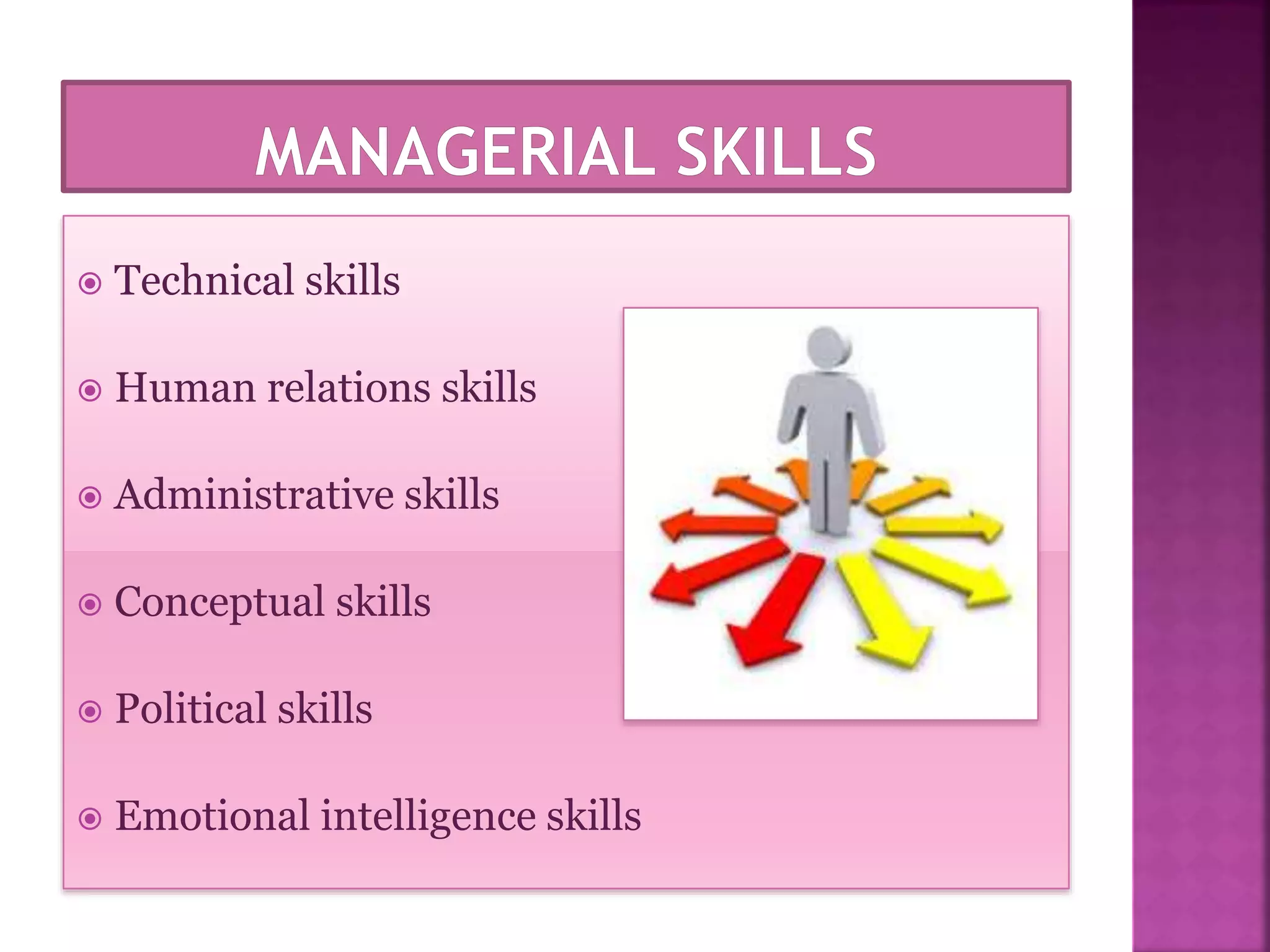
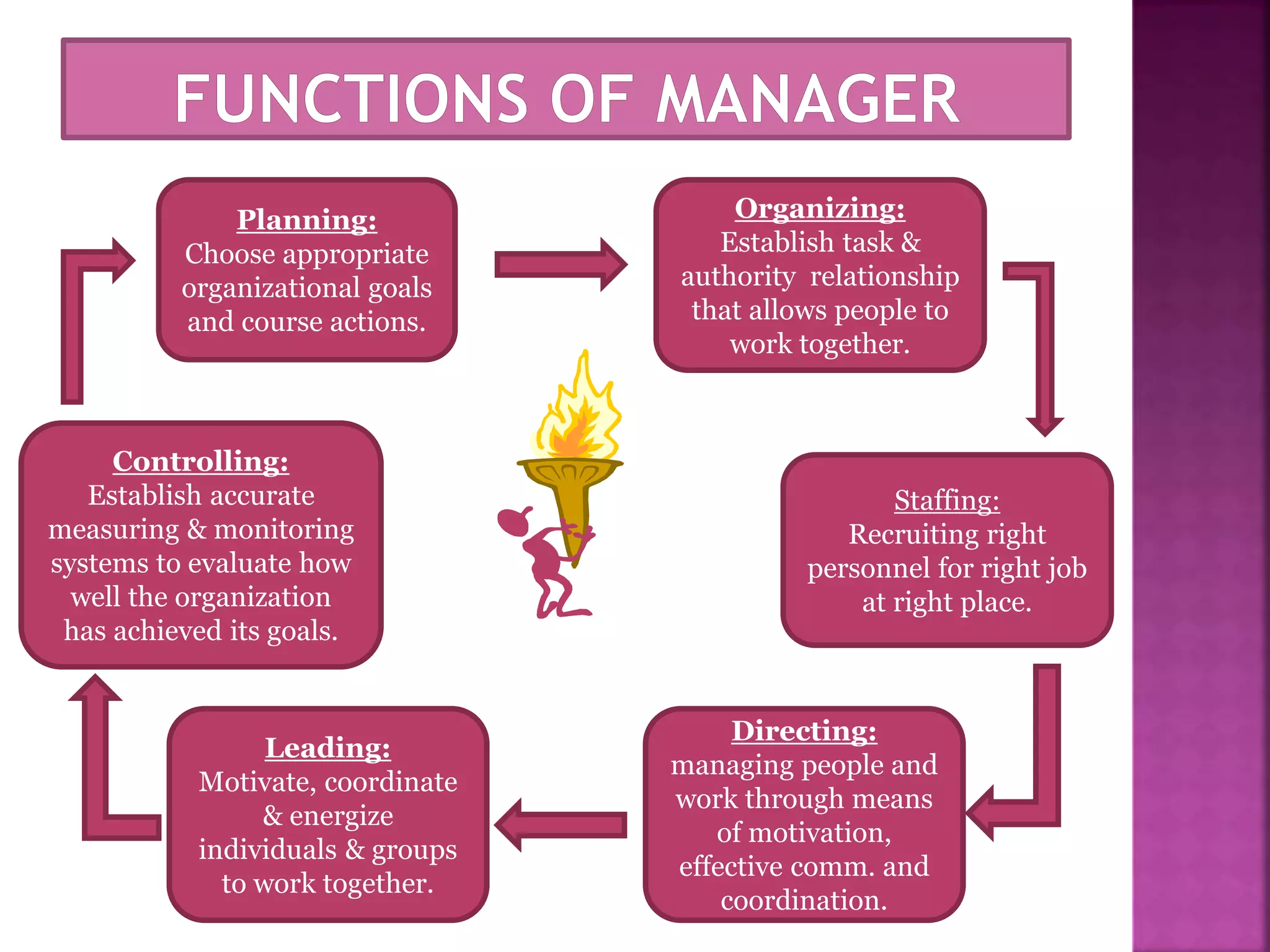
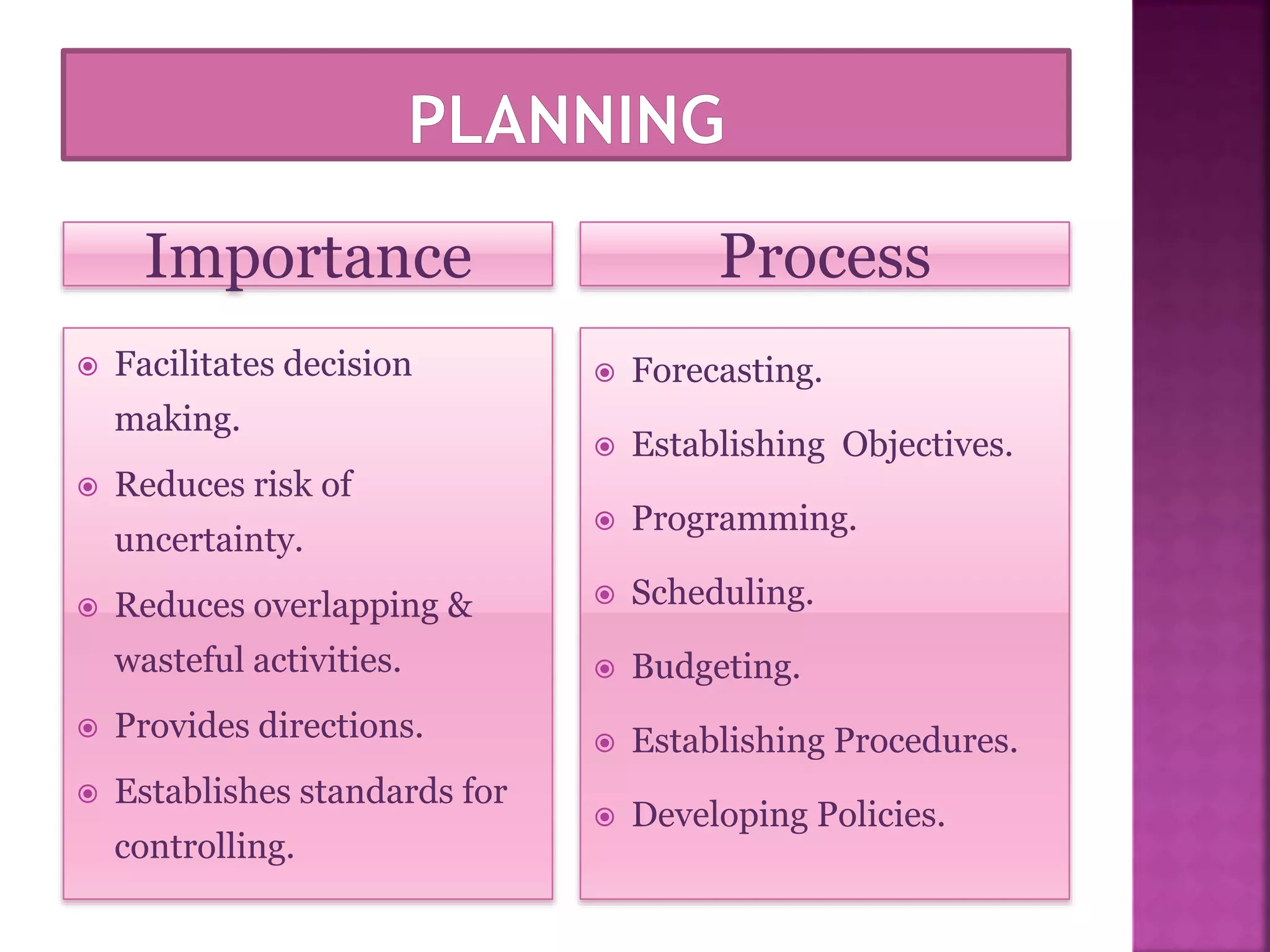
