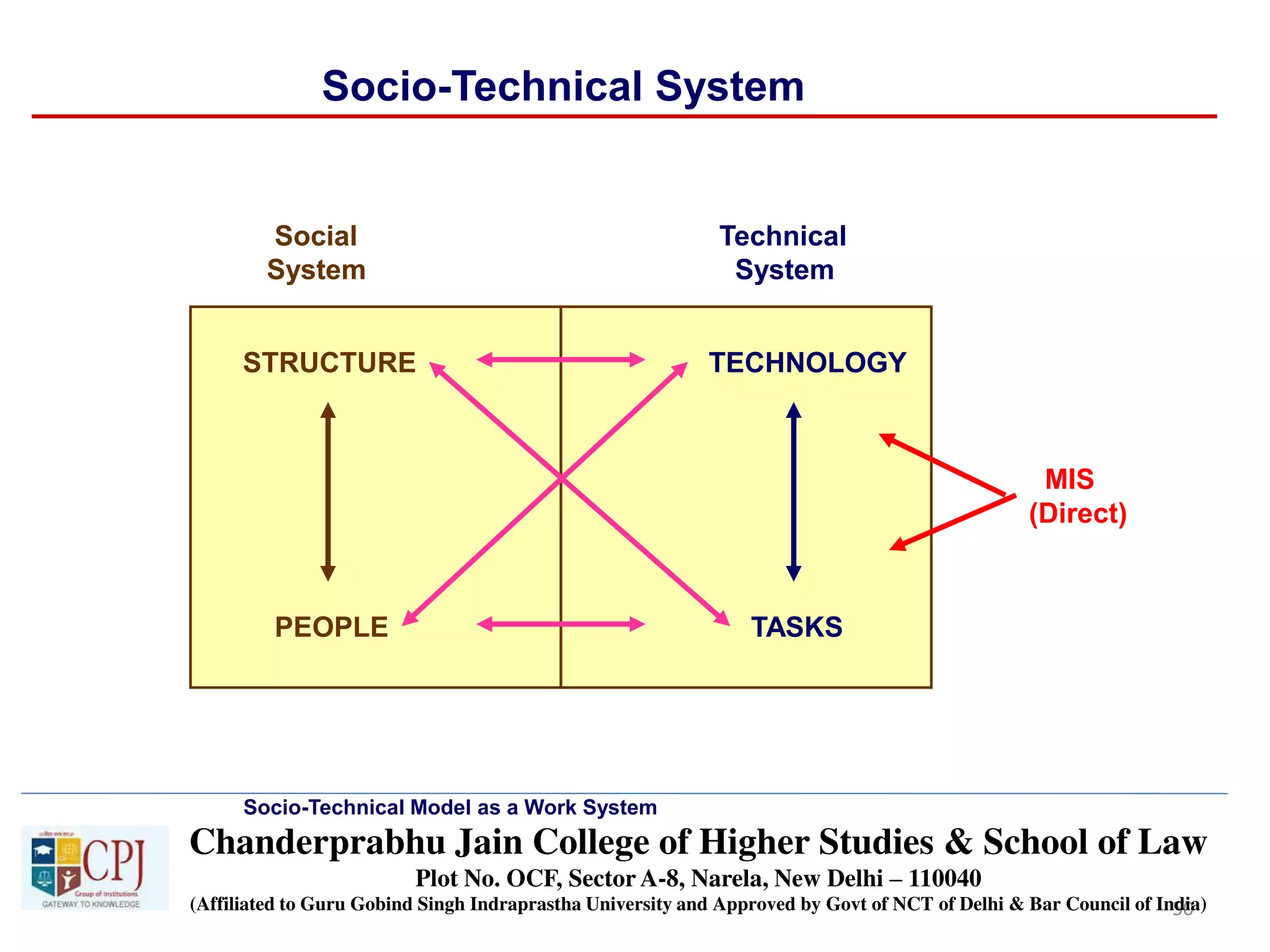
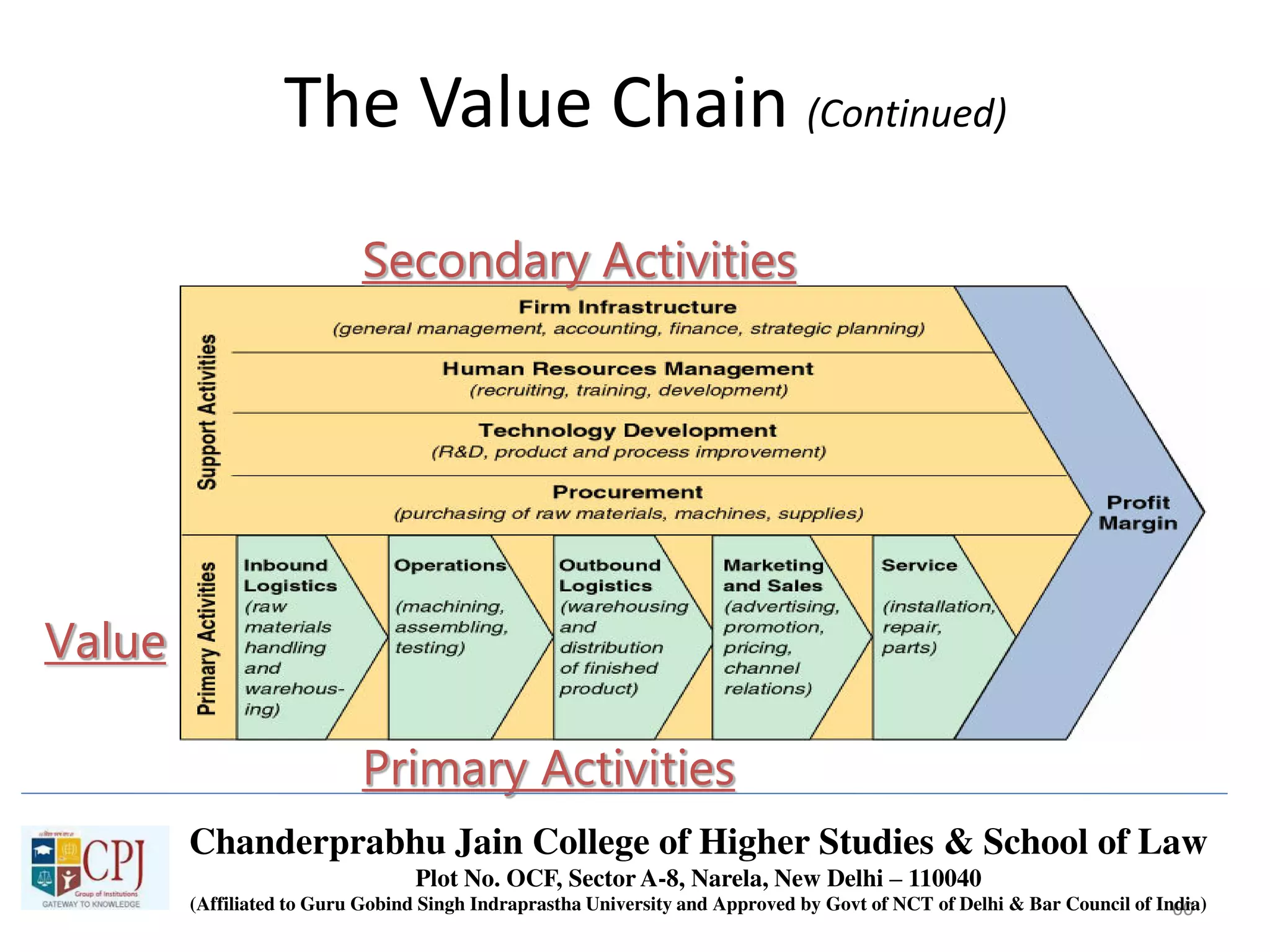
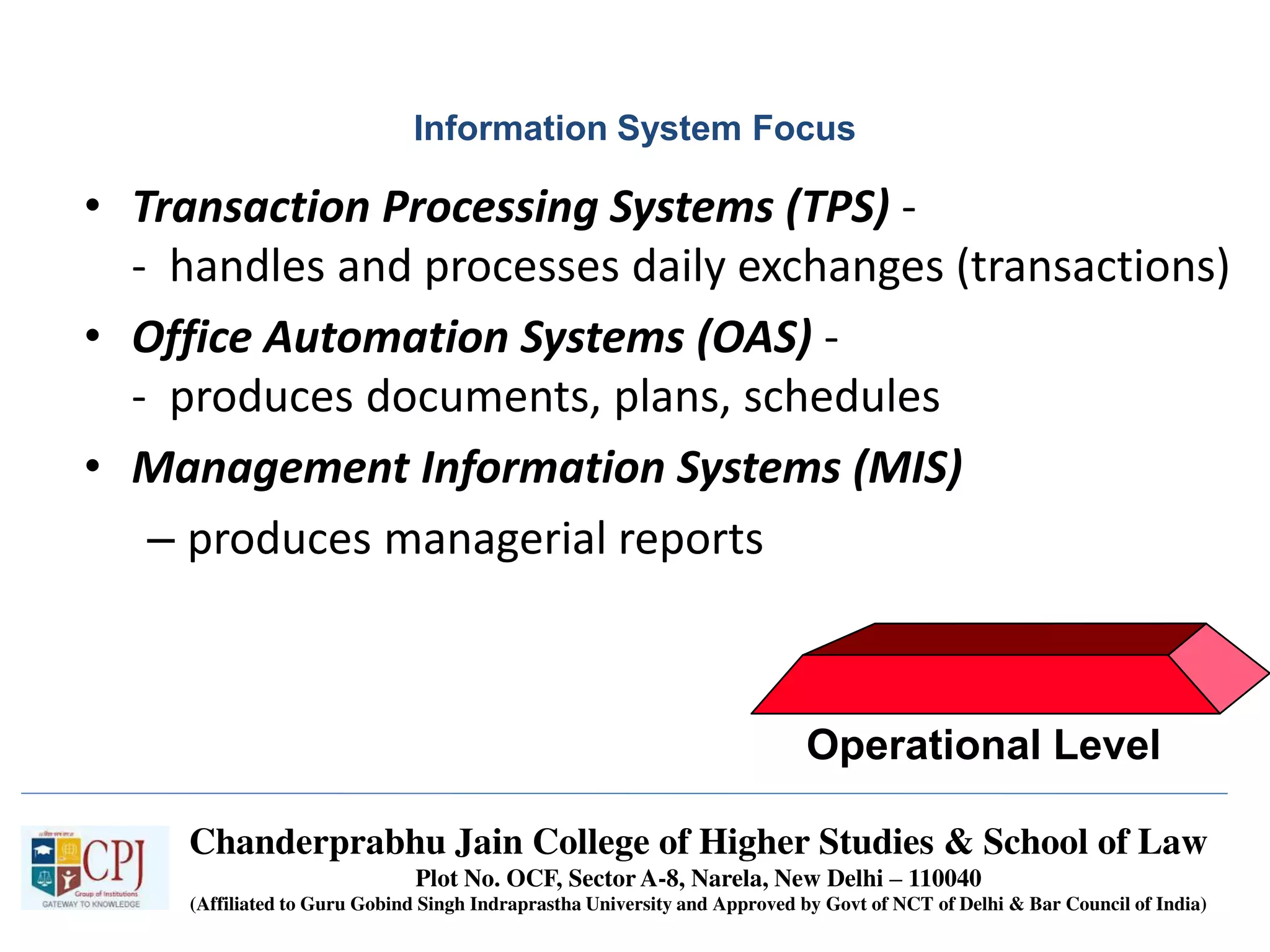
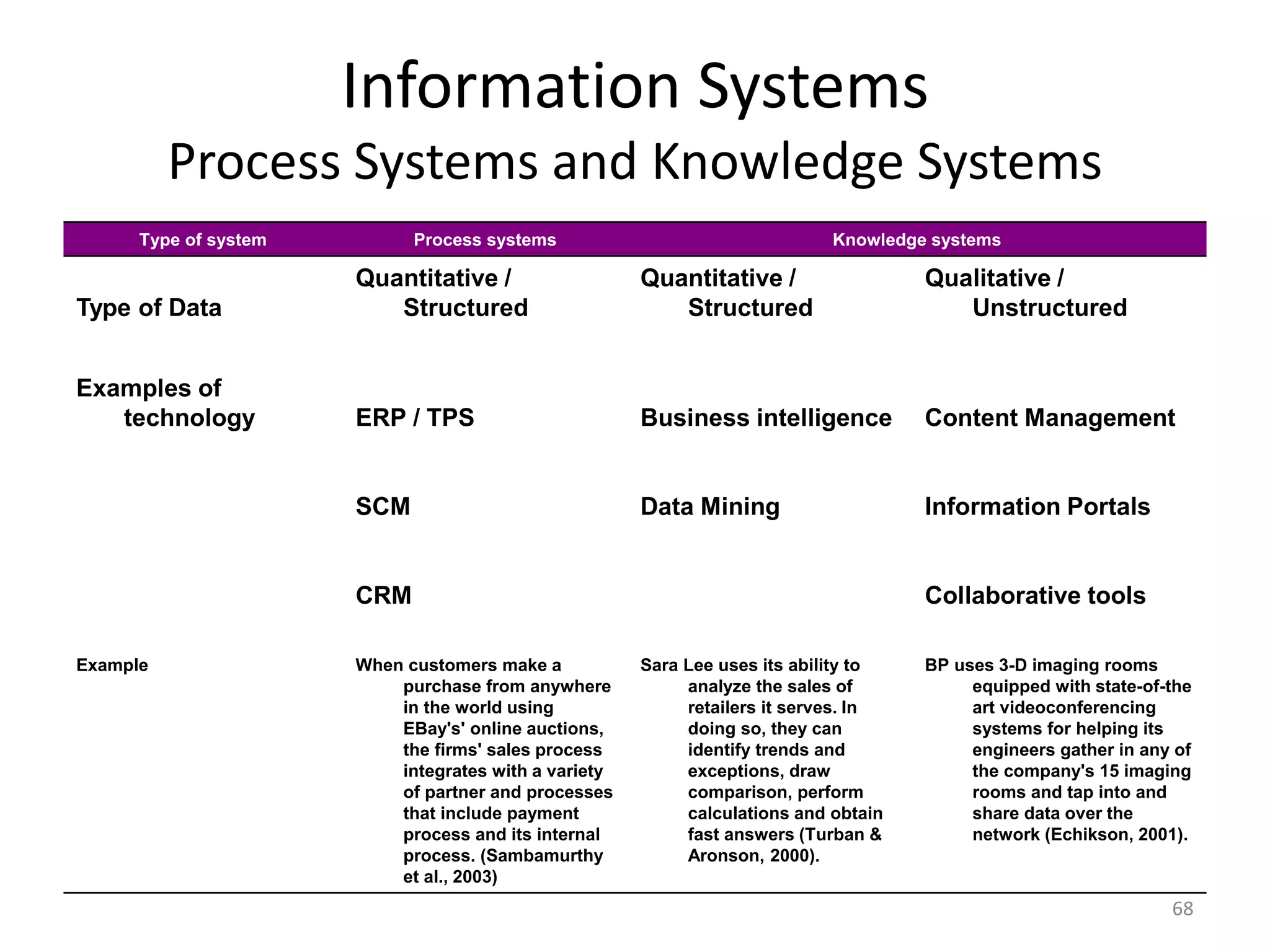
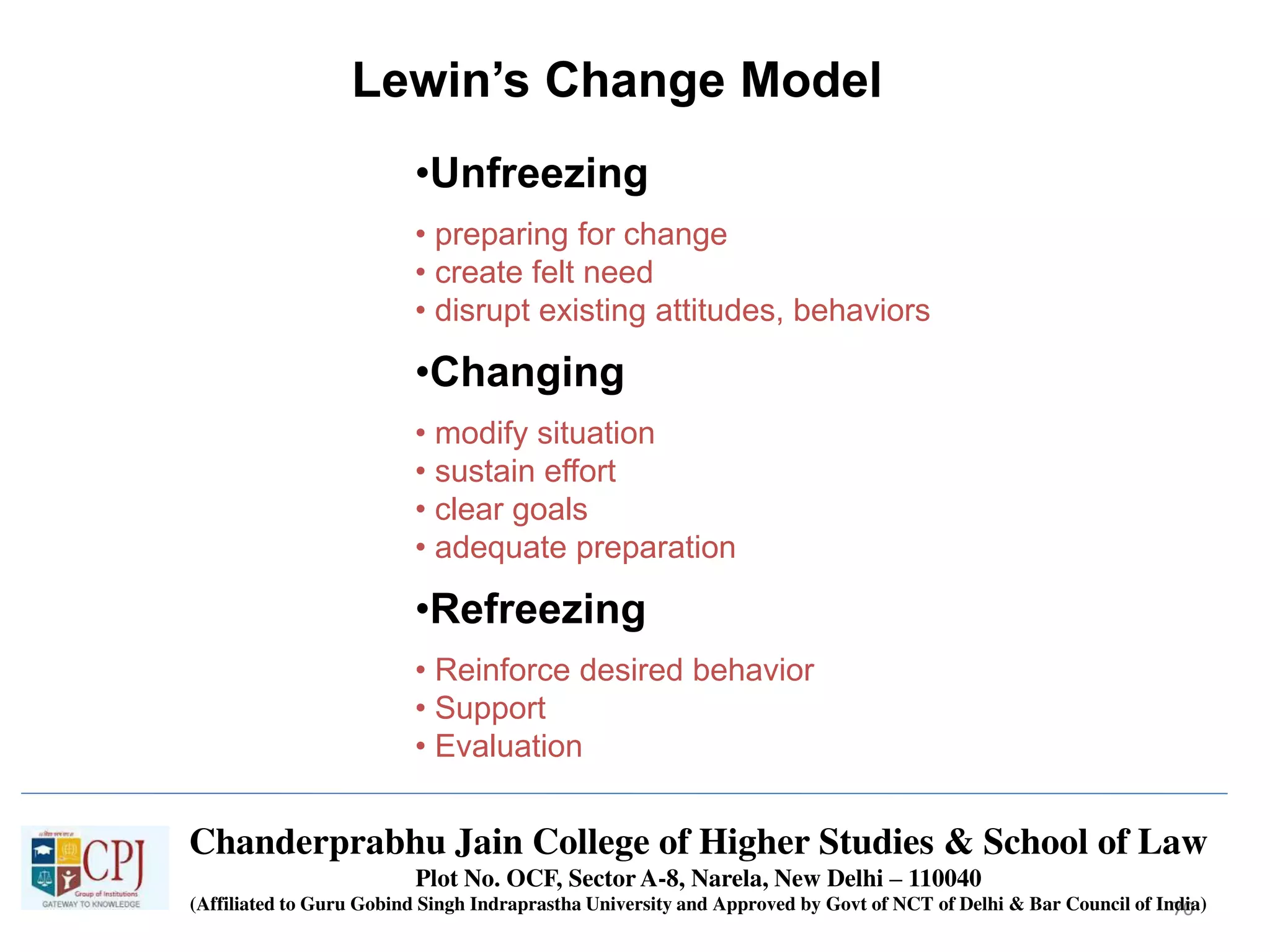
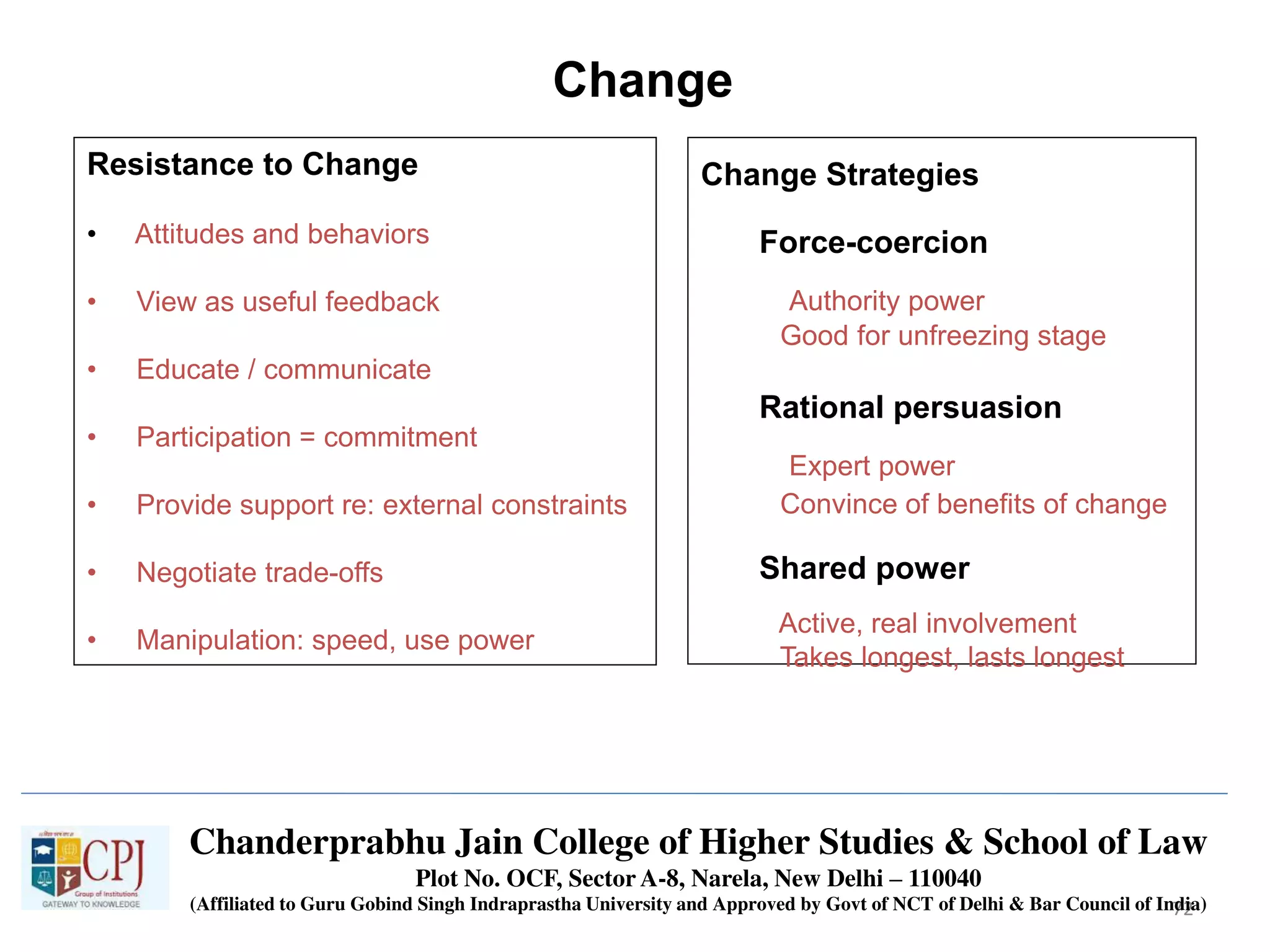
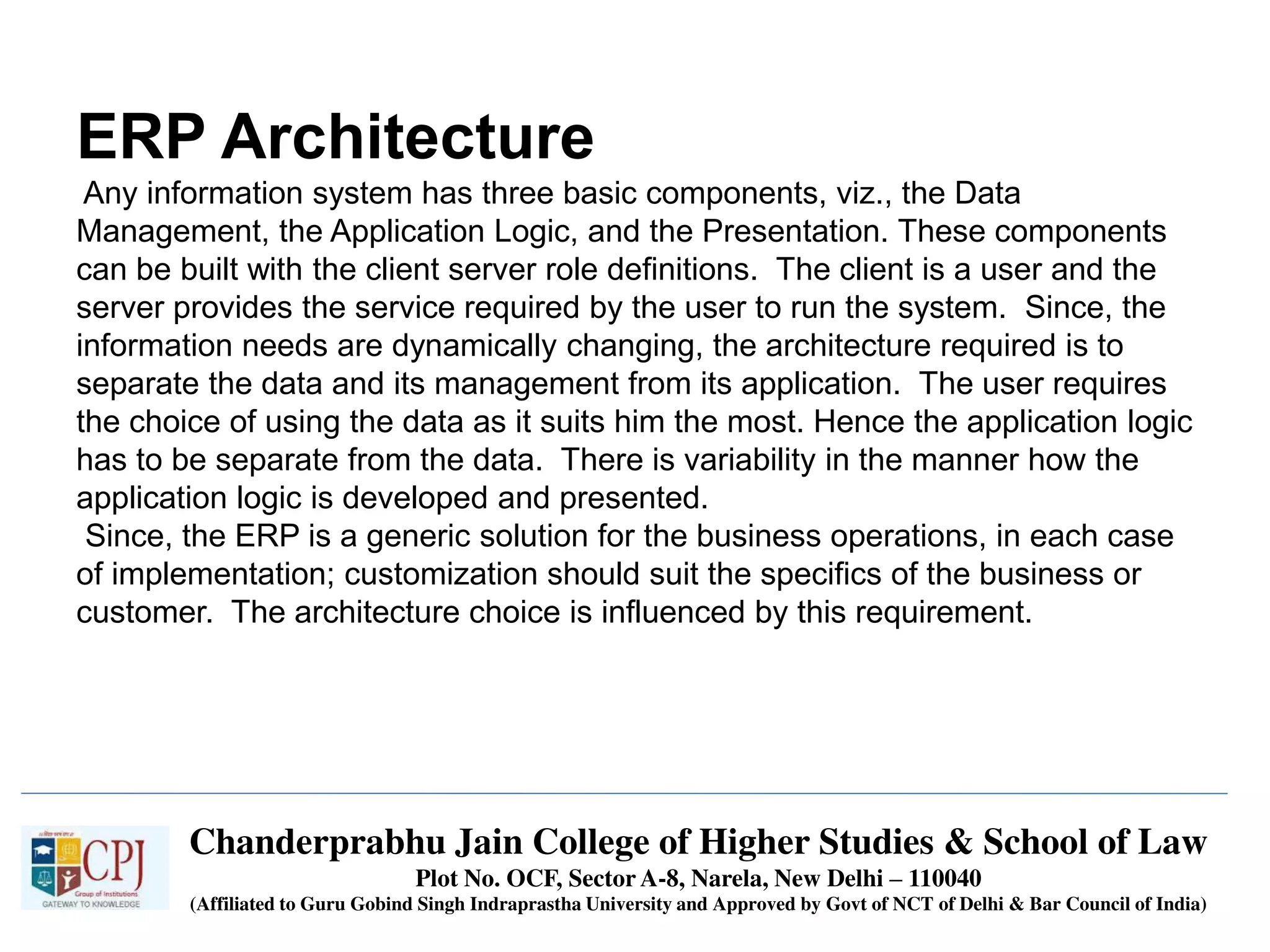
