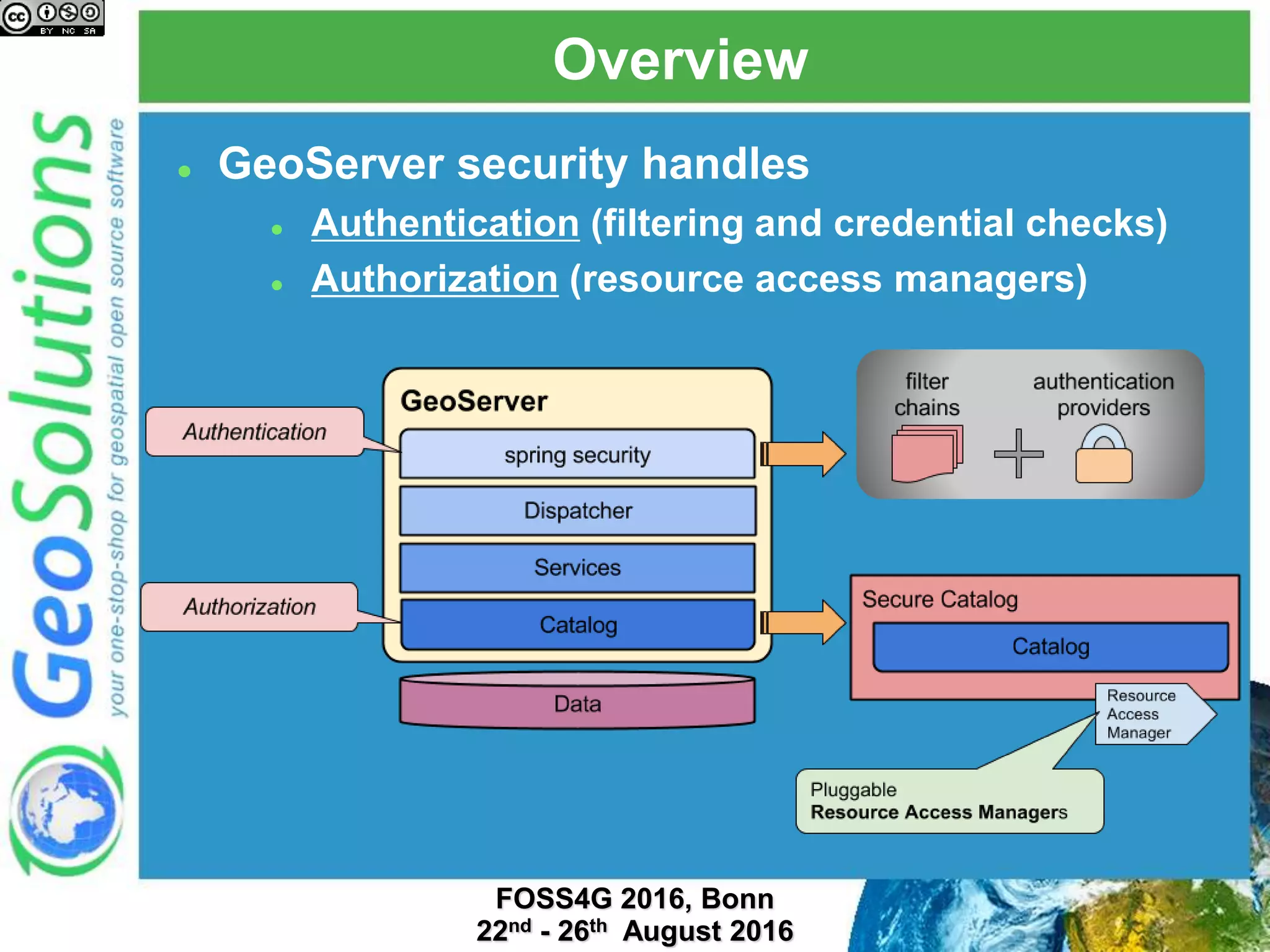
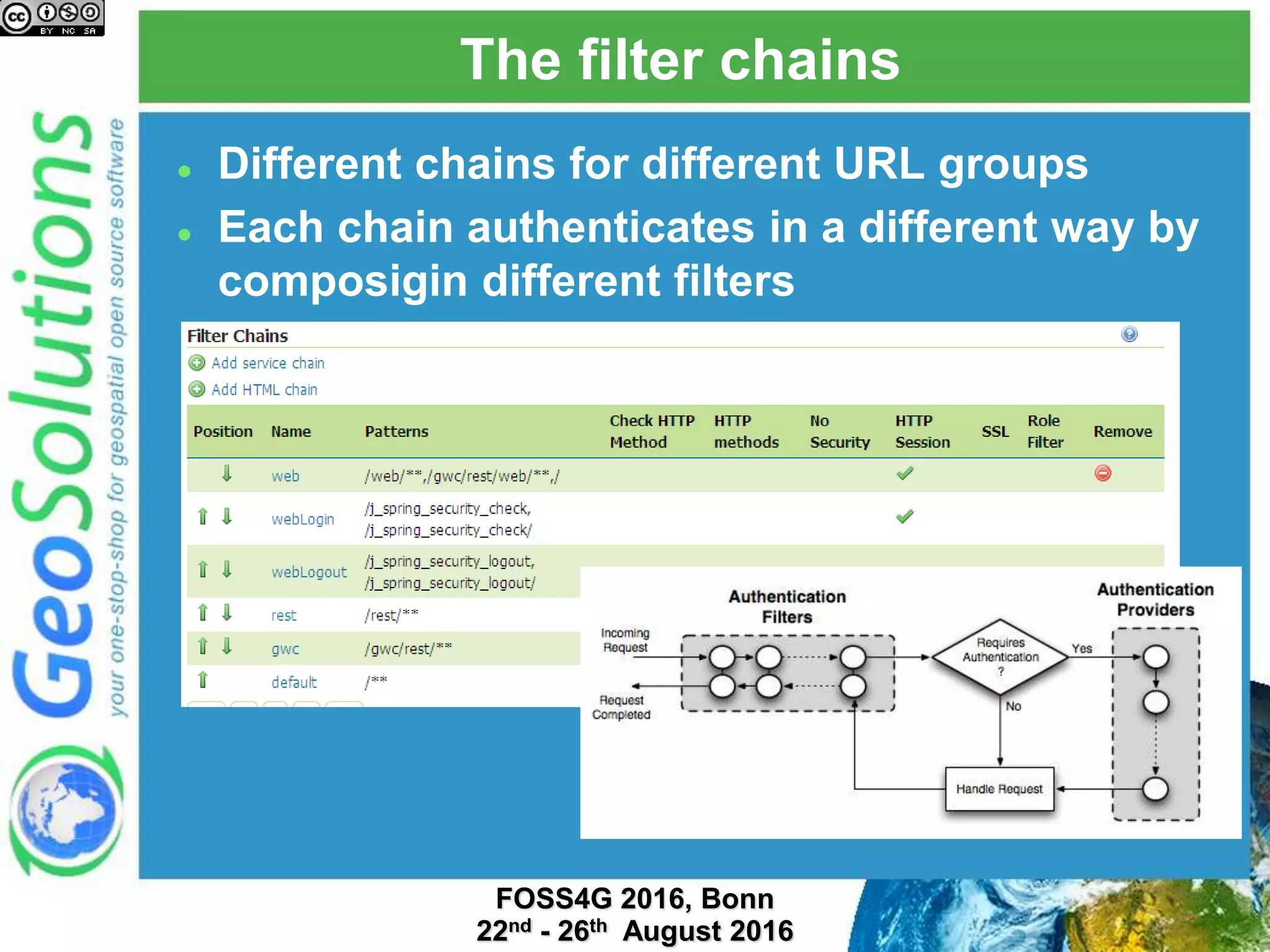
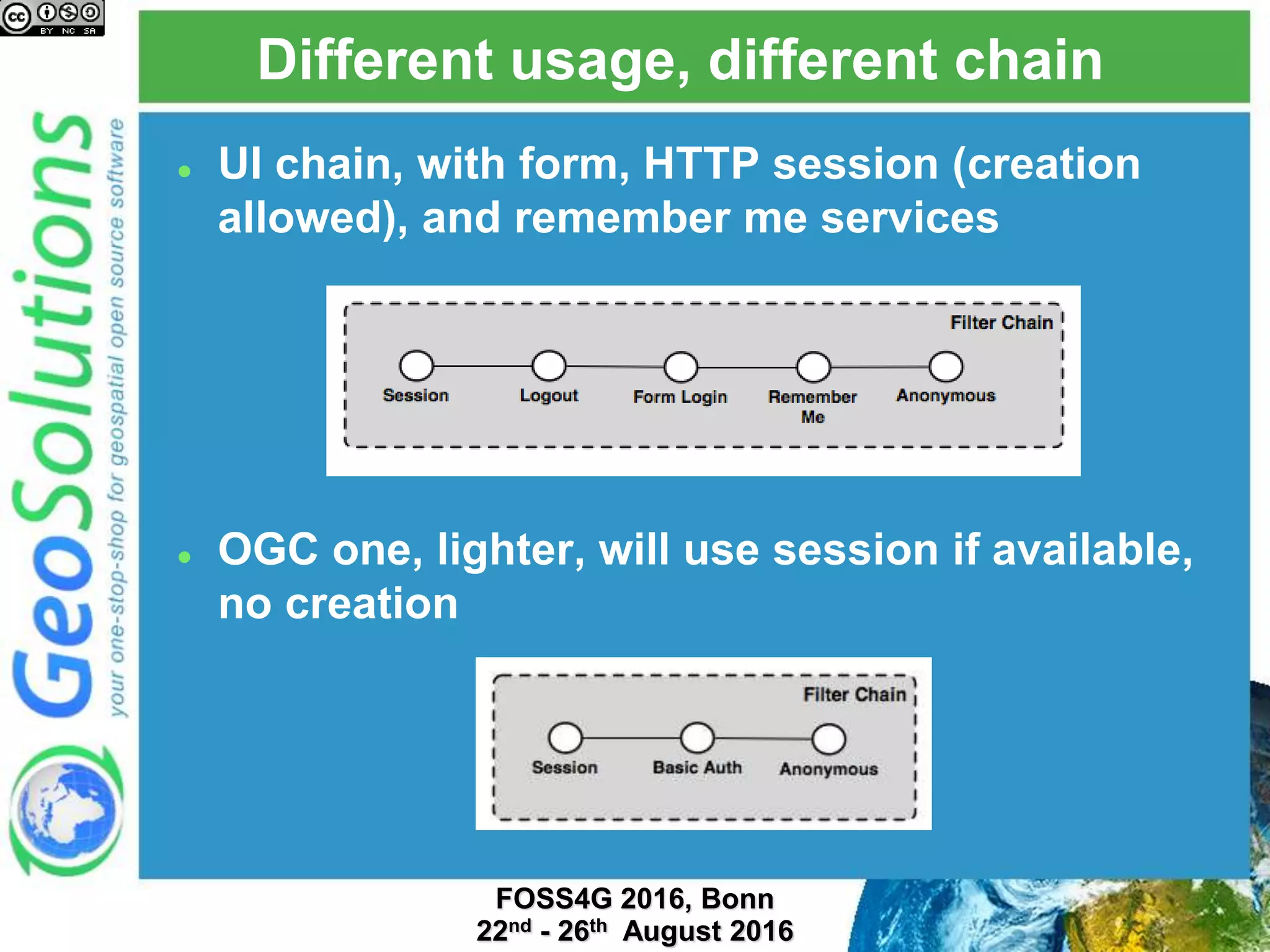
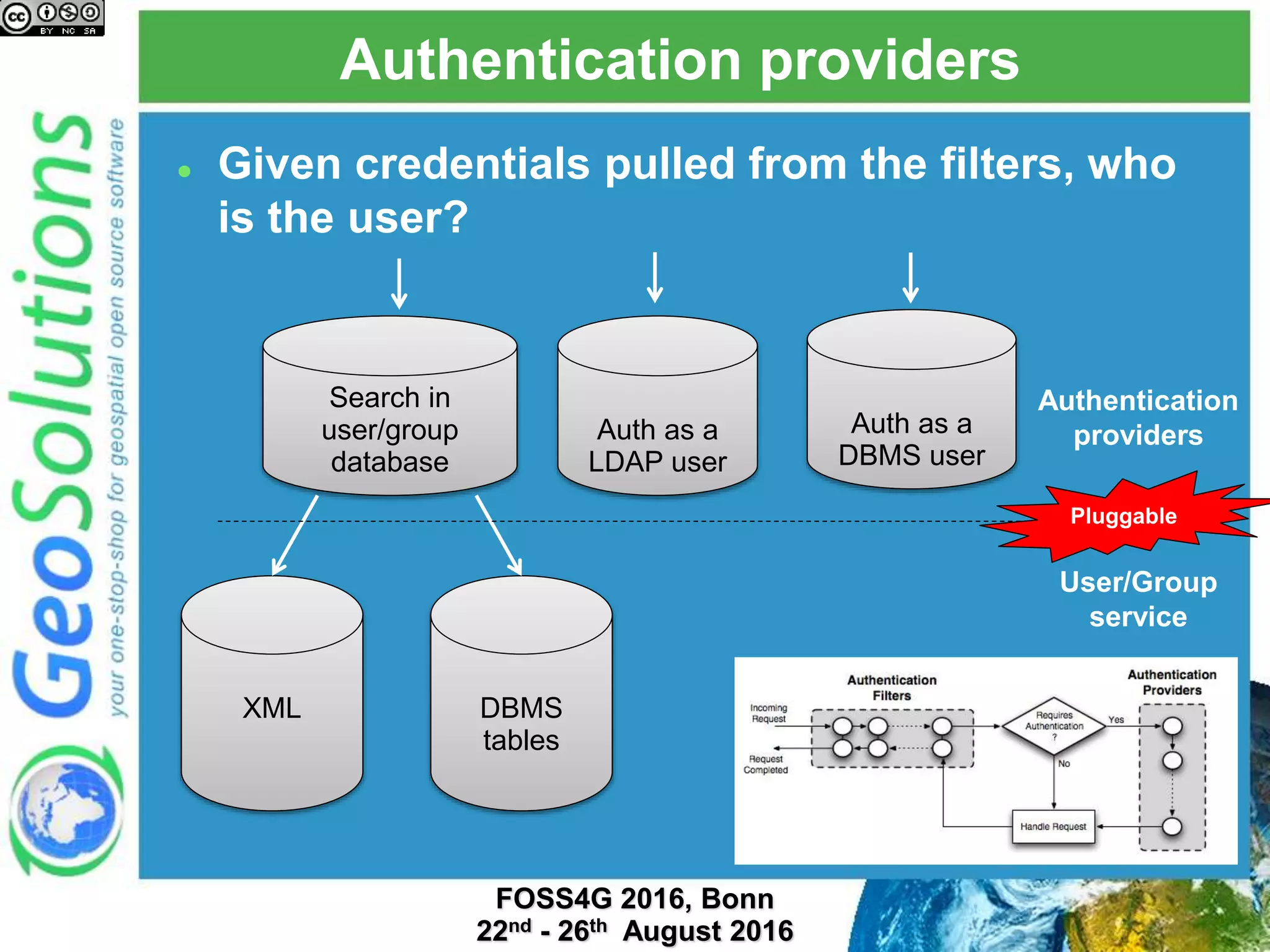
