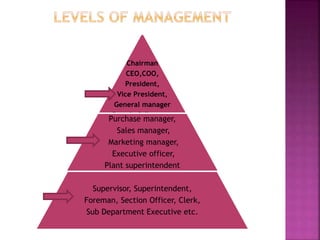
Management is a universal process that involves planning, organizing, motivating and controlling resources to achieve organizational goals effectively and efficiently. It can be viewed as both an art and a science, applying principles and creativity. Management functions across all organizations, including businesses and non-profits. Effective management establishes an environment where people can work towards common objectives while also pursuing personal goals like growth, recognition and good working conditions. Coordination is essential across the management functions of planning, organizing, staffing, directing and controlling.