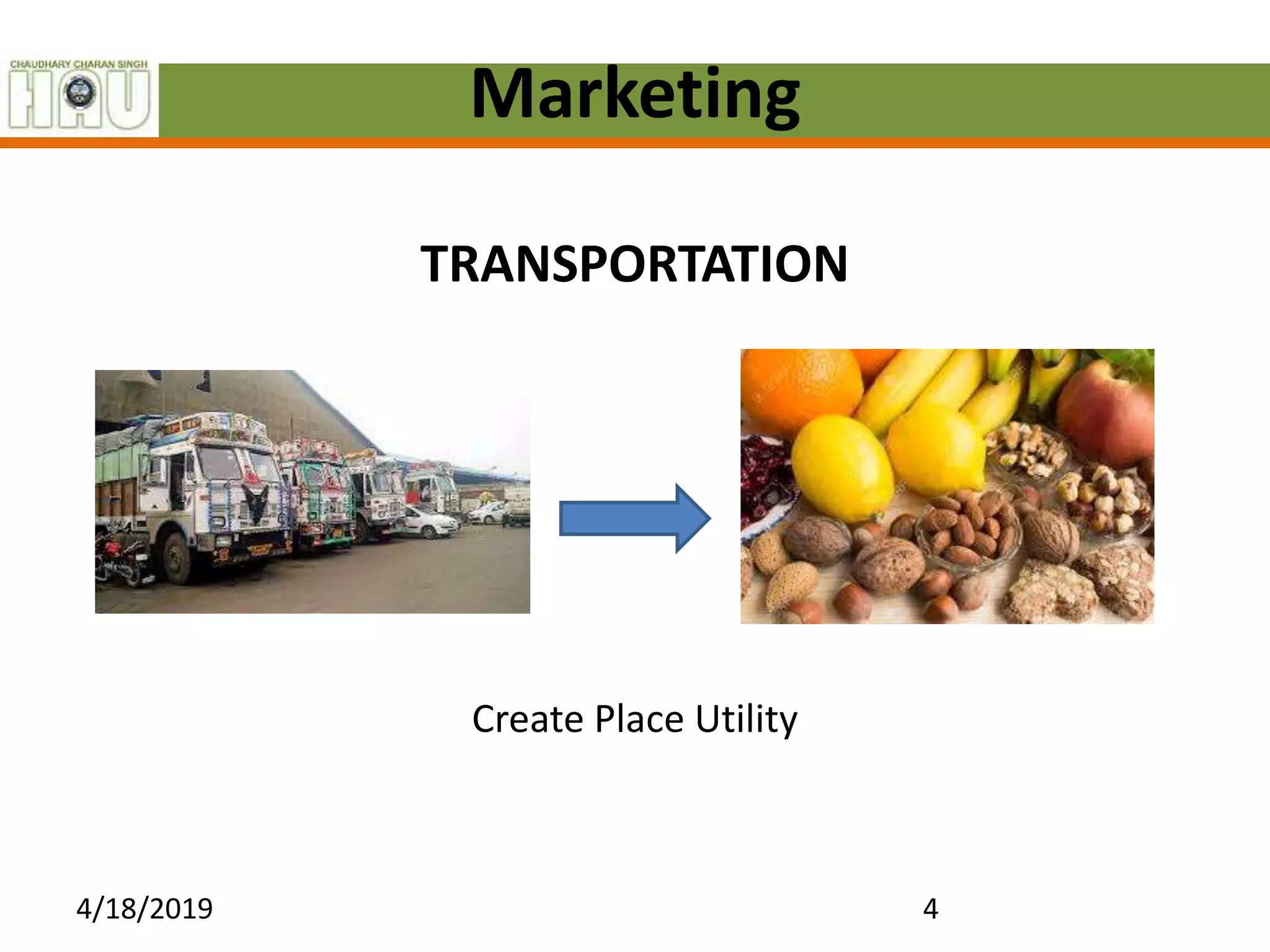
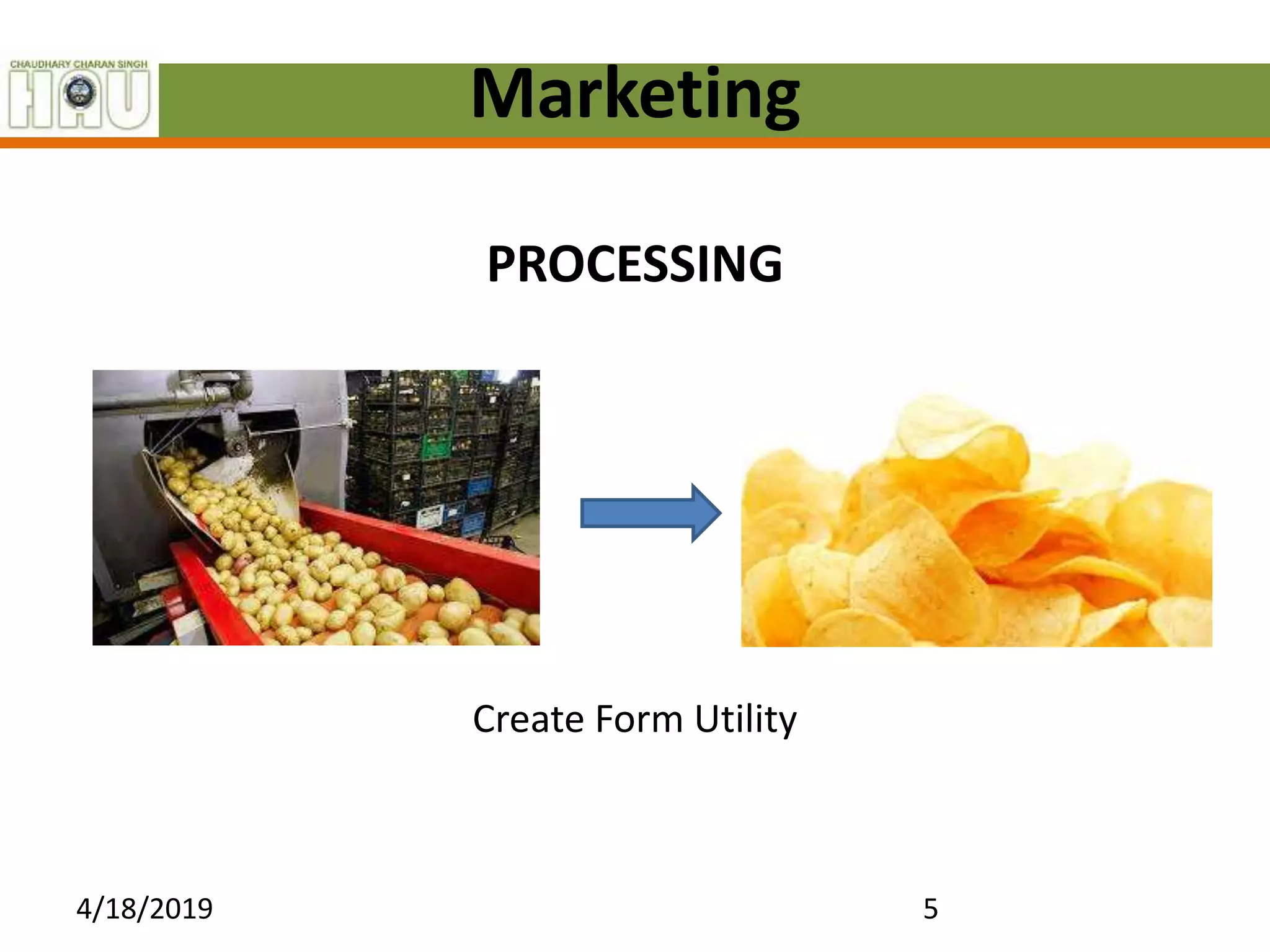
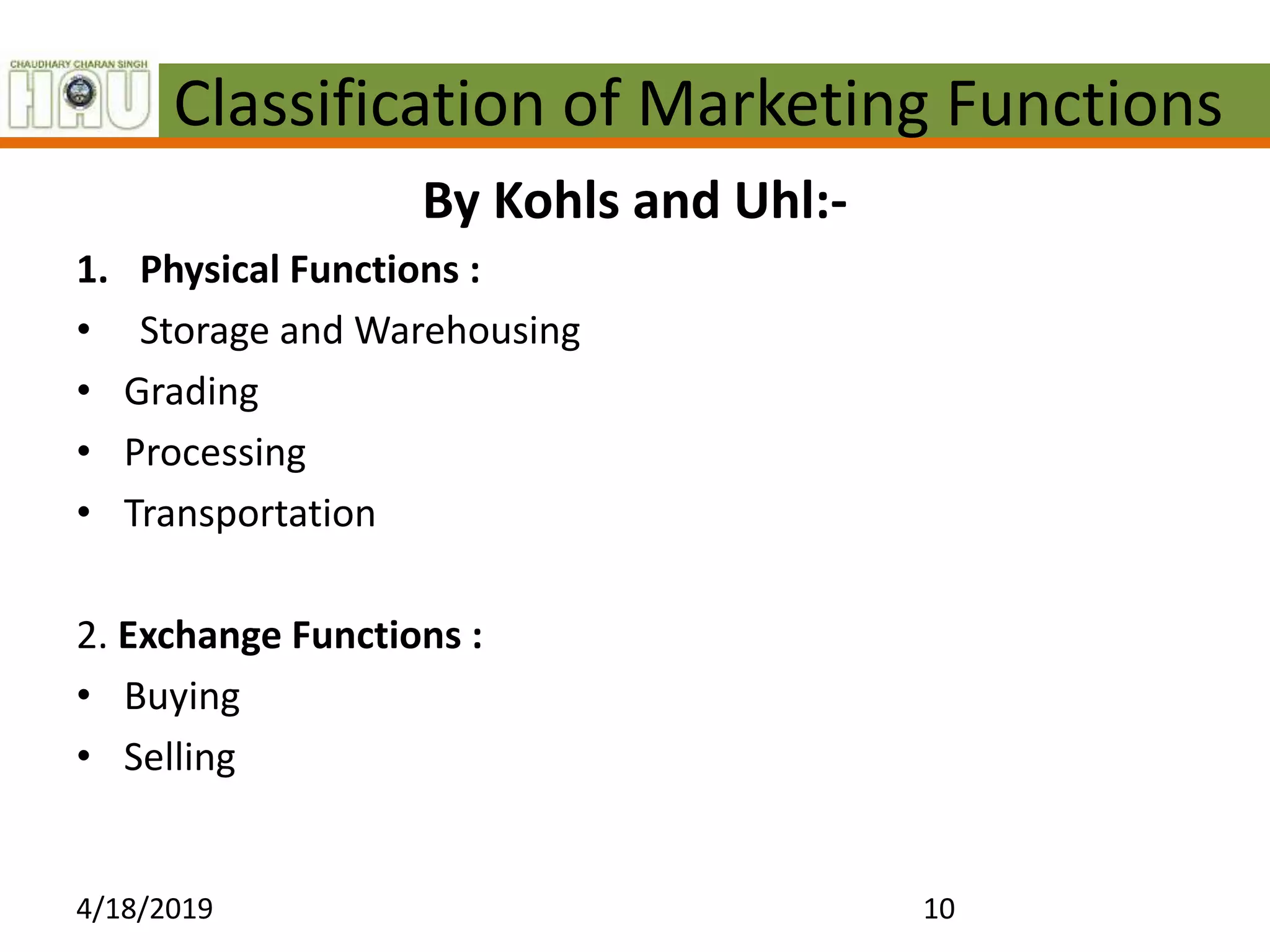
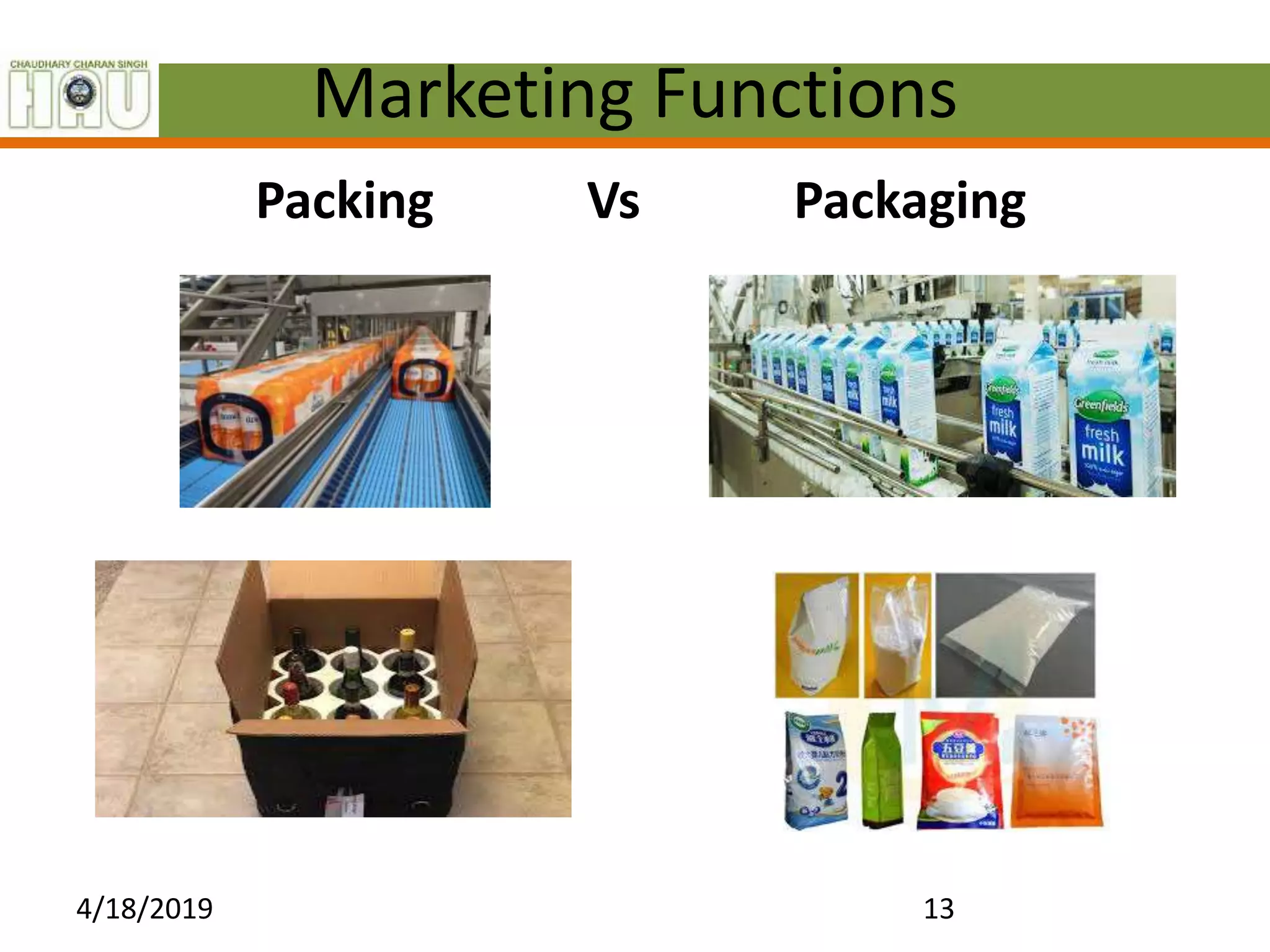
This document discusses several key marketing functions including packaging, transportation, grading, storage, processing, buying and selling, market information, and financing. It provides definitions and explanations of each function, as well as their advantages. For example, it explains that packaging protects goods, identifies brands, and reduces costs. Transportation widens markets and facilitates trade. Grading and standardization help farmers get better prices and consumers find quality products. Storage preserves goods and stabilizes prices. Processing changes raw materials into usable forms. Market information must be accurate, relevant and timely. Financing meets the capital needs of marketing agencies.