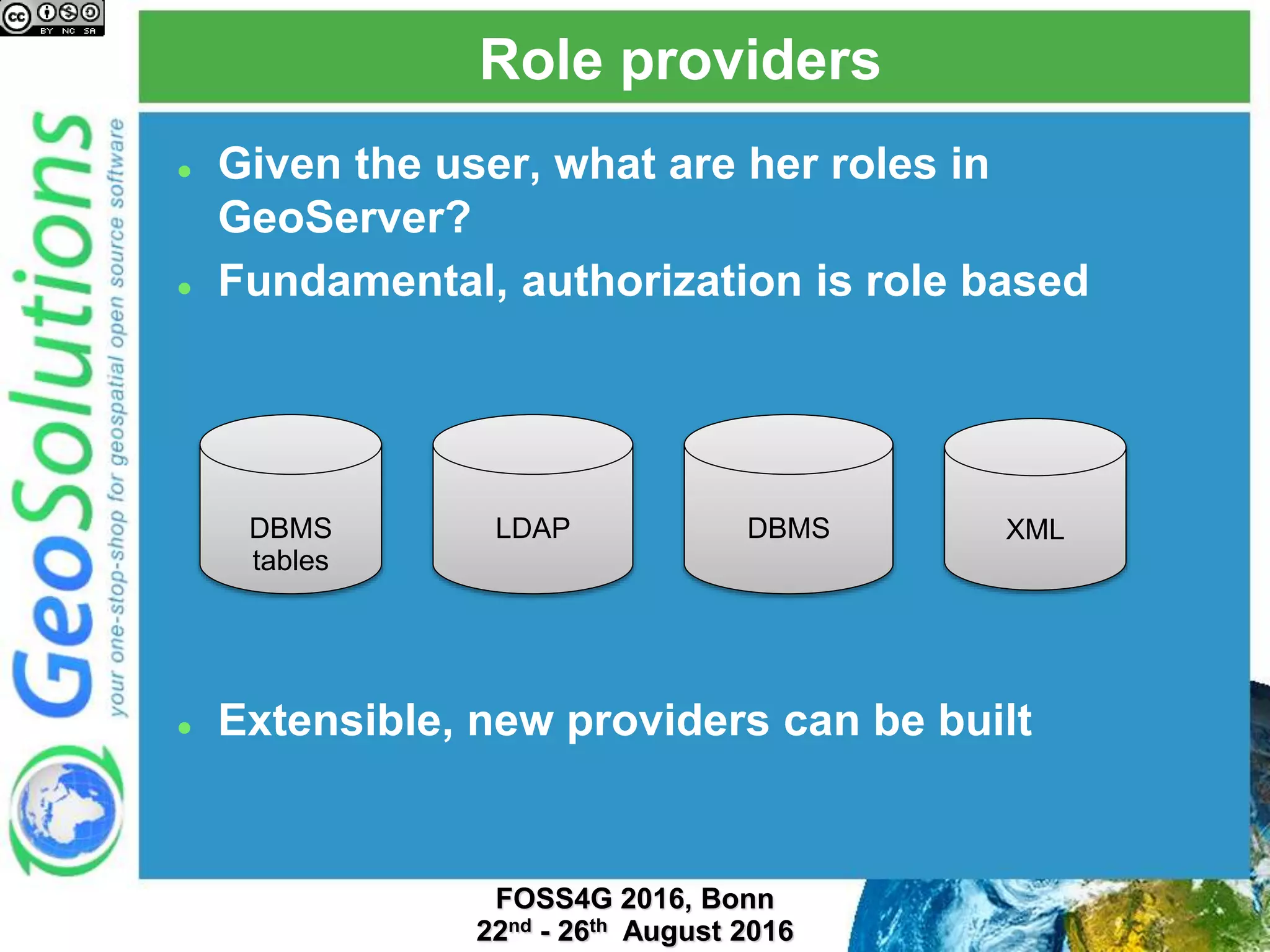
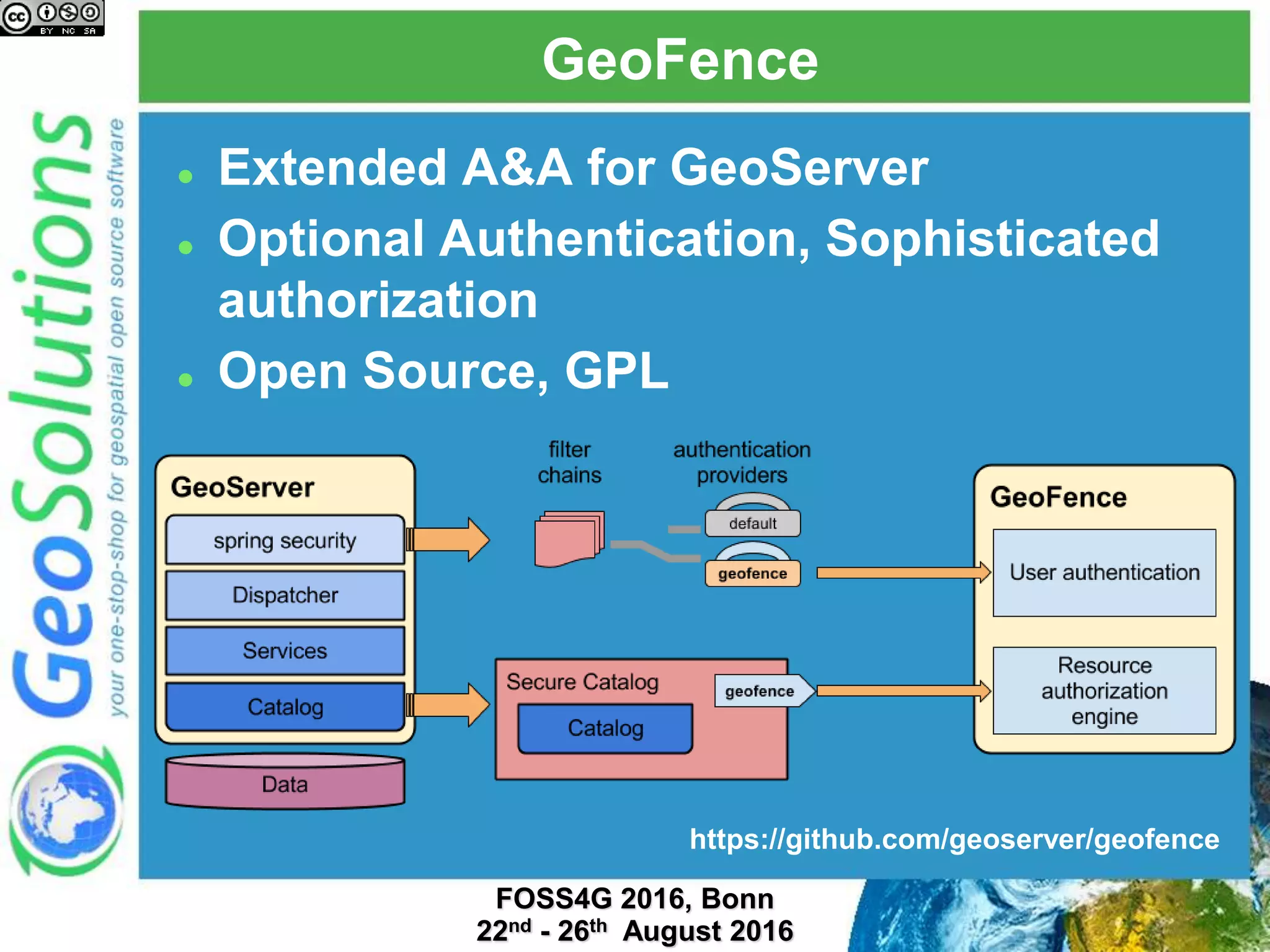
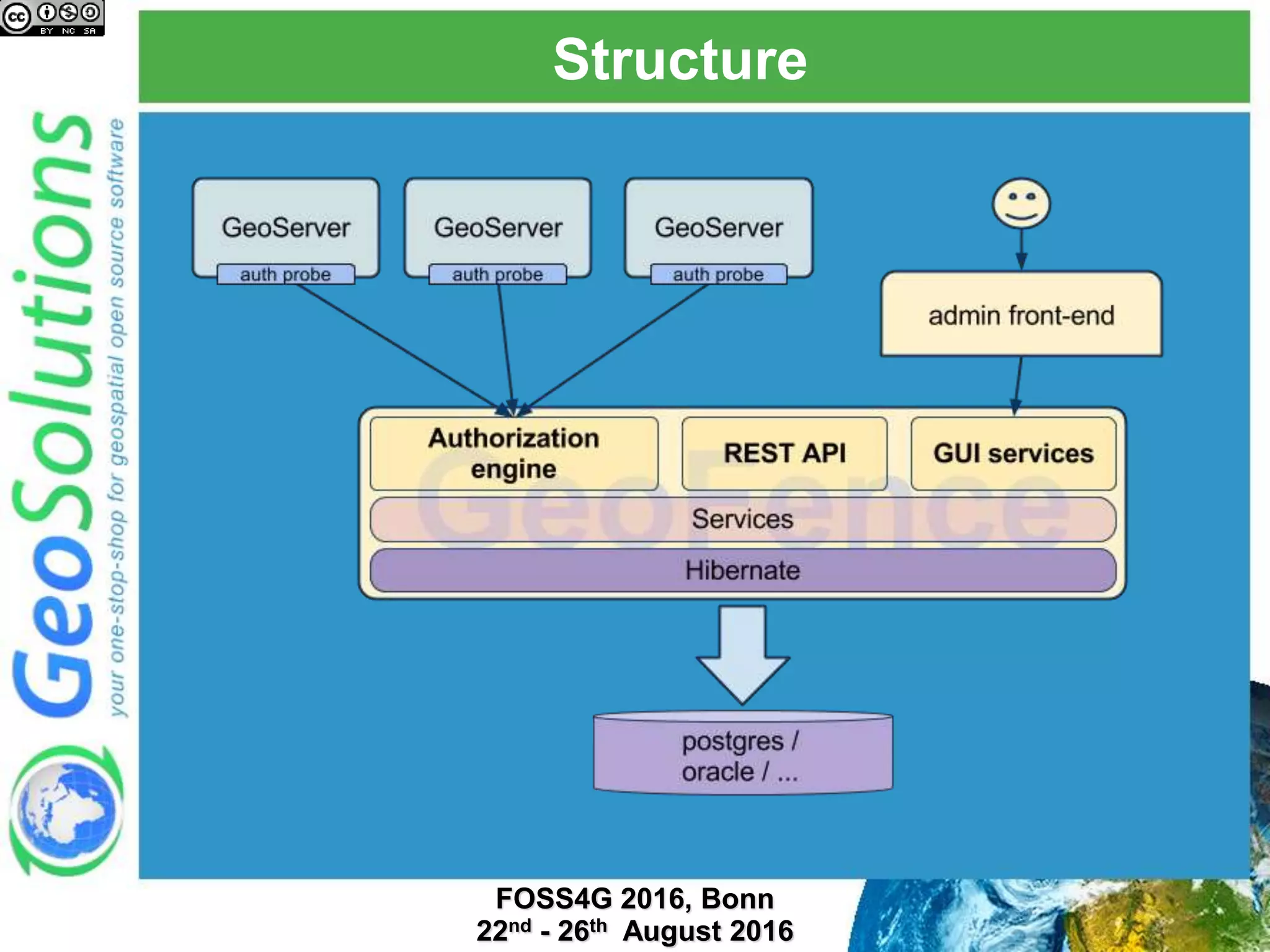
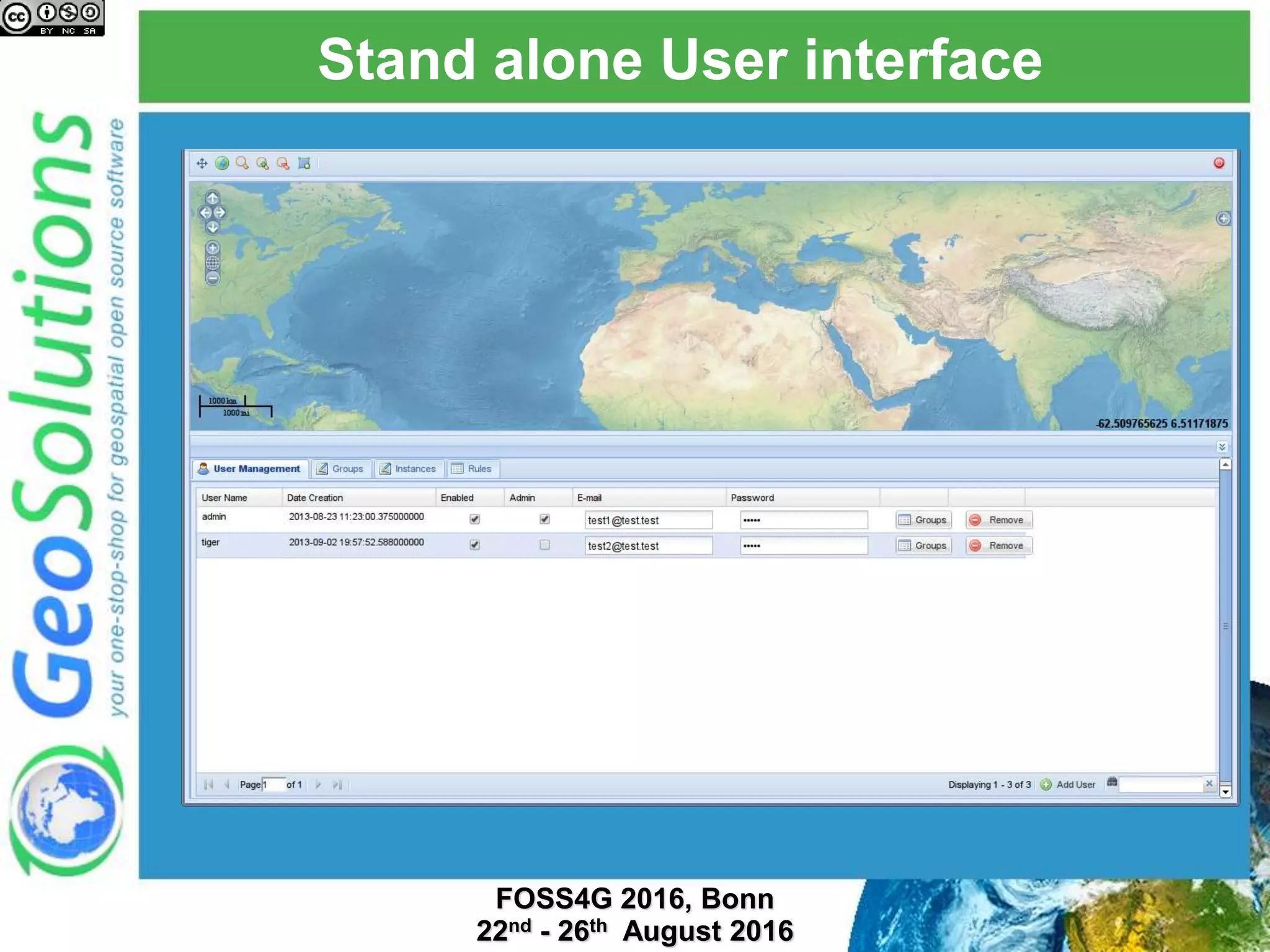
