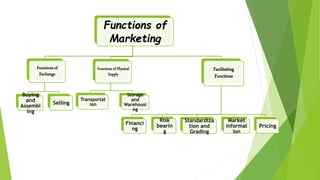
This document discusses the key functions of marketing. It outlines the functions of exchange which include buying, assembling, and selling goods. It also discusses the physical supply functions such as transportation, storage, and warehousing. Additionally, it covers the facilitating functions of financing, risk bearing, standardization and grading, market information, and pricing. These functions work together in the marketing process to facilitate the exchange of goods between producers and consumers.