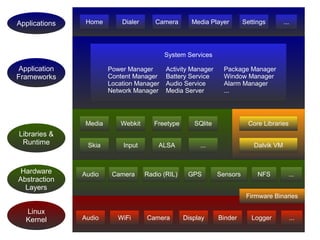
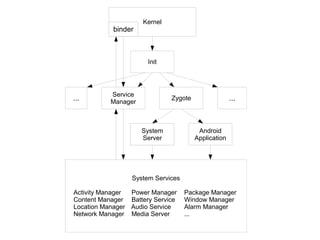
This document provides an overview of porting Android to new platforms. It discusses the Android software stack, the Android Open Source Project structure, the AOSP code structure, common Android hardware abstraction layers, device configuration files, the AOSP build process, the Android boot process, and Android debugging tools.