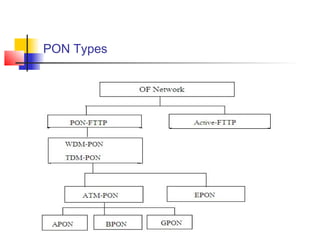
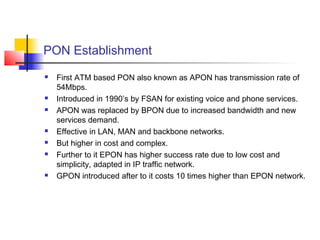
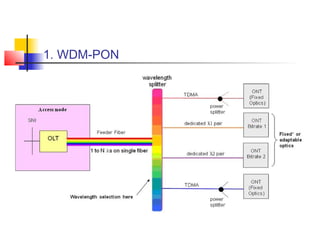
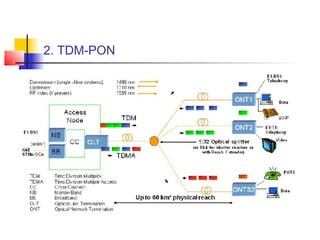
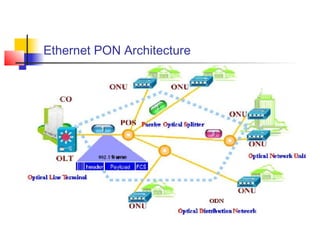
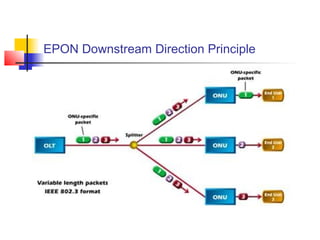
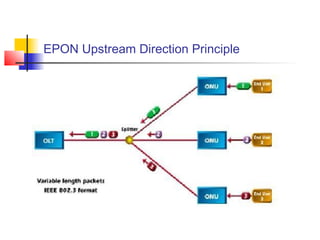
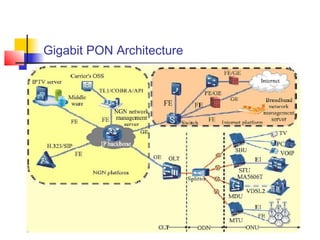
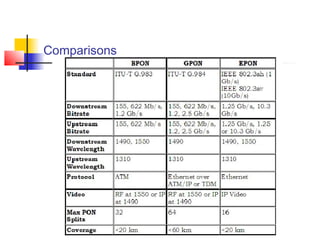
Passive Optic Network (PON) provides a point-to-multipoint fiber connection between an optical line terminal at the operator's central office and multiple optical network units near customers. PON uses passive splitters to enable a single fiber to serve multiple premises, reducing network installation costs compared to point-to-point architecture. Major PON technologies include Ethernet PON (EPON), which uses Ethernet packet transmission, and Gigabit PON (GPON), which supports higher speeds of up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream. PON is increasingly seen as an affordable way to deliver high-speed broadband and triple-play services to both urban and rural areas.