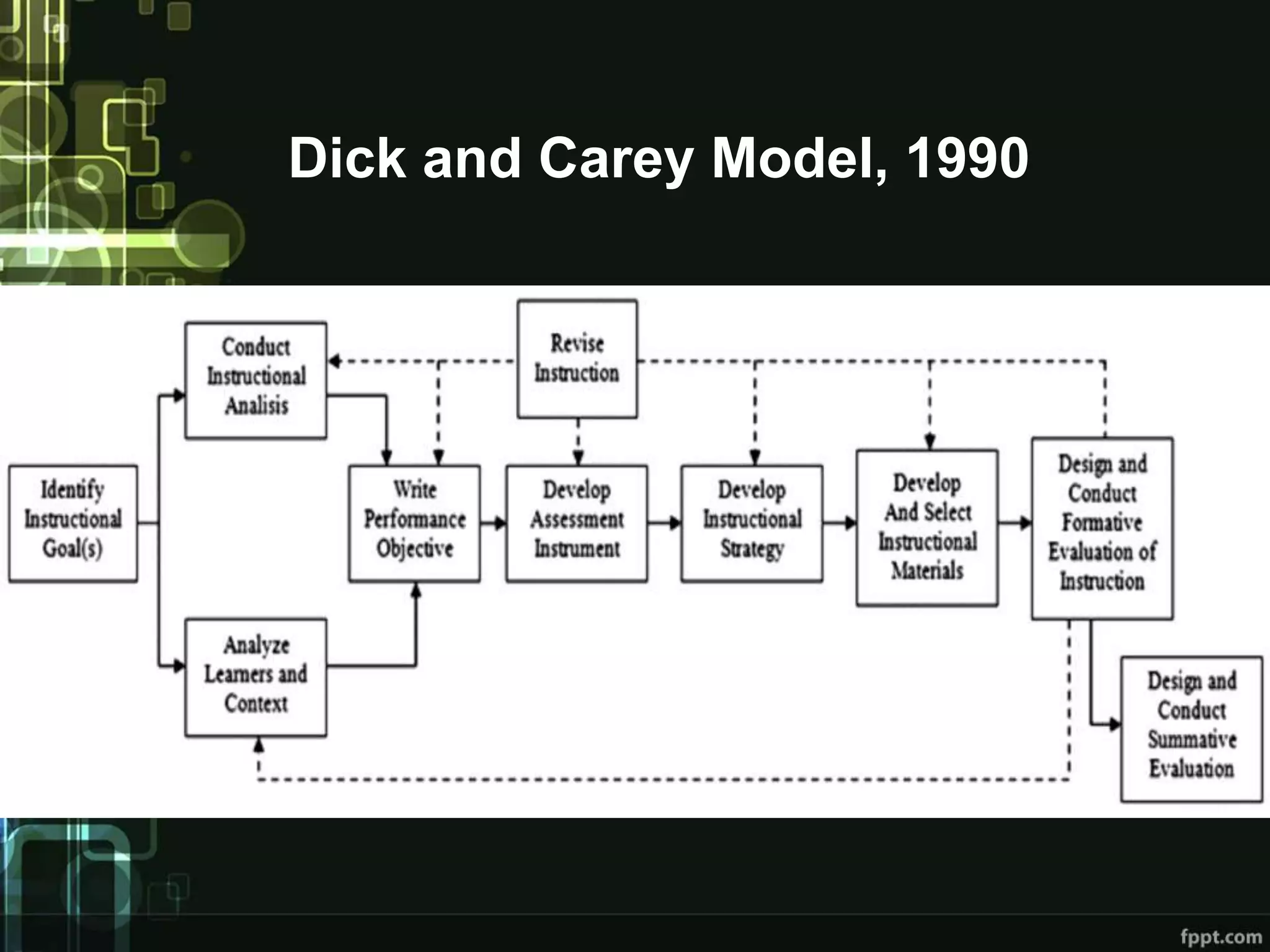
The document outlines instructional design principles and models, emphasizing systematic planning to create effective educational experiences. It details various instructional design models, particularly the Dick and Carey model, which includes steps from identifying instructional goals to conducting evaluations. Additionally, it emphasizes understanding learner characteristics and preferences to tailor instruction effectively.