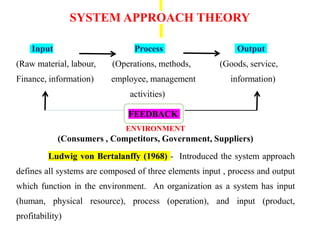
The document discusses material management and inventory control in a healthcare setting. It provides definitions of key terms like material management, inventory, and Vital-Essential-Desirable (VED) analysis. Some main points:
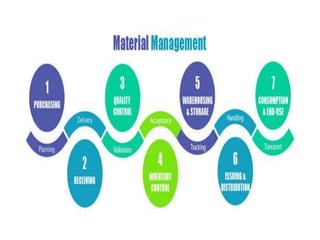
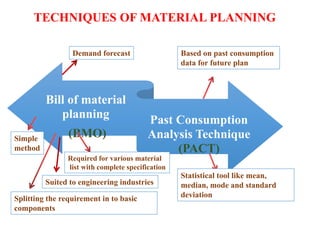
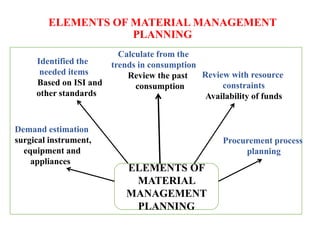
- Material management involves planning, purchasing, storing, and controlling materials to provide services at minimum cost. About 40% of healthcare budgets are spent on procuring and managing supplies.
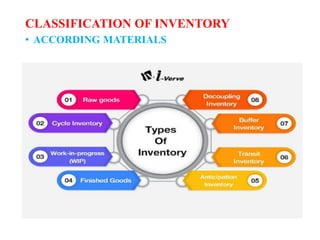
- Inventory is stock held to meet future demand and provide a buffer between availability and need. It is classified as official (for clinical use) and unofficial (for non-clinical use).
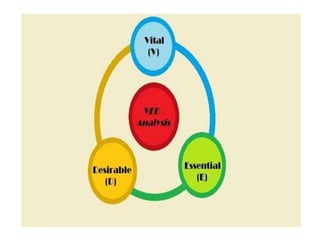
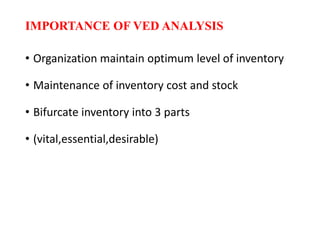
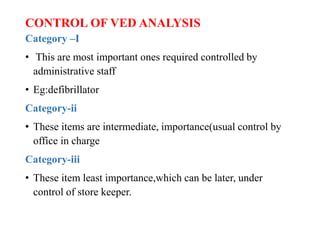
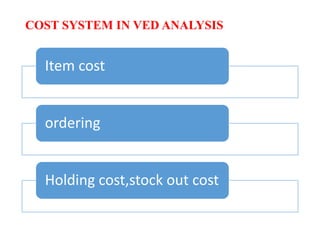
- VED analysis classifies inventory based on criticality - vital items are most critical and cannot be out of stock,