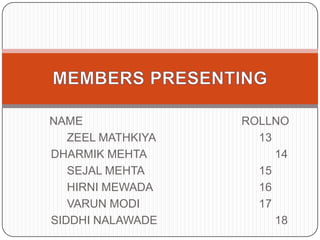
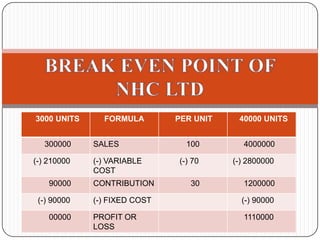
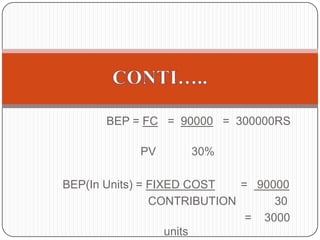
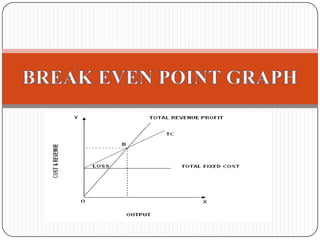
This document provides an introduction to the concept of marginal costing. It defines marginal costing as accounting that distinguishes between fixed and variable costs, charging variable costs to cost units and writing off fixed costs against the total contribution. The document outlines the key features, advantages, and disadvantages of marginal costing. It also provides an example of calculating the break-even point and profit-volume ratio of a company called NHC Foods Ltd. The document concludes that marginal costing supports managerial decision making.