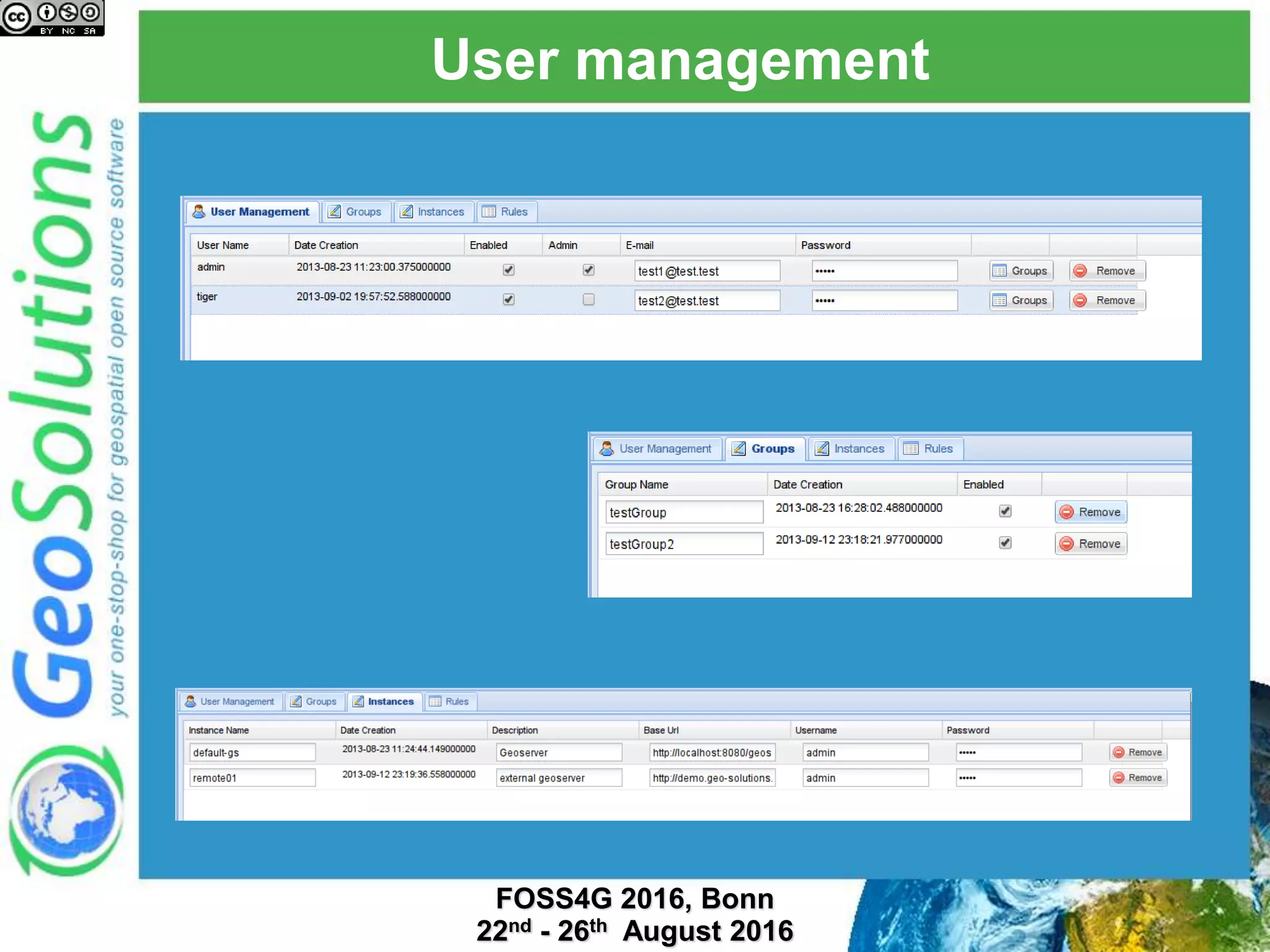
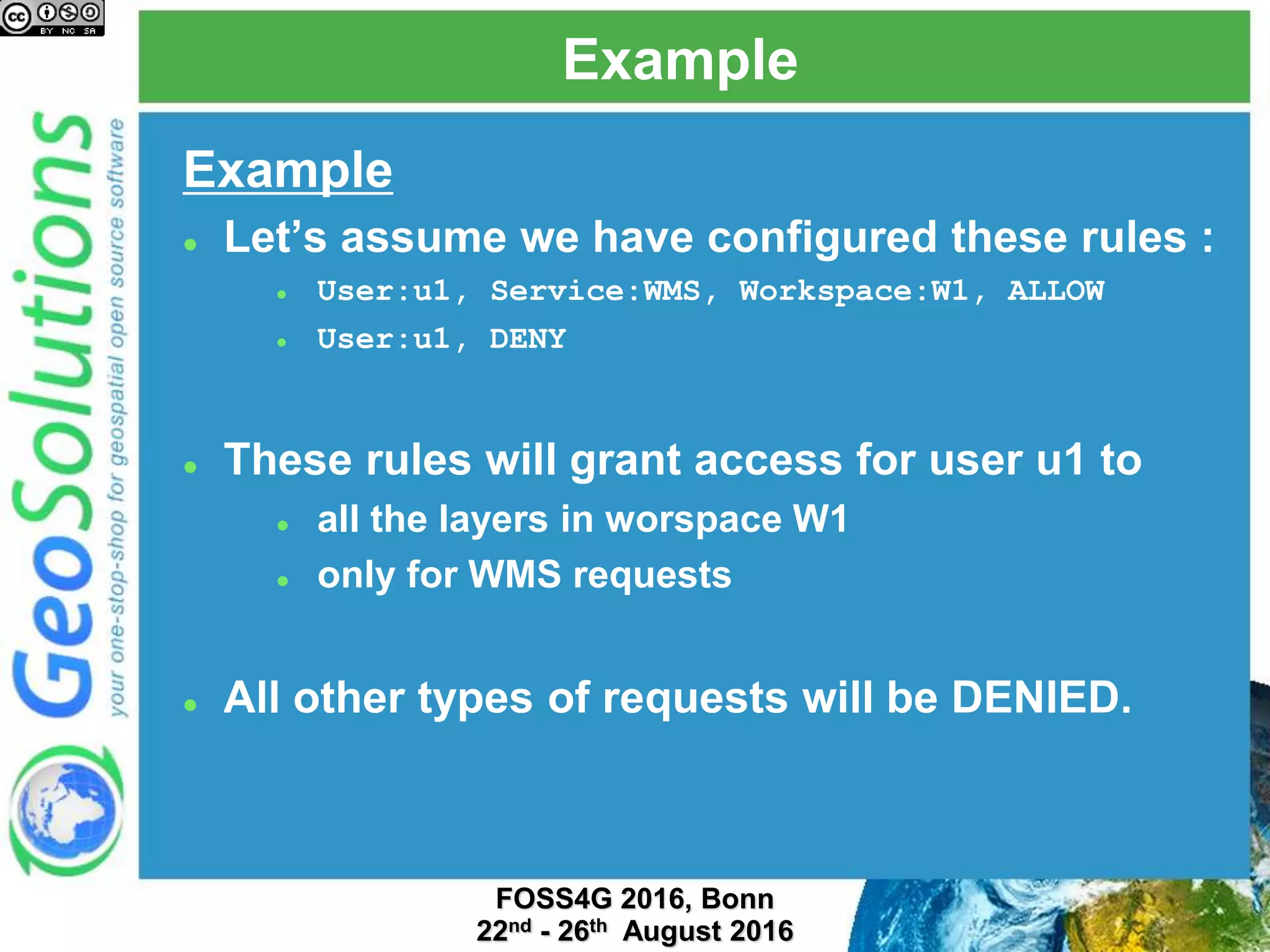
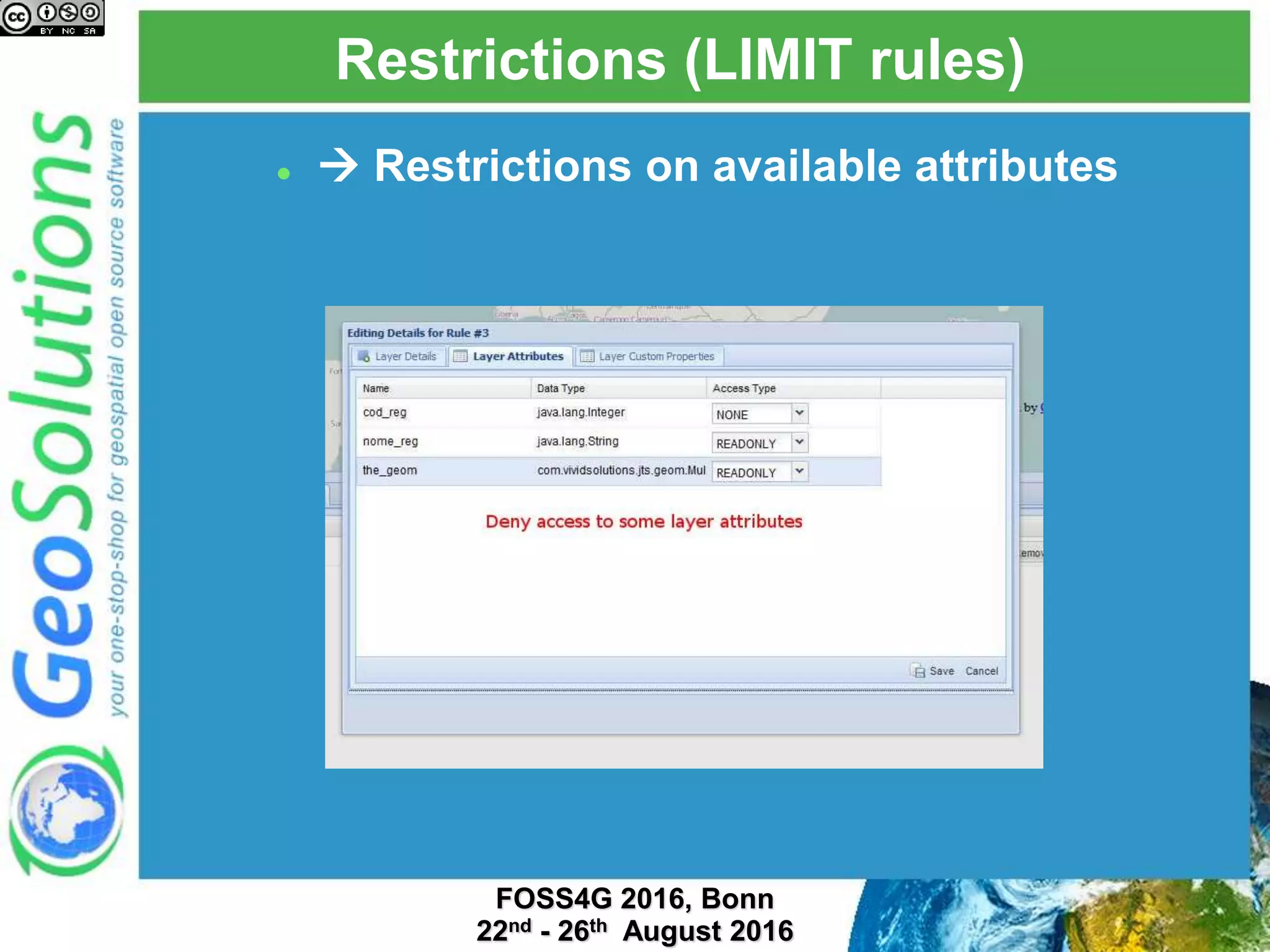
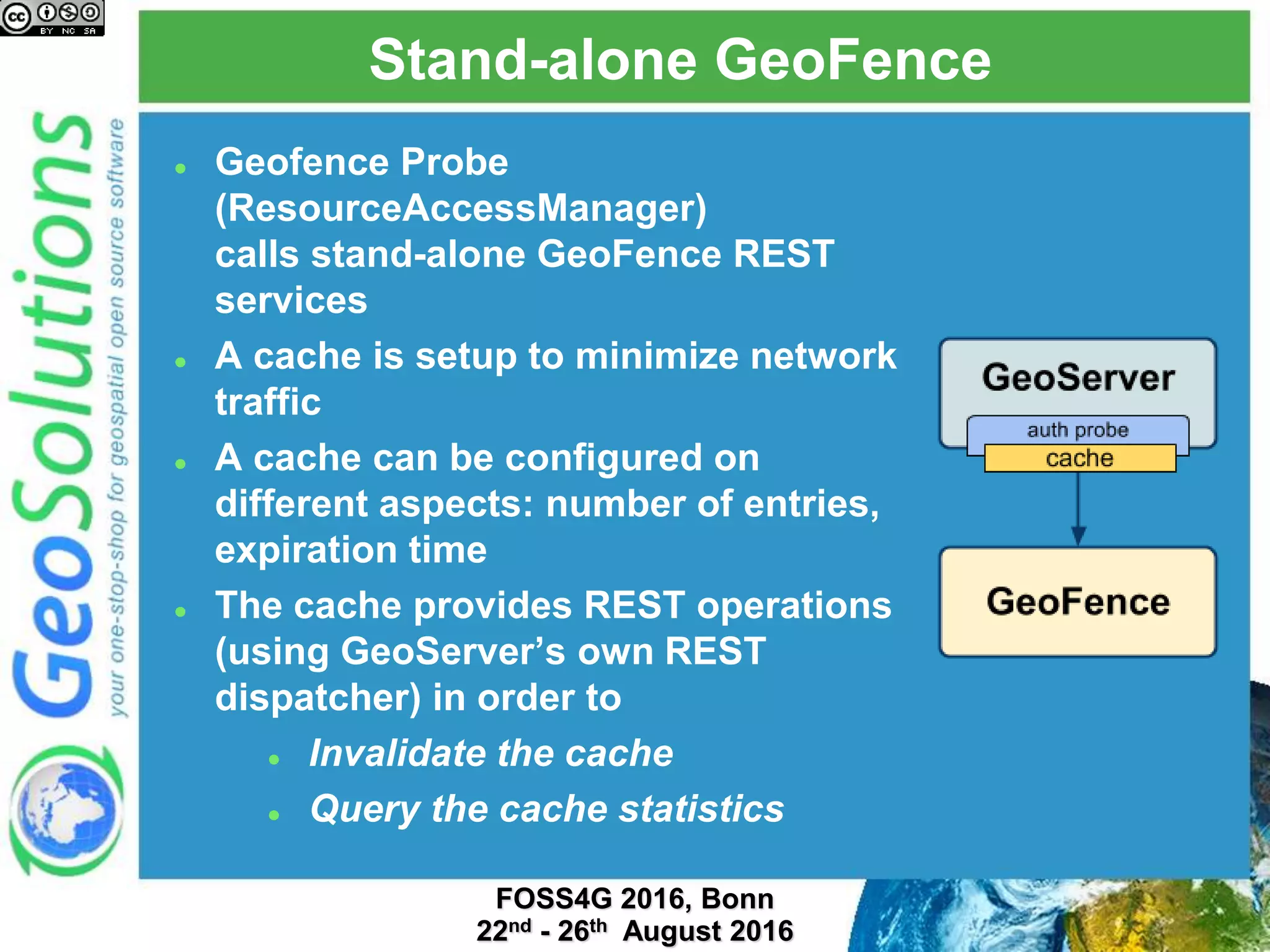
