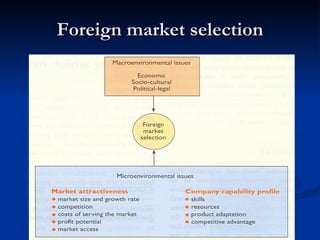
This document outlines the process for selecting foreign markets, including 4 main steps:
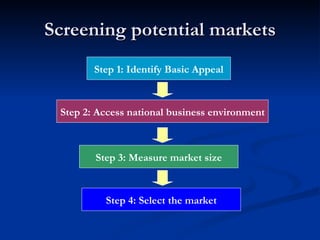
1) Identify the basic appeal by considering demand factors, resource availability, and cultural/local forces.
2) Assess the national business environment by analyzing political/legal forces, economic forces, and information availability.
3) Measure the size of the market using variables like growth rate and consumption capacity.
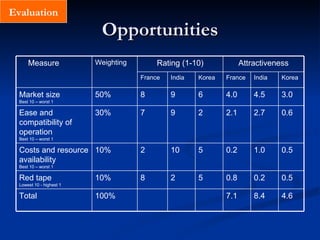
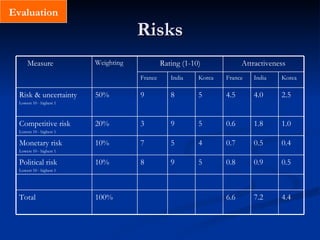
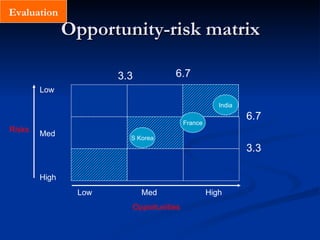
4) Select the market by evaluating opportunities and risks, with opportunities including market size, ease of operations, and costs/resources, and risks covering political, monetary, competitive, and uncertainty factors. Markets are then plotted on an opportunity-risk matrix to identify the best choices.