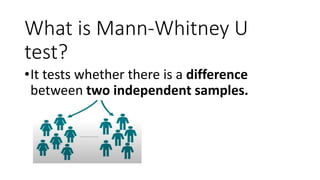
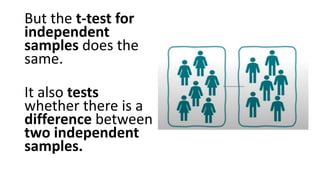
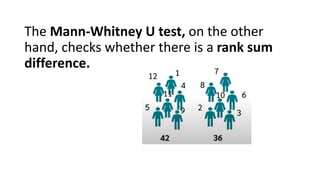
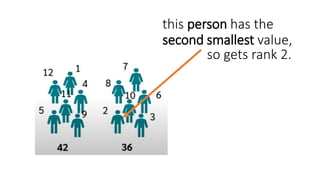
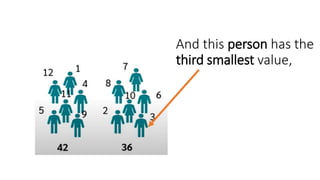
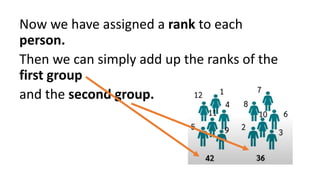
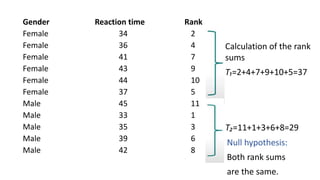
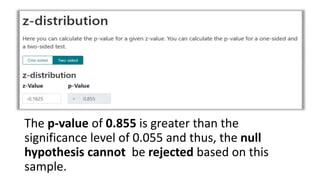
The Mann-Whitney U test is a non-parametric test used to determine if there are differences between two independent groups on a continuous or ordinal dependent variable. It compares the ranks of the values rather than the values themselves. The test checks for differences in rank sums between the two groups rather than differences in means, as the t-test does. The advantage is that the data does not need to be normally distributed. An example is provided to demonstrate how to calculate rank sums and test for differences between groups of female and male reaction times.