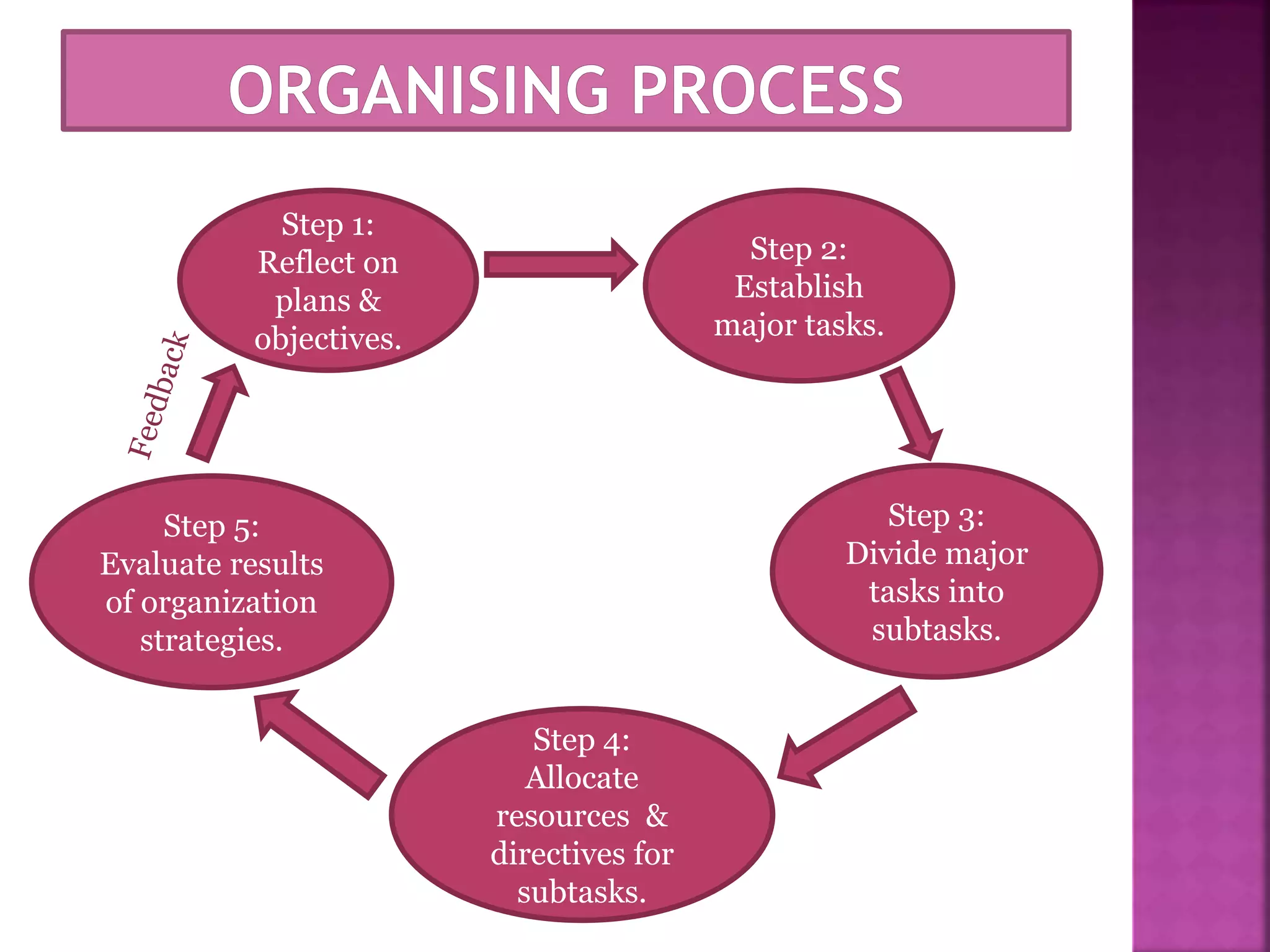
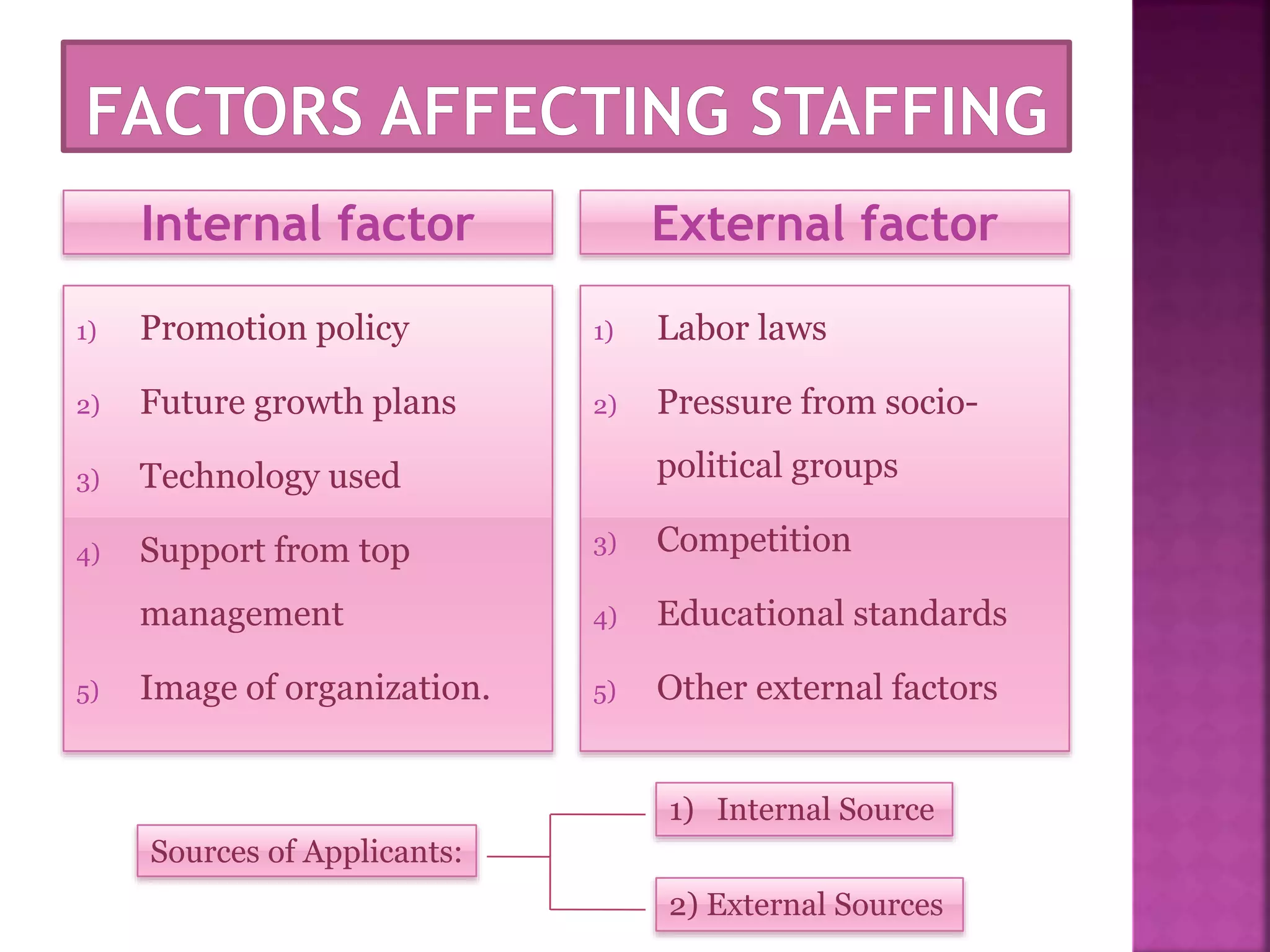
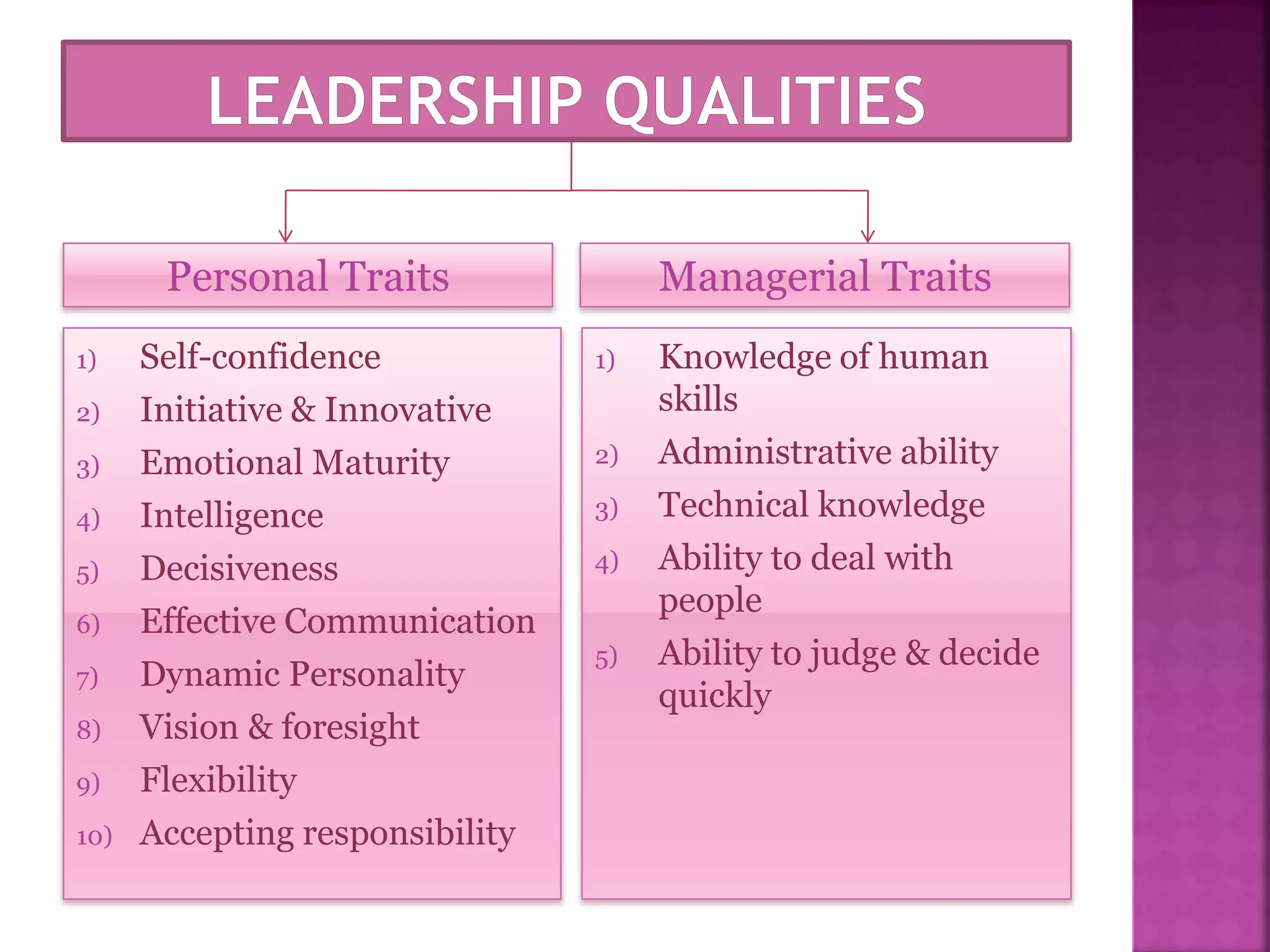
