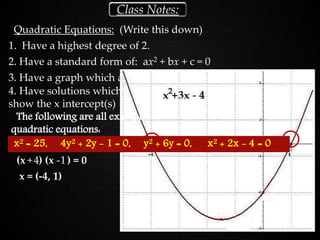
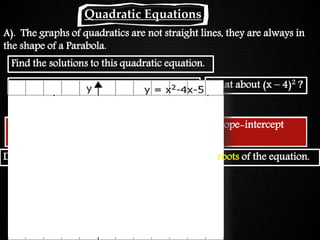
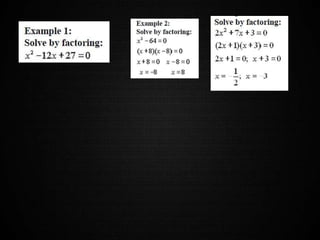
This document provides notes and examples on solving quadratic equations. It begins with an agenda for the day which includes warm up exercises, class notes on solving quadratics, and a factoring test. The class notes section defines quadratic equations, explains their standard form and graph as a parabola, and provides examples of solving various quadratics by factoring. It also discusses properties of parabolas such as having two solutions. The document concludes by providing examples and steps for solving different types of quadratics by factoring and taking square roots.