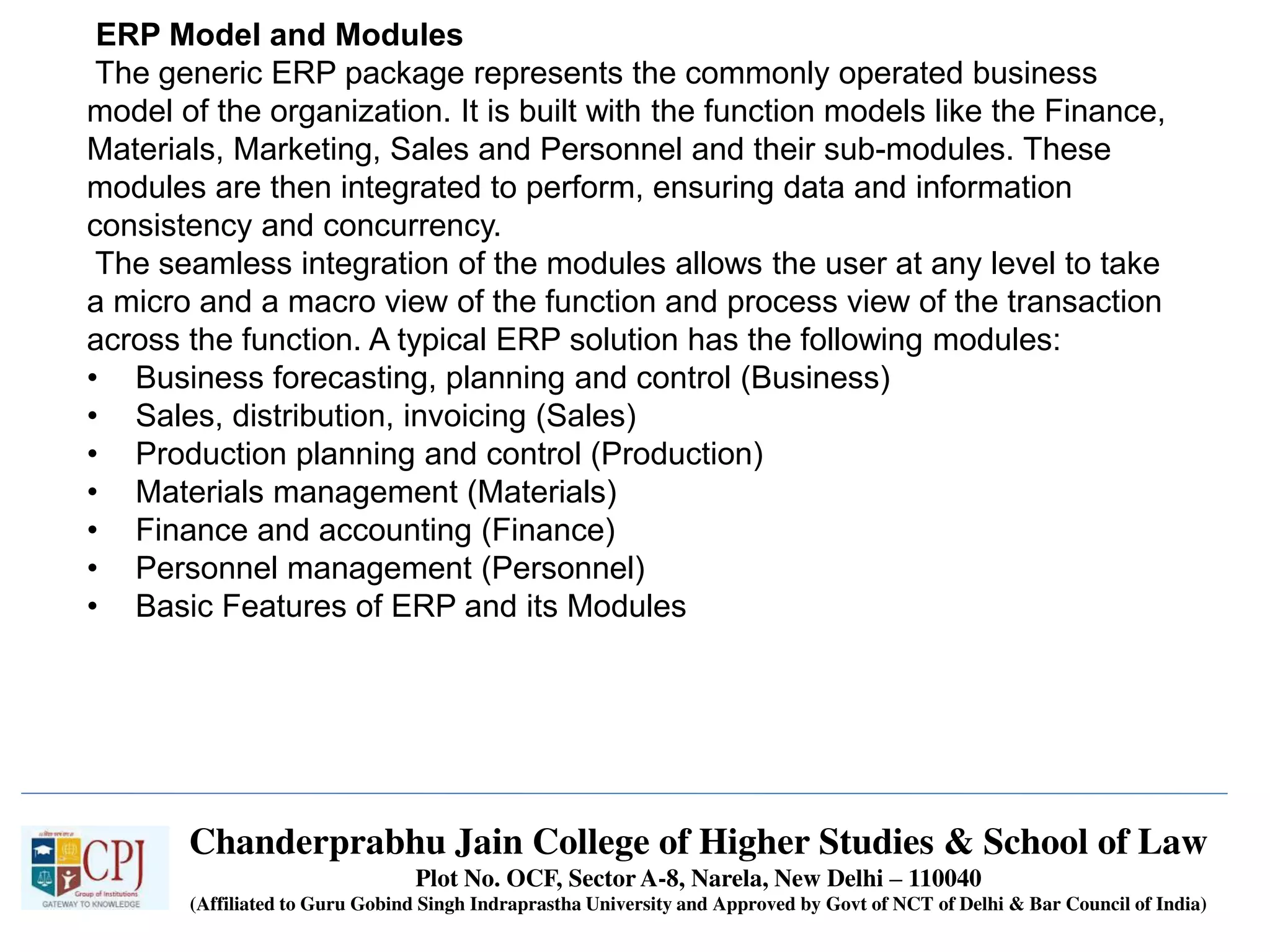
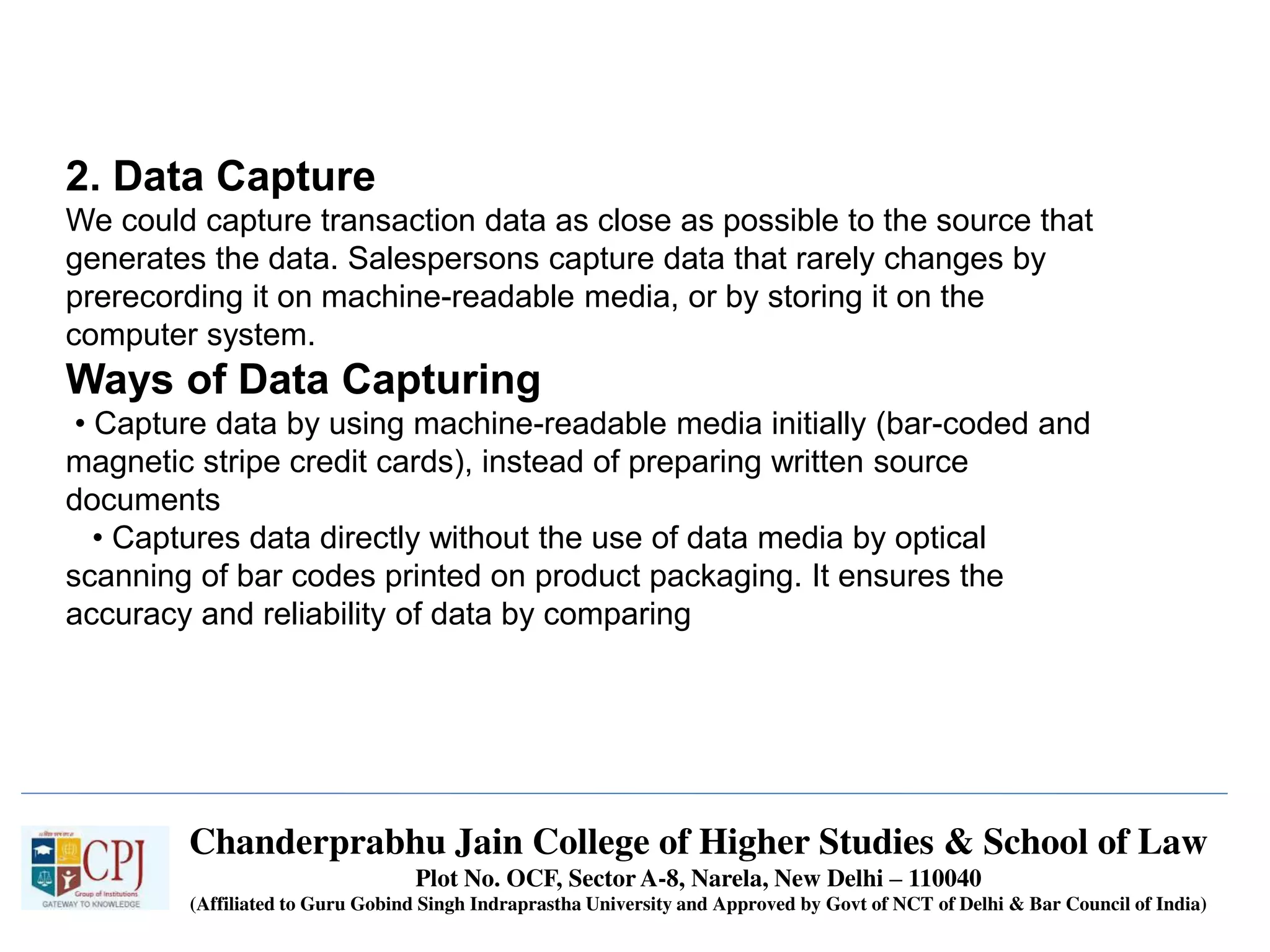
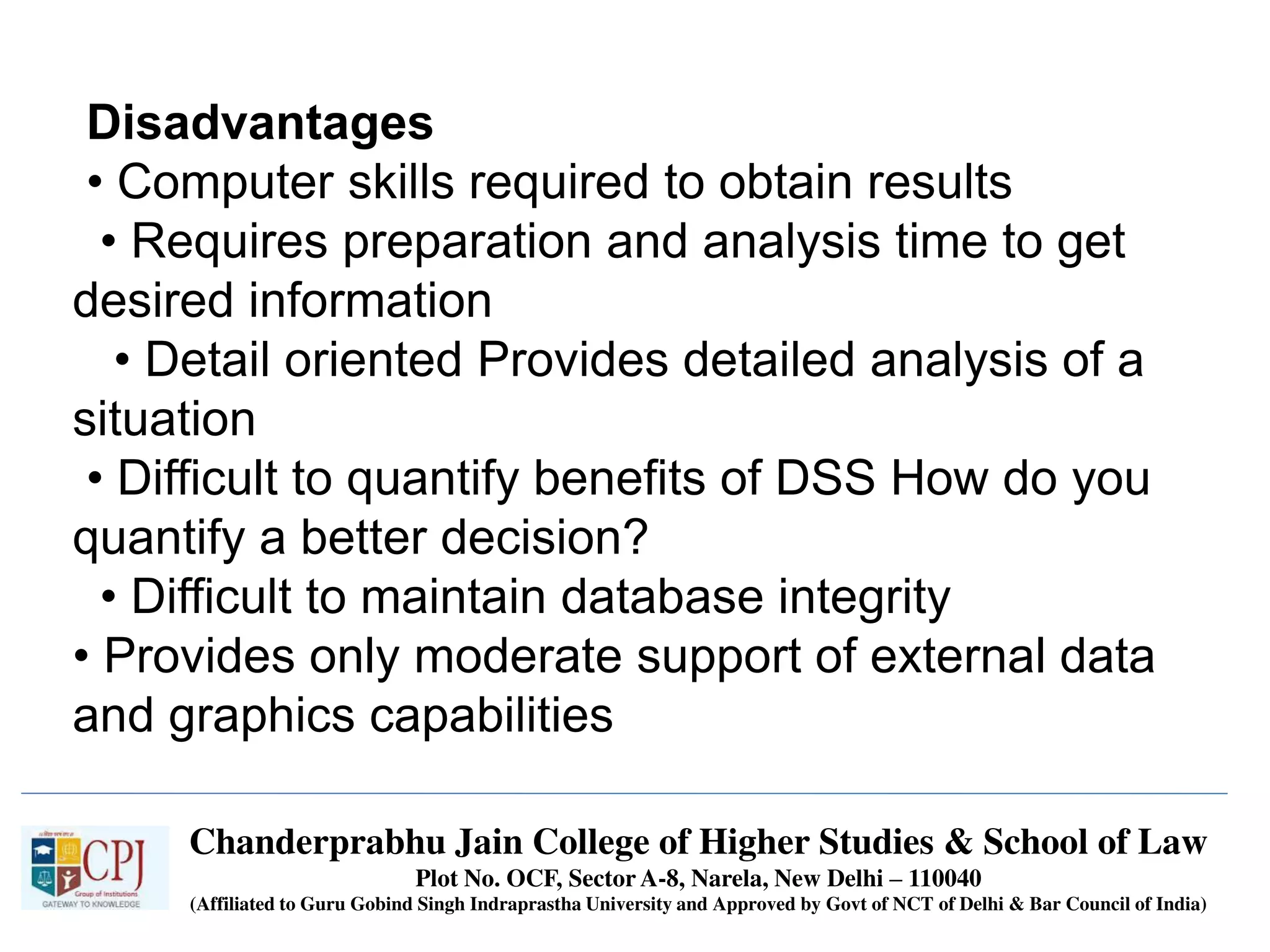
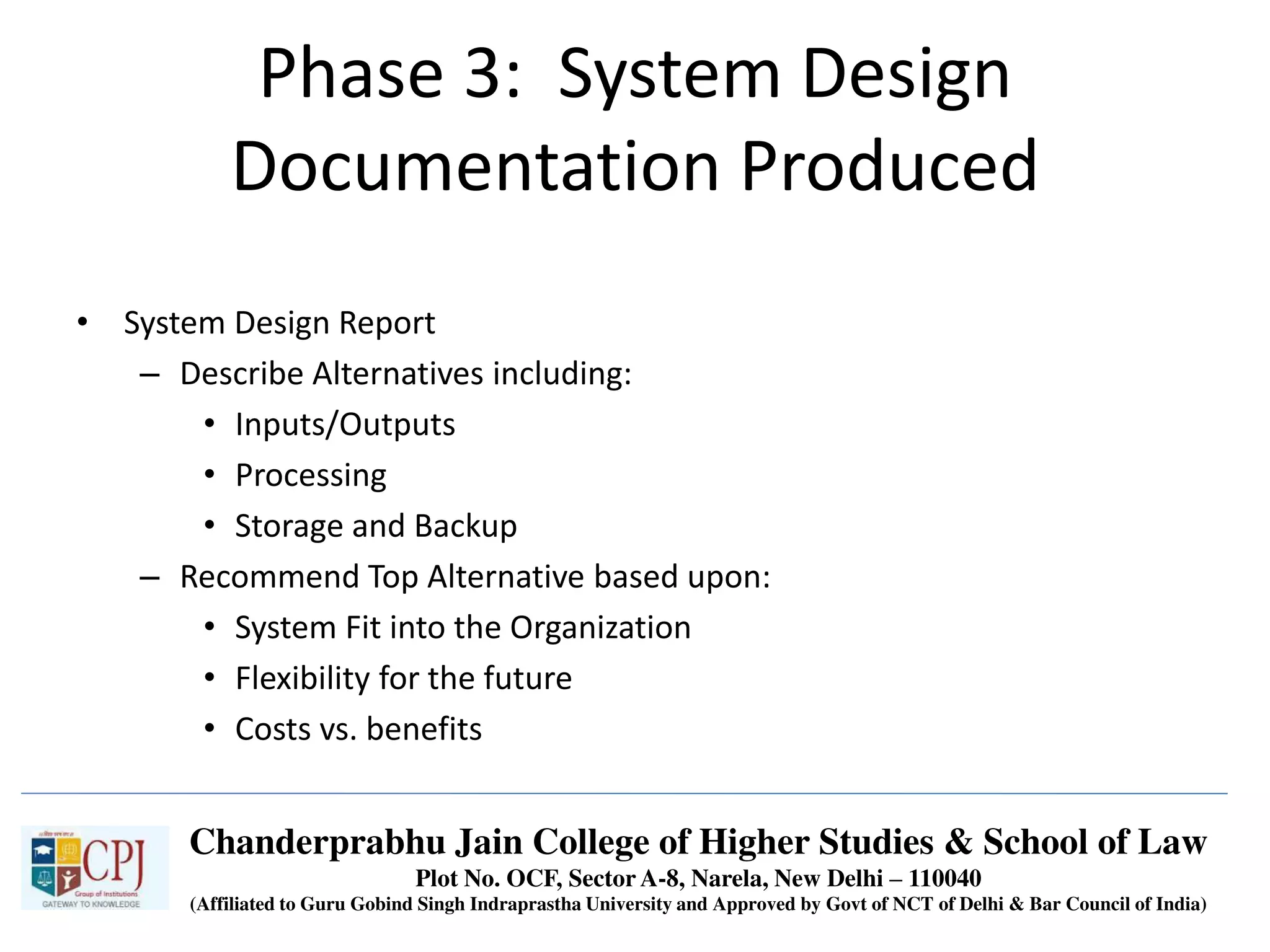
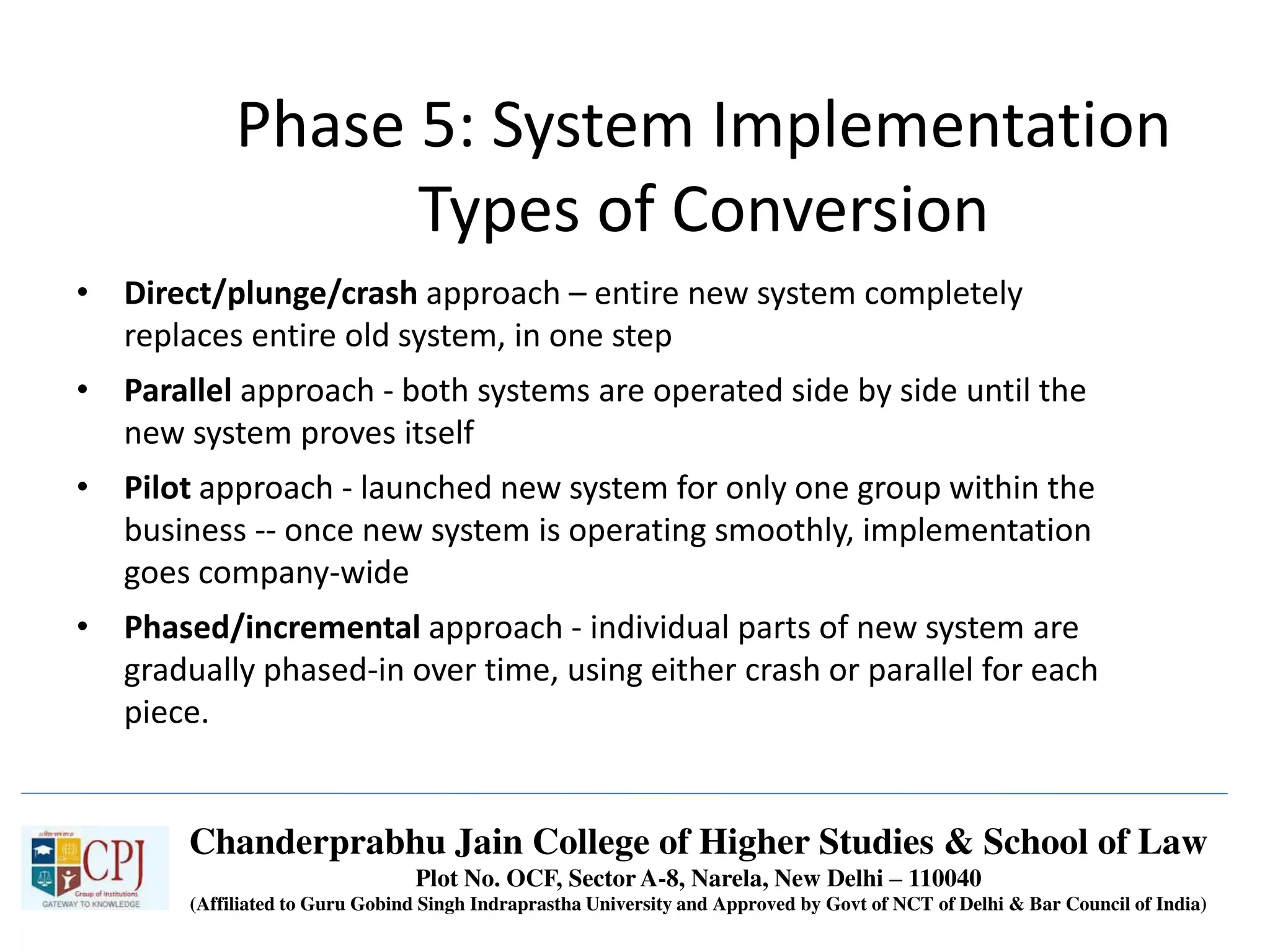
The document discusses Management Information Systems (MIS) with