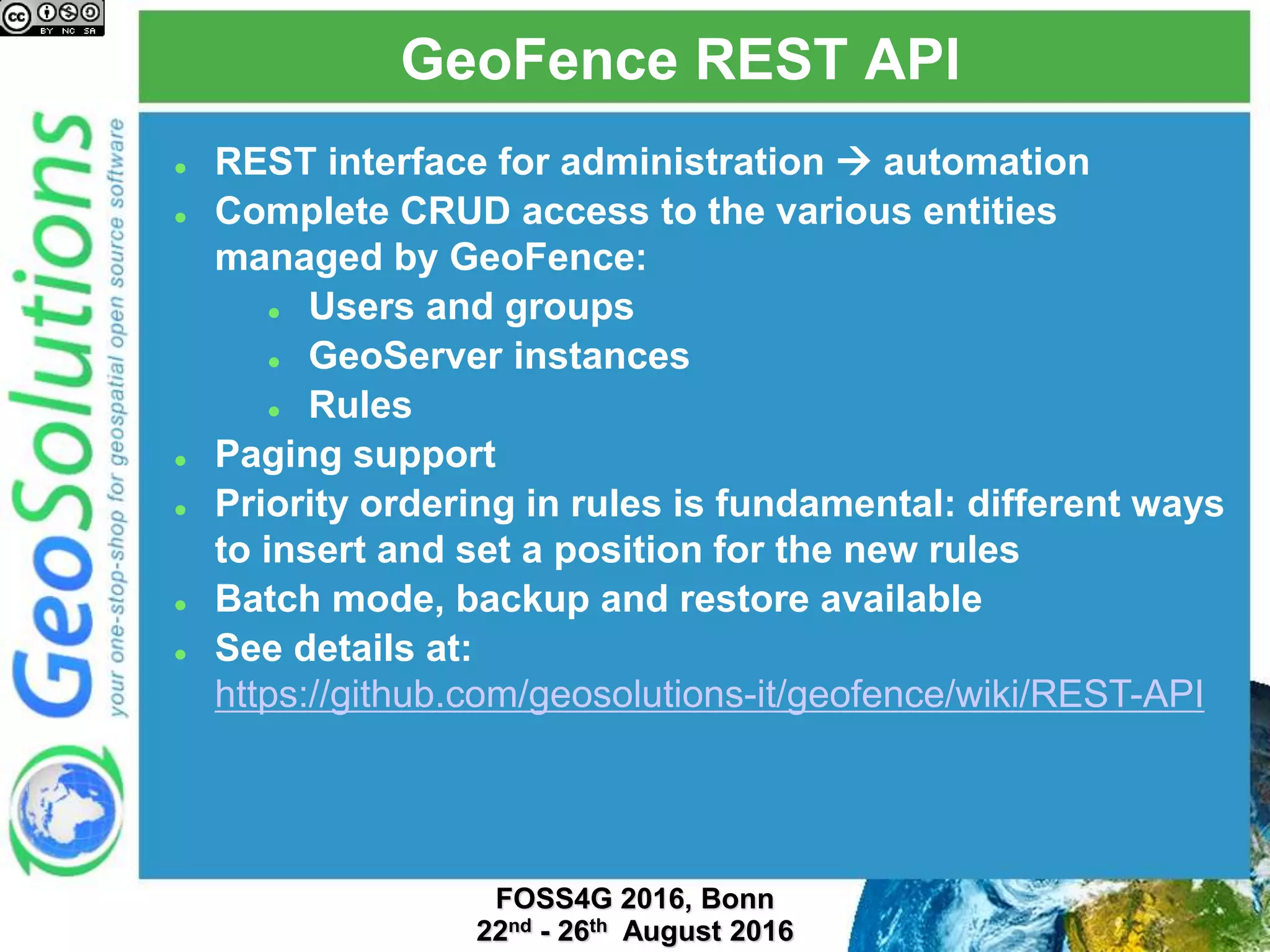
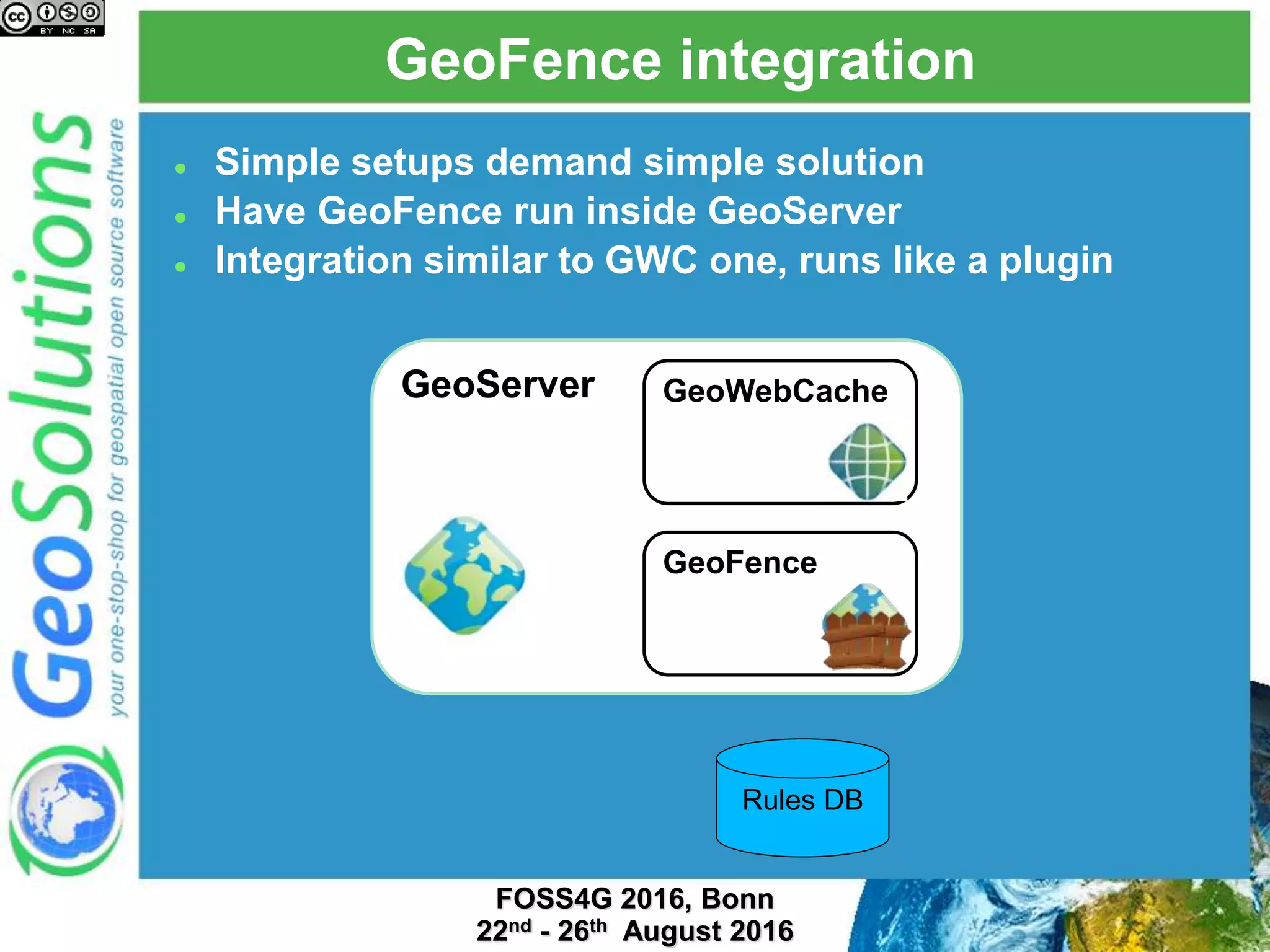
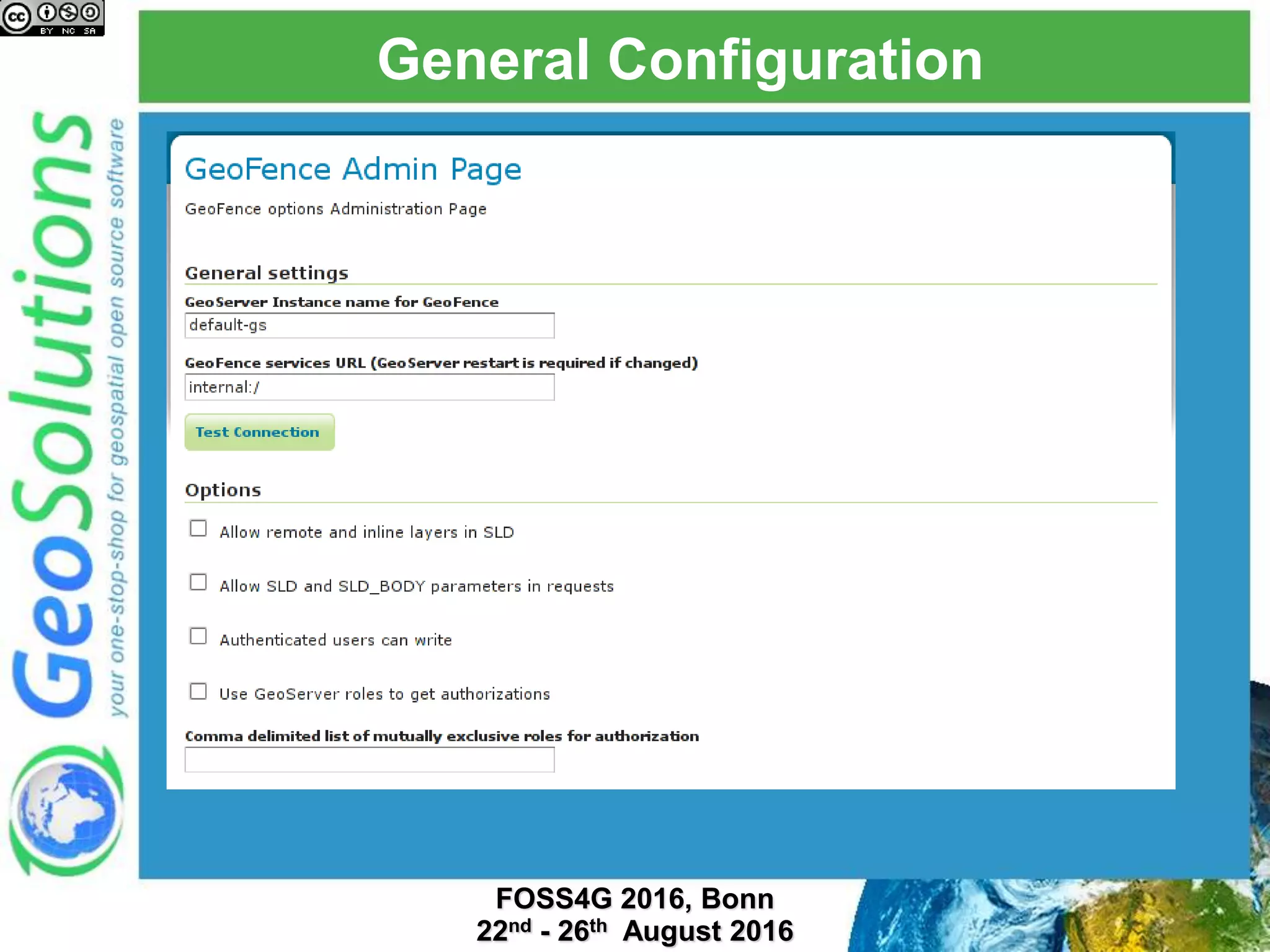
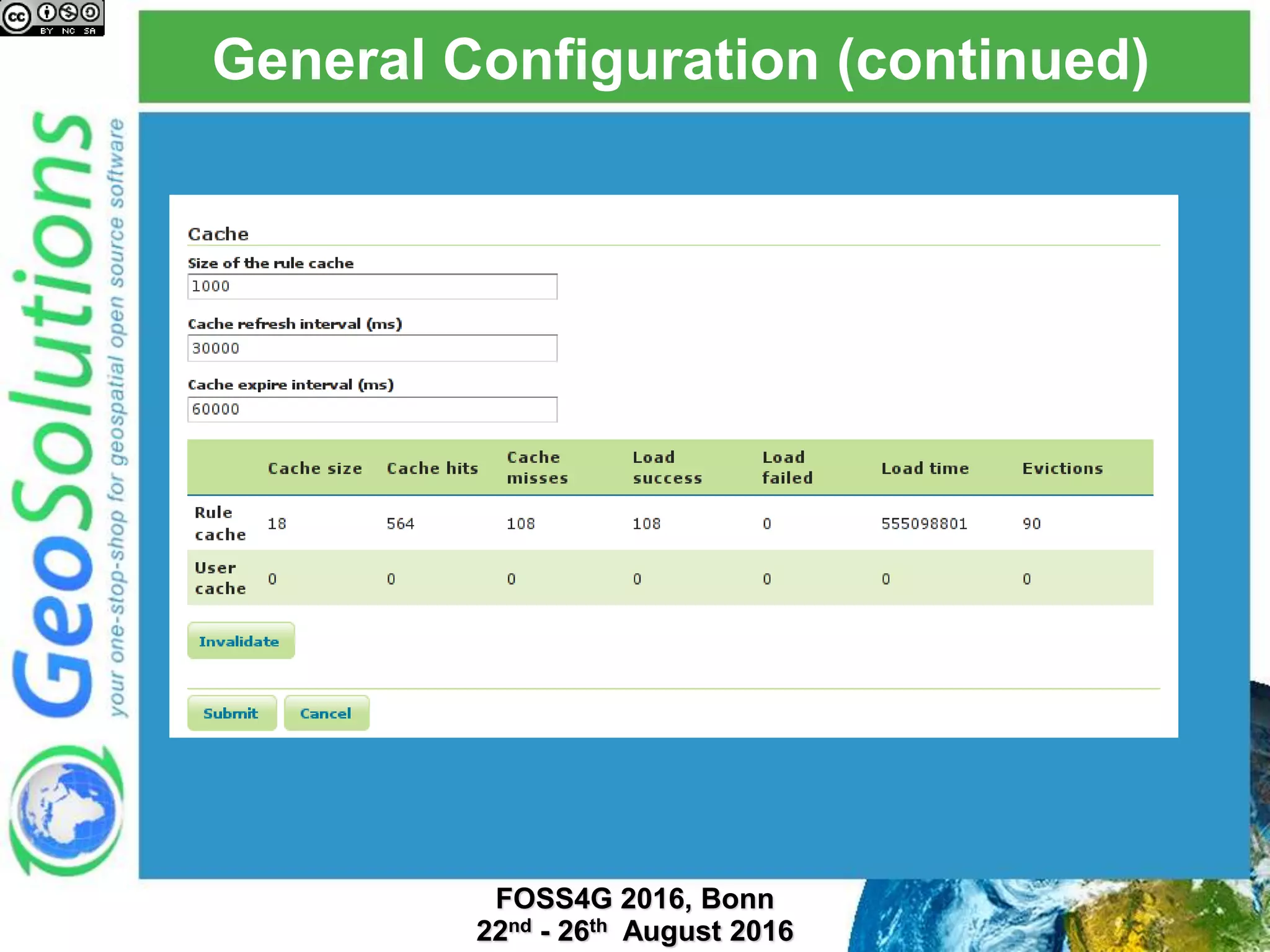
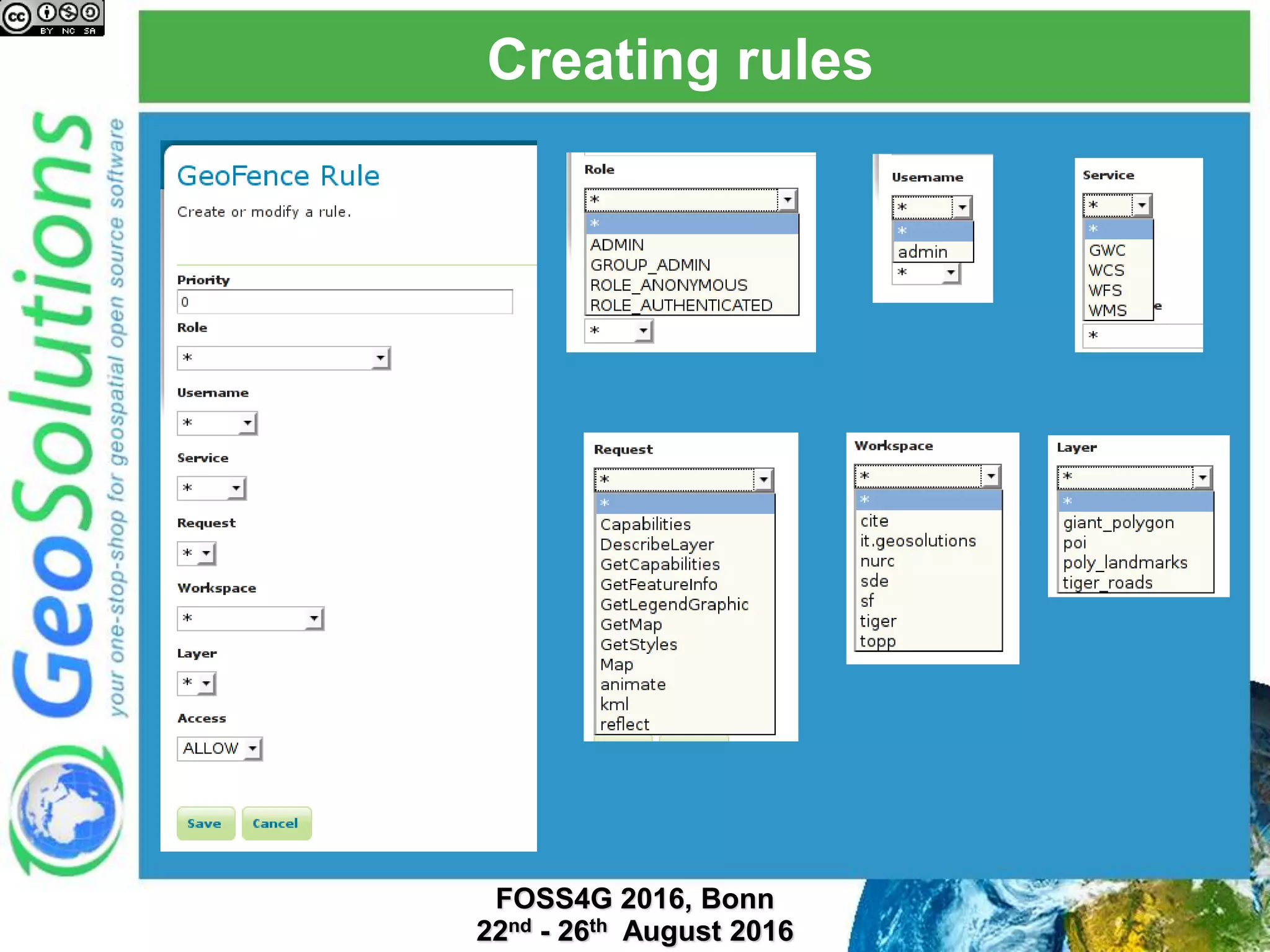
