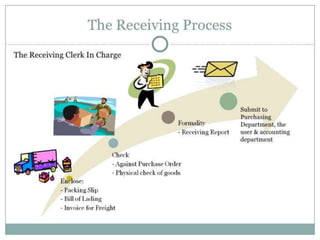
This document discusses material management in healthcare organizations. It defines material management as planning, organizing, and controlling the acquisition, storage, and distribution of materials needed by healthcare personnel. The key functions of material management are planning and sourcing, budgeting, research, procurement, receiving, storage, accounting and control, issuing, disposal, and maintenance. Effective material management aims to obtain the right materials in the right quantity, quality, time, and place while reducing costs and avoiding stockouts. Principles like POSDCORB guide material planning and procurement processes.