a focus on transaction processing systems (TPS), decision support systems (DSS), and executive information systems (EIS). It outlines the objectives of MIS, characteristics and components of TPS, and the features and types of decisions made by DSS and EIS. Additionally, it highlights the importance of these systems in managing organizational activities and decision-making processes.







































![45
SYSTEM
A system is defined as (1) a set (2) of objects (3)
together with relationships (4) between the objects and
between their attributes (5) related to each other and to
their environment (6) so as to form a whole.
SET — any well defined collection of elements or objects within some
frame of reference
OBJECTS — objects are elements of a system [INPUTS (serial, probable,
or feedback), PROCESS (transformation), OUTPUTS (Intended, waste, or
pollution)] Efficiency - ratio of output to input
RELATIONSHIPS — the bonds that link objects together (Symbiotic,
synergistic, and redundant)
ATTRIBUTES — attributes a properties of both objects and
relationships (defining/accompanying characteristics)
ENVIRONMENT — includes not only that which lies outside the system’s
complete control but that which at the same time also determines in some
way the system’s performance.
Chanderprabhu Jain College of Higher Studies & School of Law
Plot No. OCF, Sector A-8, Narela, New Delhi – 110040
(Affiliated to Guru Gobind Singh Indraprastha University and Approved by Govt of NCT of Delhi & Bar Council of India)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bbacam-307-181210065547/75/Management-Information-System-45-2048.jpg)