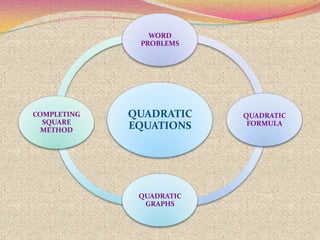
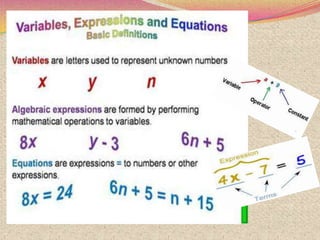
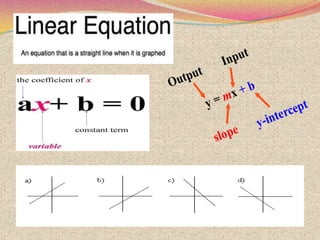
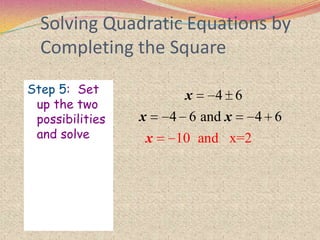
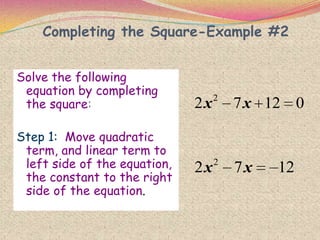
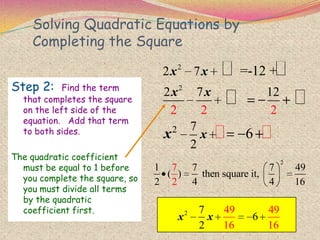
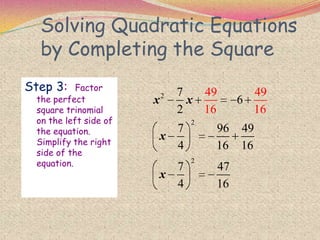
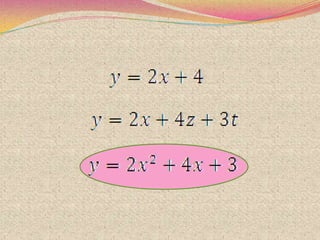The document discusses various topics relating to quadratic equations including:
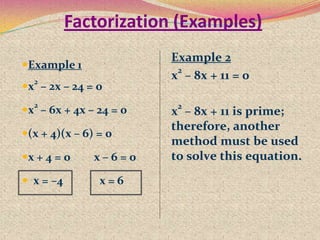
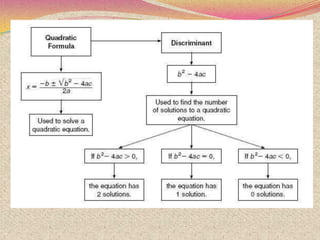
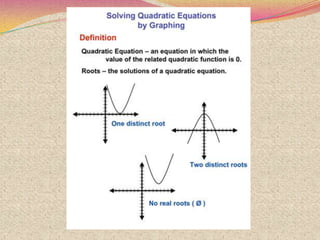
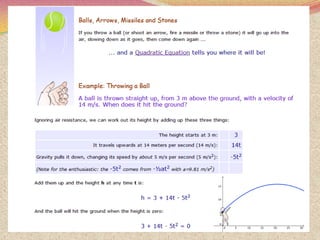
1) Methods for solving quadratic equations such as completing the square, factorization, and the quadratic formula.
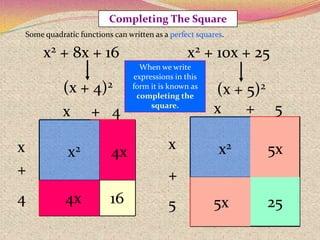
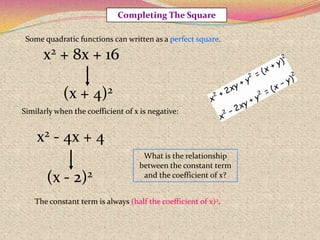
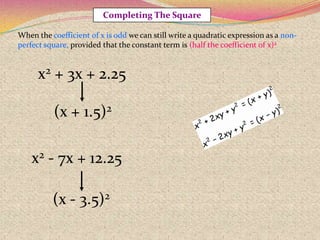
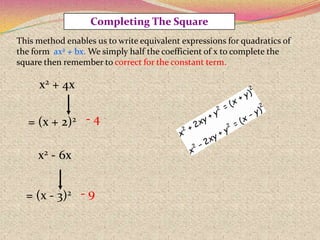
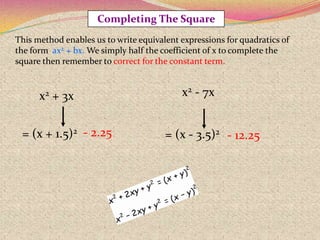
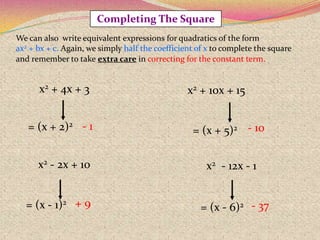
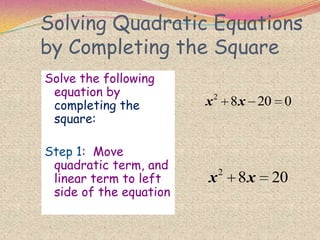
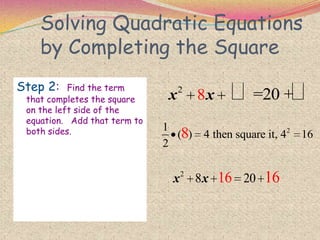
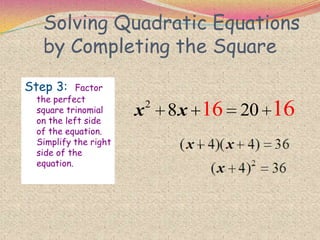
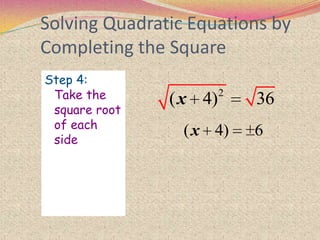
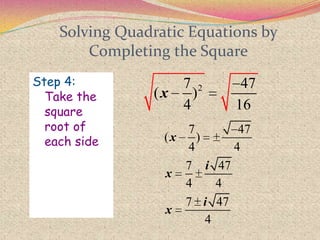
2) The steps for using the completing the square method which involves rewriting the quadratic in the form of a perfect square trinomial.
3) Examples are provided to demonstrate how to use completing the square to solve quadratic equations.