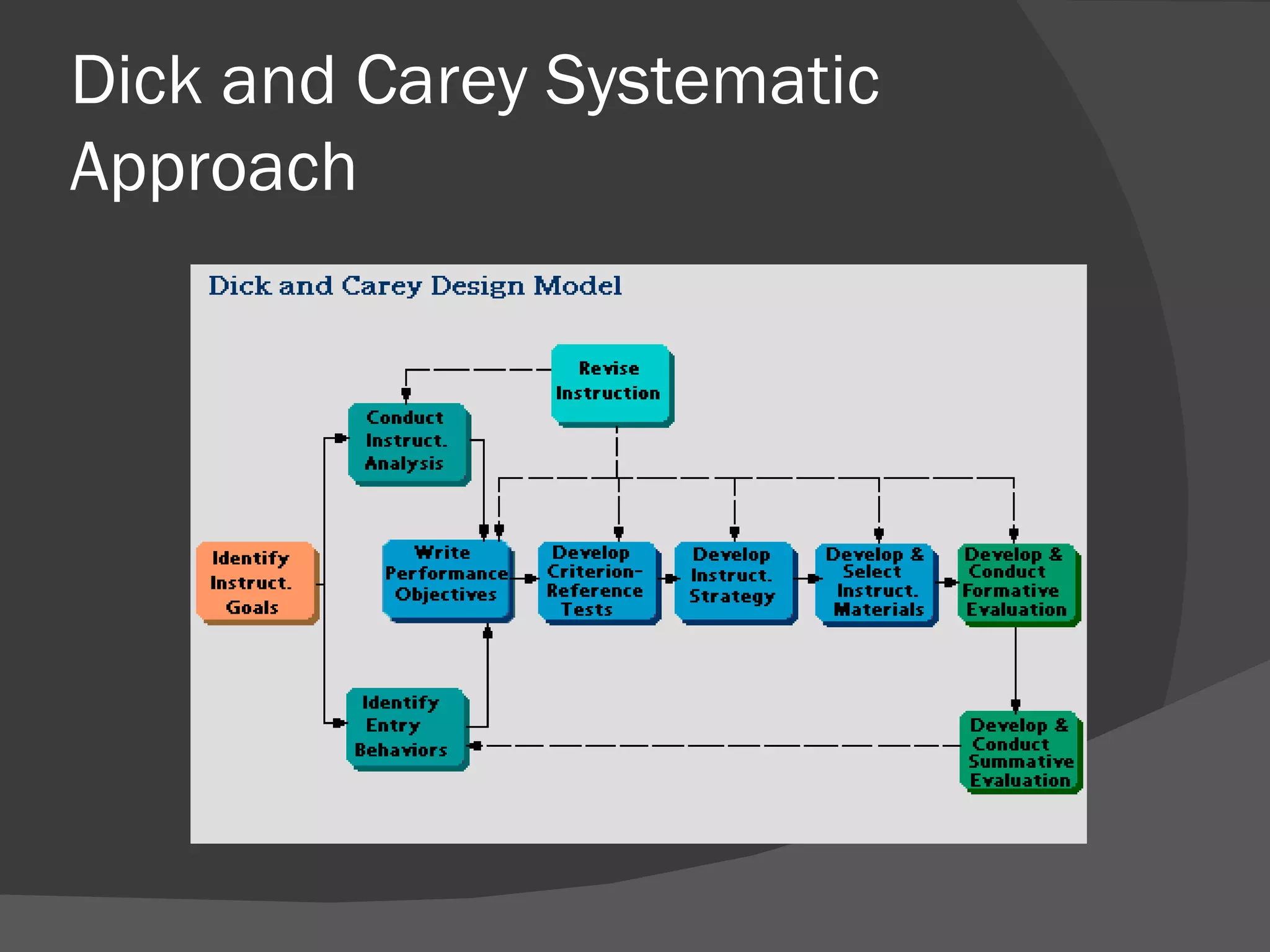
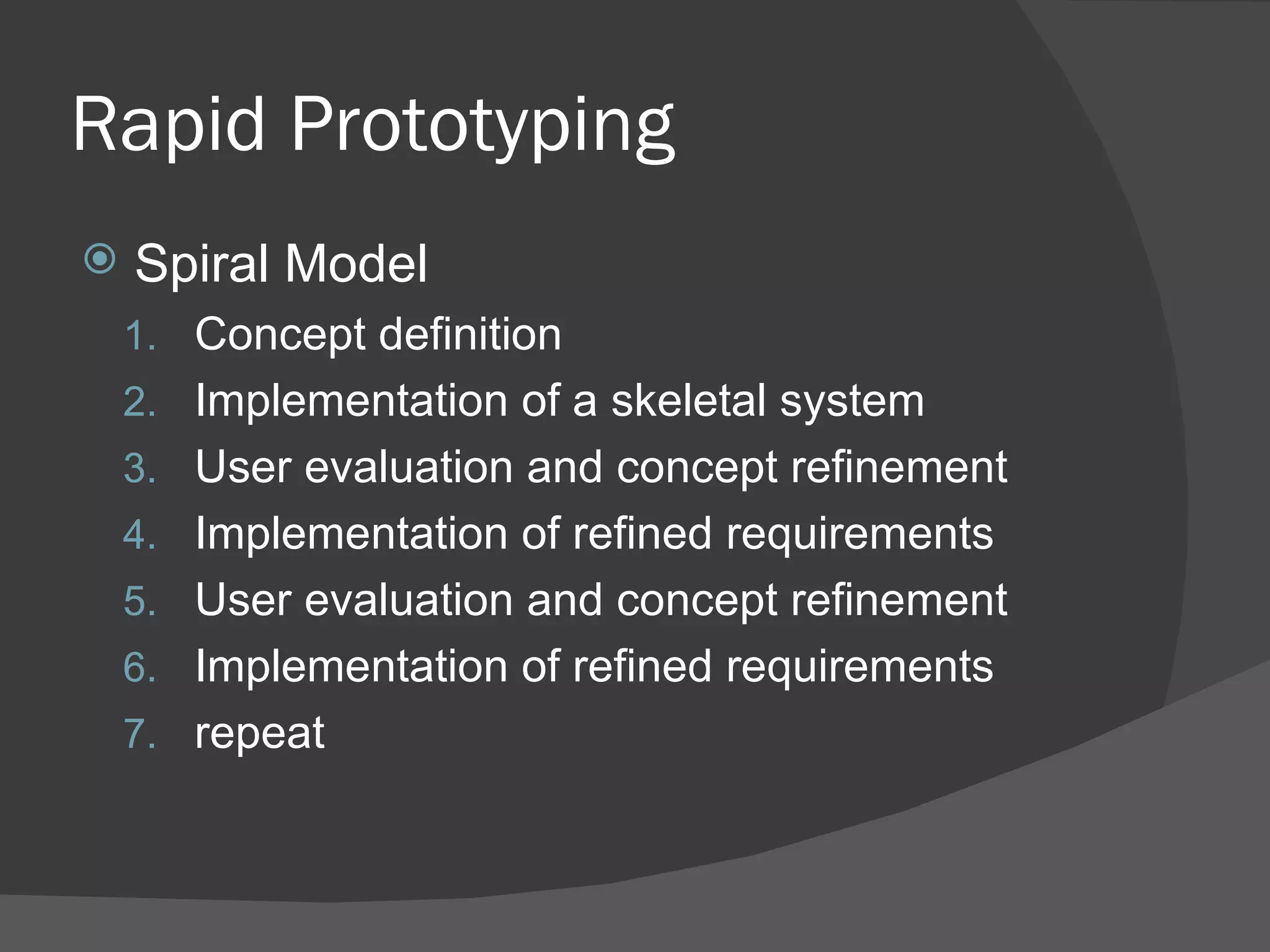
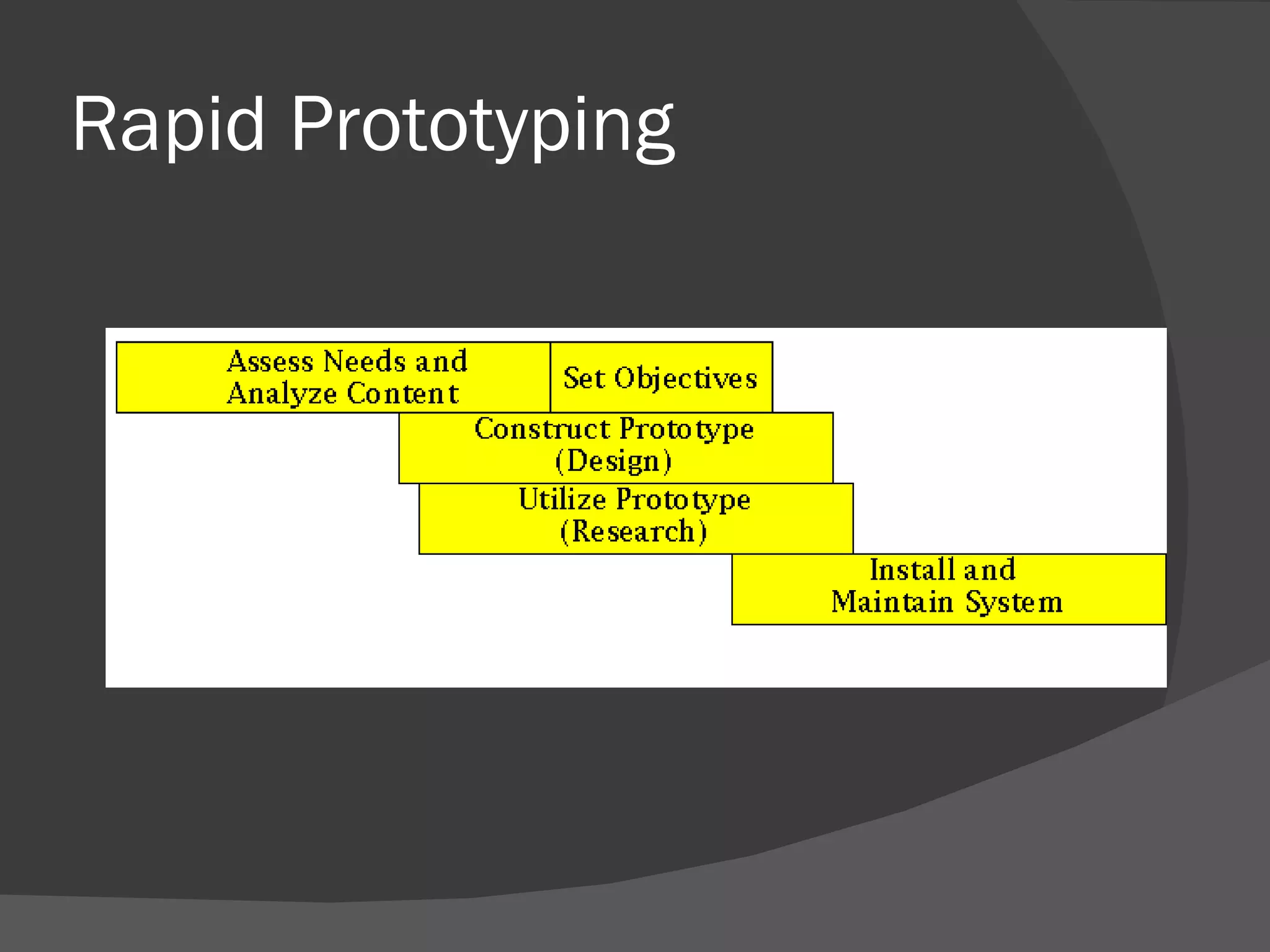
This document discusses instructional design models and approaches. It describes the Dick and Carey systematic approach, which outlines 9 components for developing instruction from assessing needs to revising instruction based on evaluation. Another model discussed is rapid prototyping, which involves continual design-evaluation cycles. Both models have strengths and weaknesses - Dick and Carey can be more tedious while rapid prototyping moves quickly, and the best approach depends on the specific instructional situation and needs.