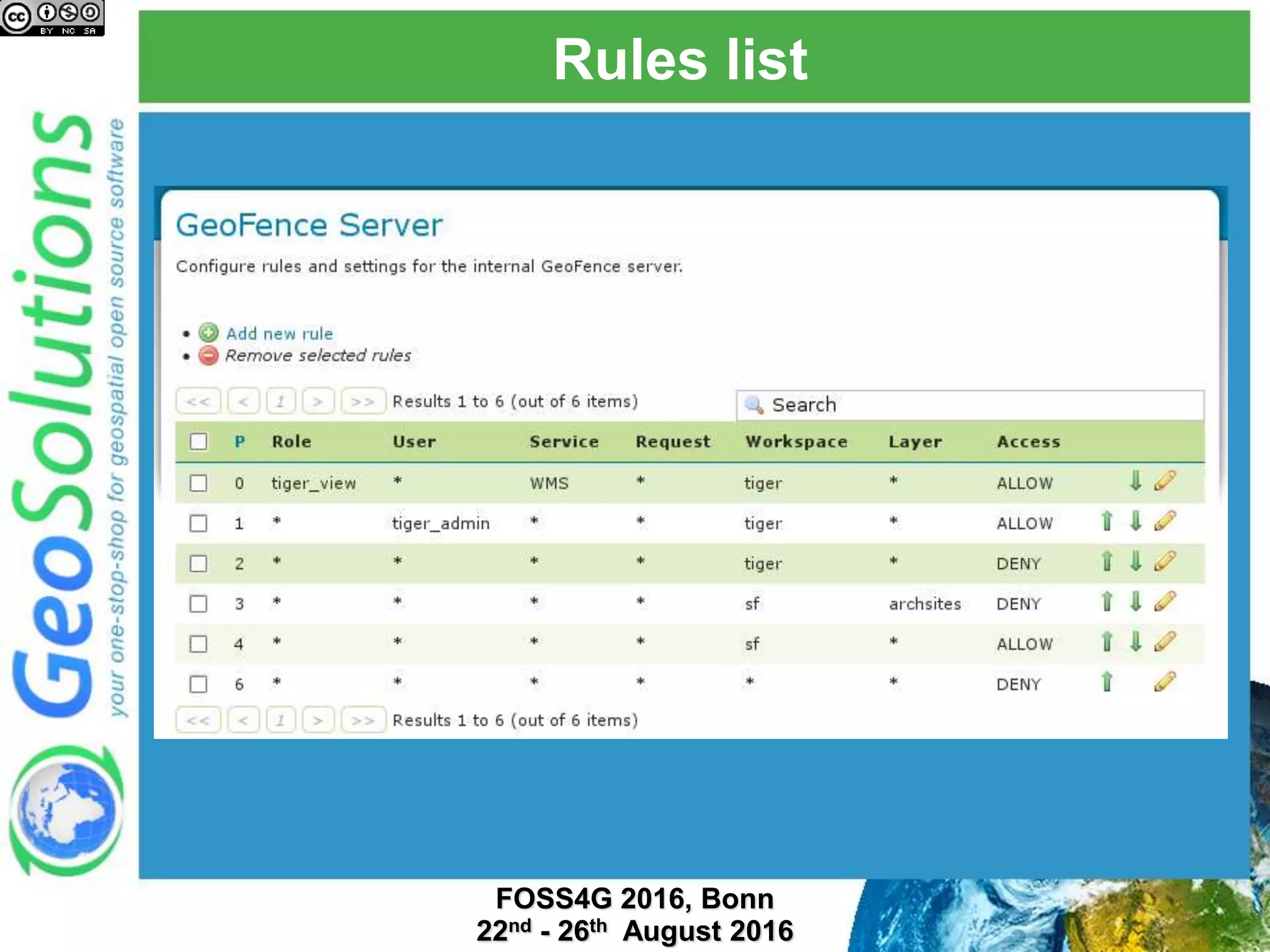
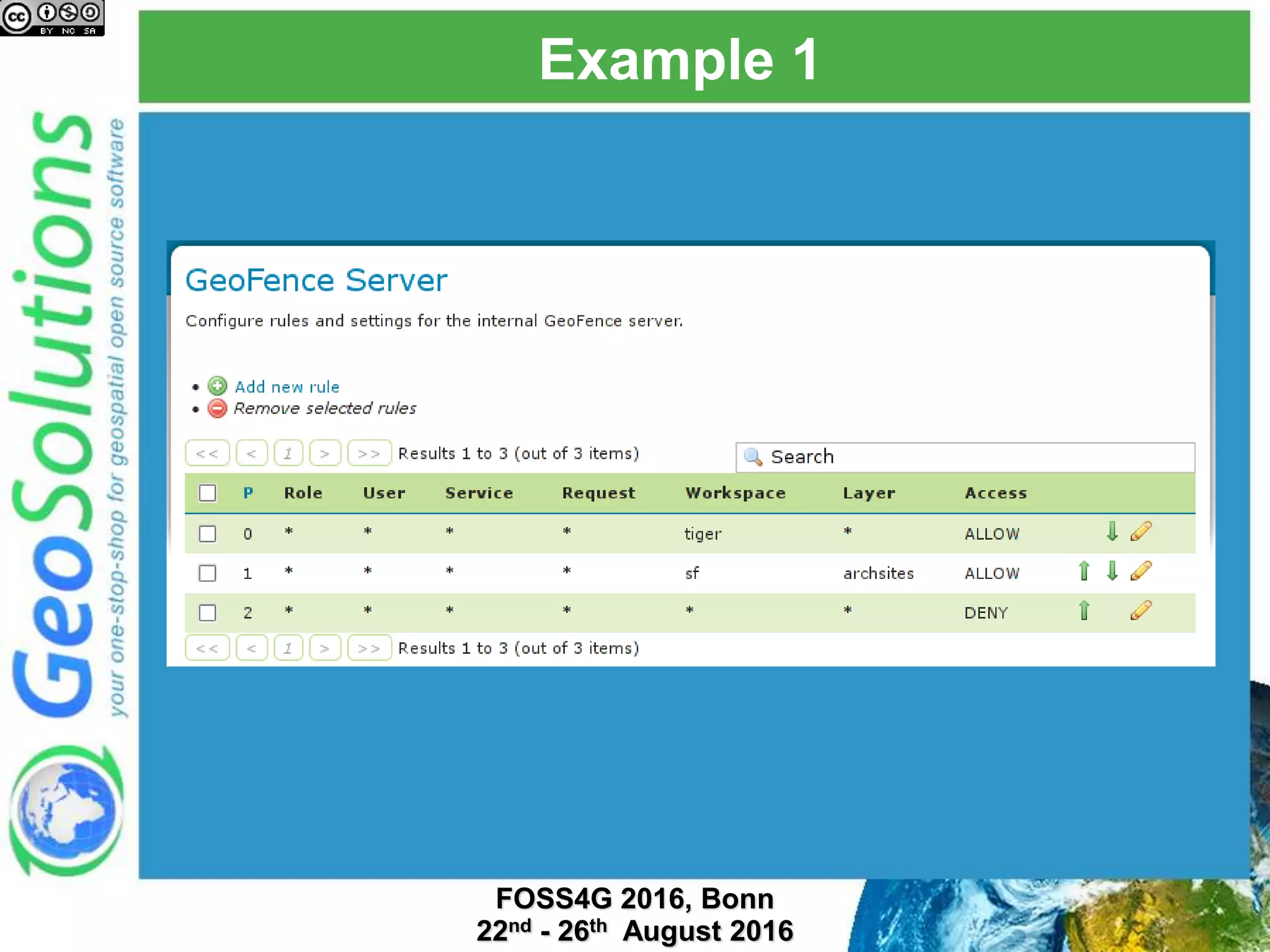
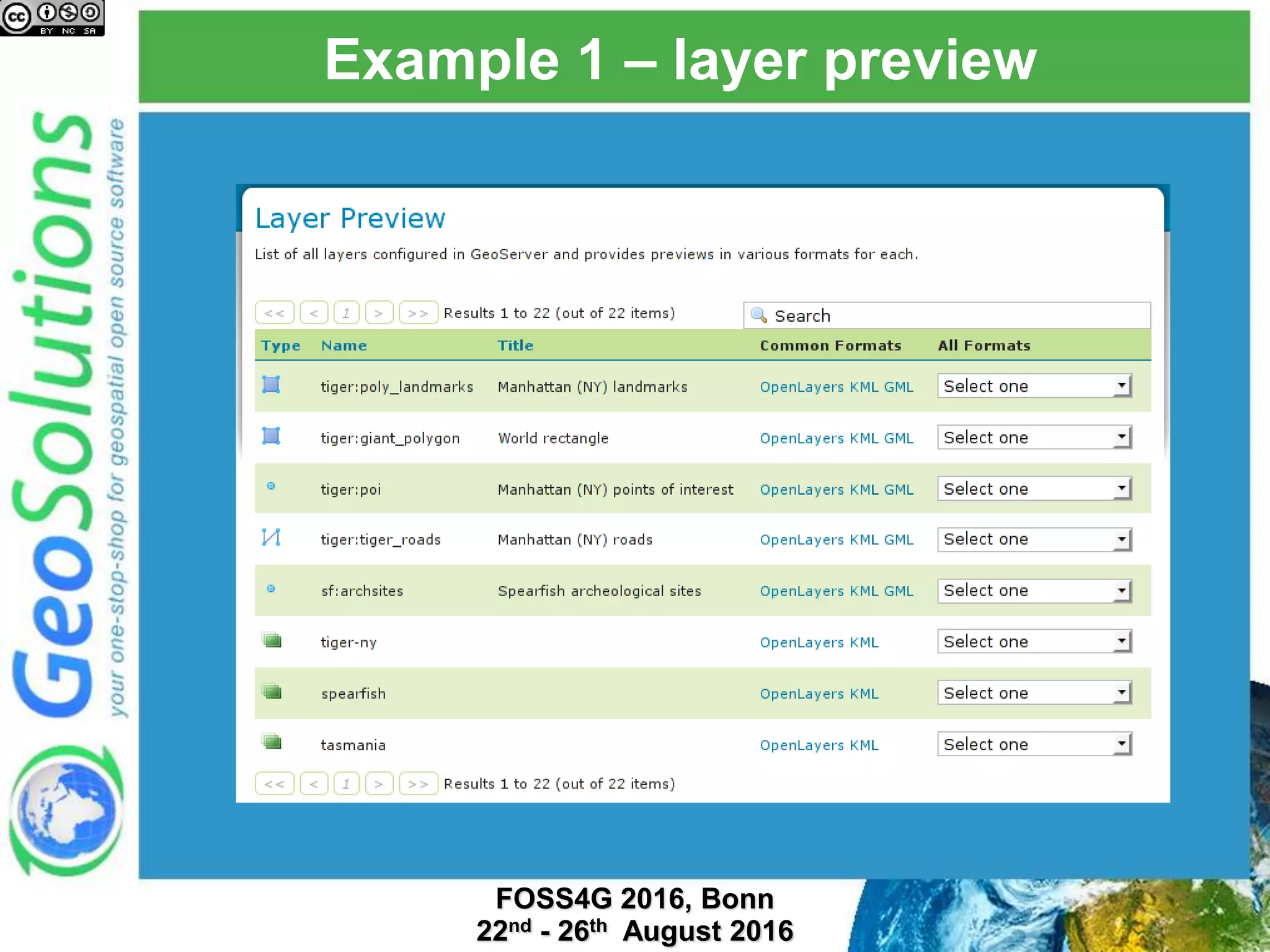
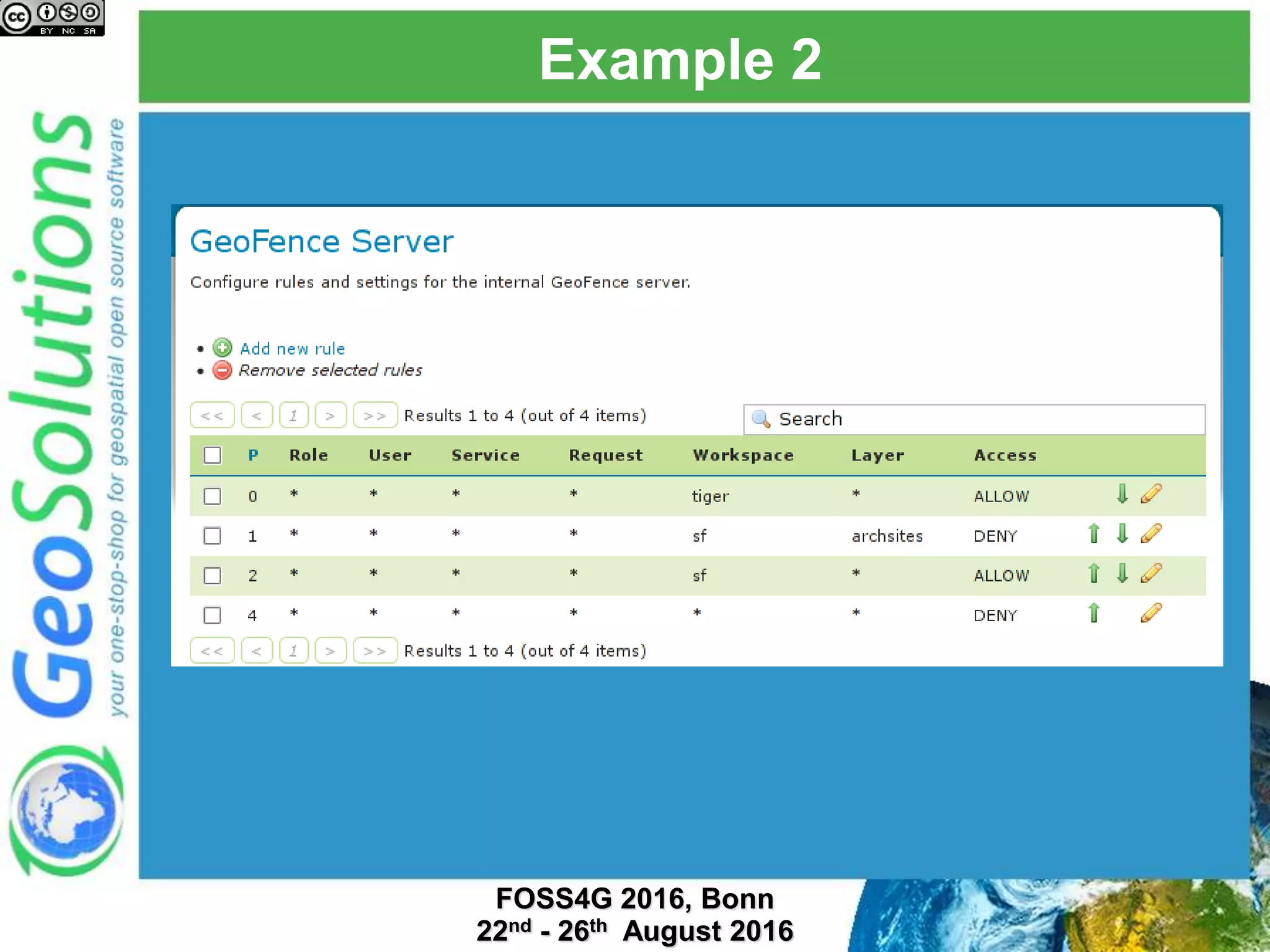
The document discusses security management in GeoServer using Geofence, detailing authentication and authorization processes for user access control. It explains how different authentication methods can be implemented through various filter chains and emphasizes the role-based authorization system. Additionally, it covers the Geofence framework's functionality in managing user permissions and rules within GeoServer, including its integration and REST API for user management and rule configuration.