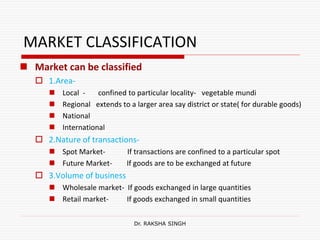
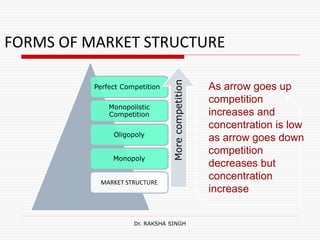
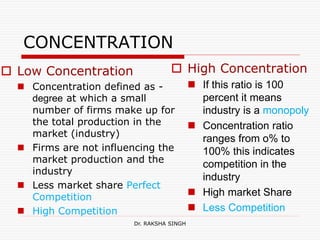
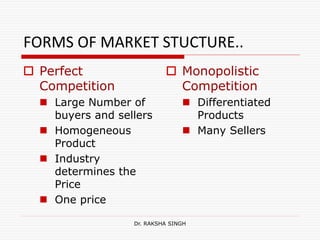
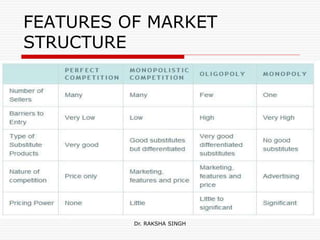
This document discusses market structure and its various forms. It defines a market and lists its key features such as buyers and sellers, competition, interaction, existence of commodities, price, and knowledge. The document then classifies markets based on area, nature of transactions, volume of business, time period, level of regulation, and sellers. It also discusses different forms of market structure from perfect competition to monopoly based on the number of firms and level of product differentiation. Concentration and its effect on competition are explained. Finally, some Hindi translations of market structure terms are provided.