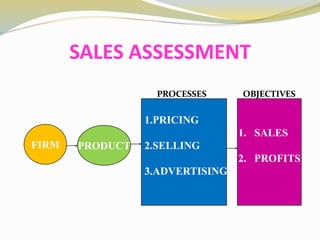
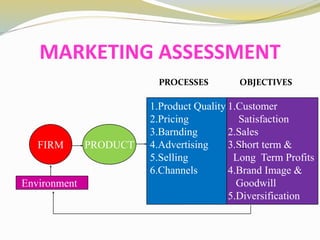
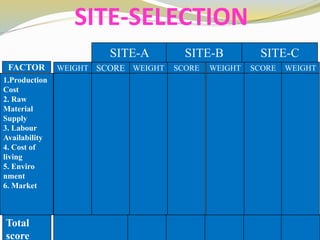
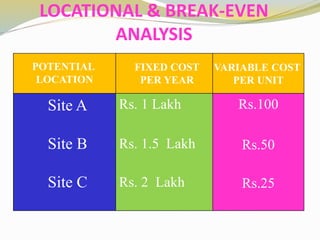
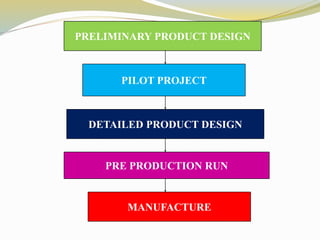
The document discusses various aspects of competency and entrepreneurial competency. It provides definitions and examples of competency, core competencies of different companies, tests for what constitutes a competency, and risks of ignoring competencies. It also discusses identifying business opportunities, assessing various factors related to starting a business like market demand, competition, production processes, product design, and the top 10 competencies for entrepreneurial success such as integrity, conceptual thinking, risk taking, and people focus.