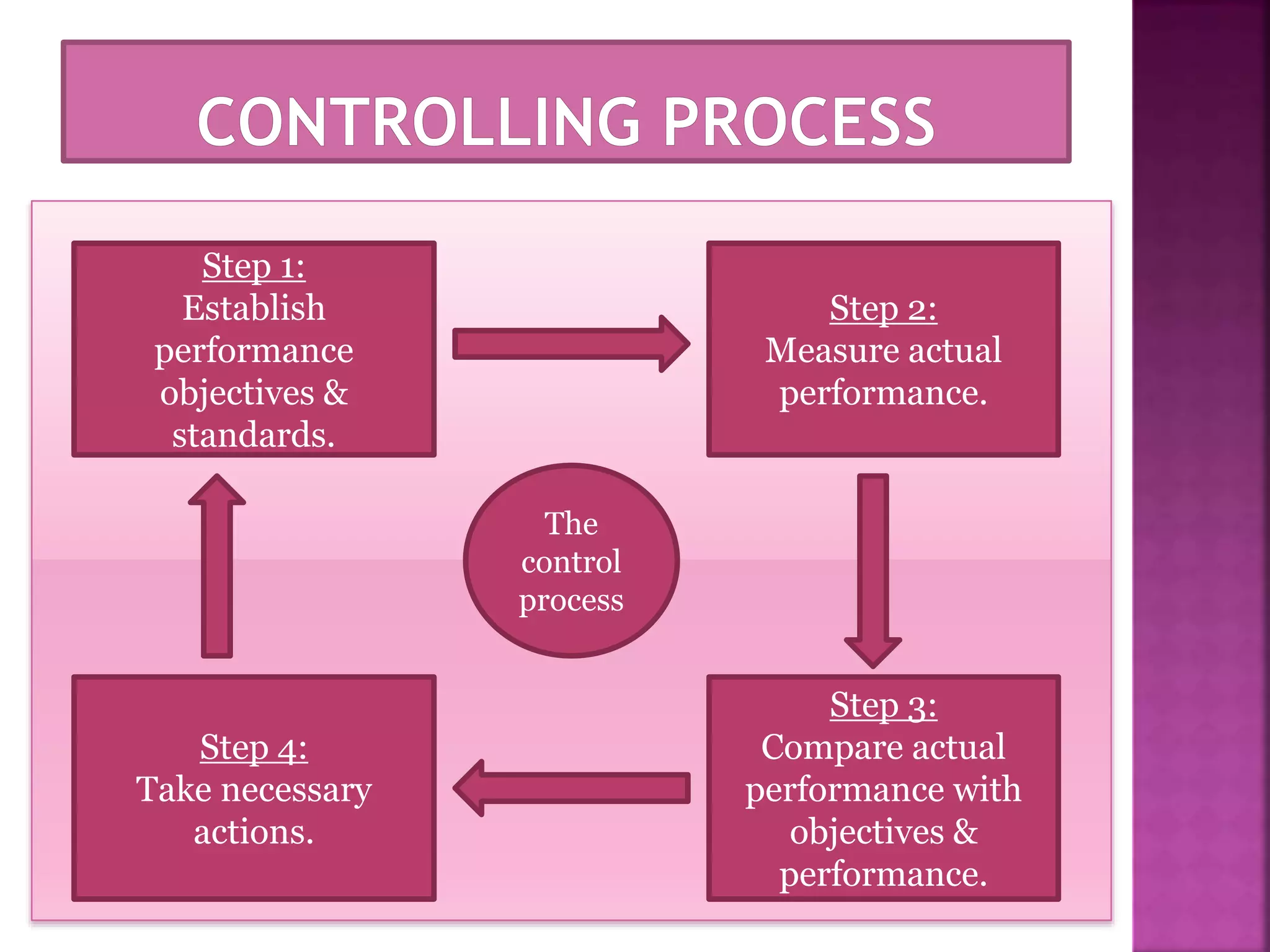
The document discusses the key functions of management - planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. It defines each function and explains their importance to effectively achieve organizational goals. Planning involves determining objectives and how to achieve them. Organizing establishes roles and responsibilities within the organizational structure. Leading includes motivating employees and coordinating work. Controlling monitors performance against objectives and provides feedback for continuous improvement. Effective management of resources through these functions is important for organizational success.