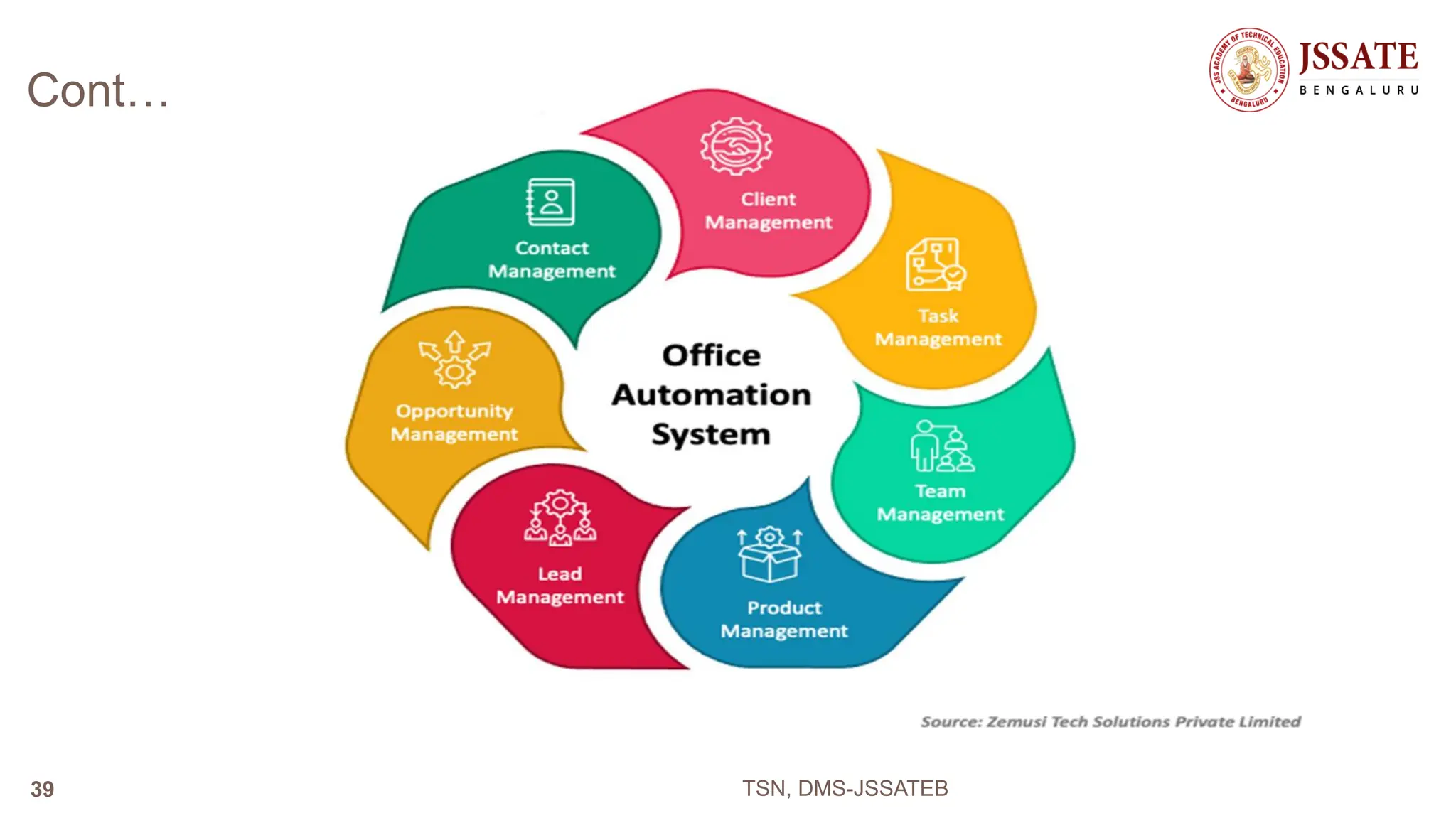
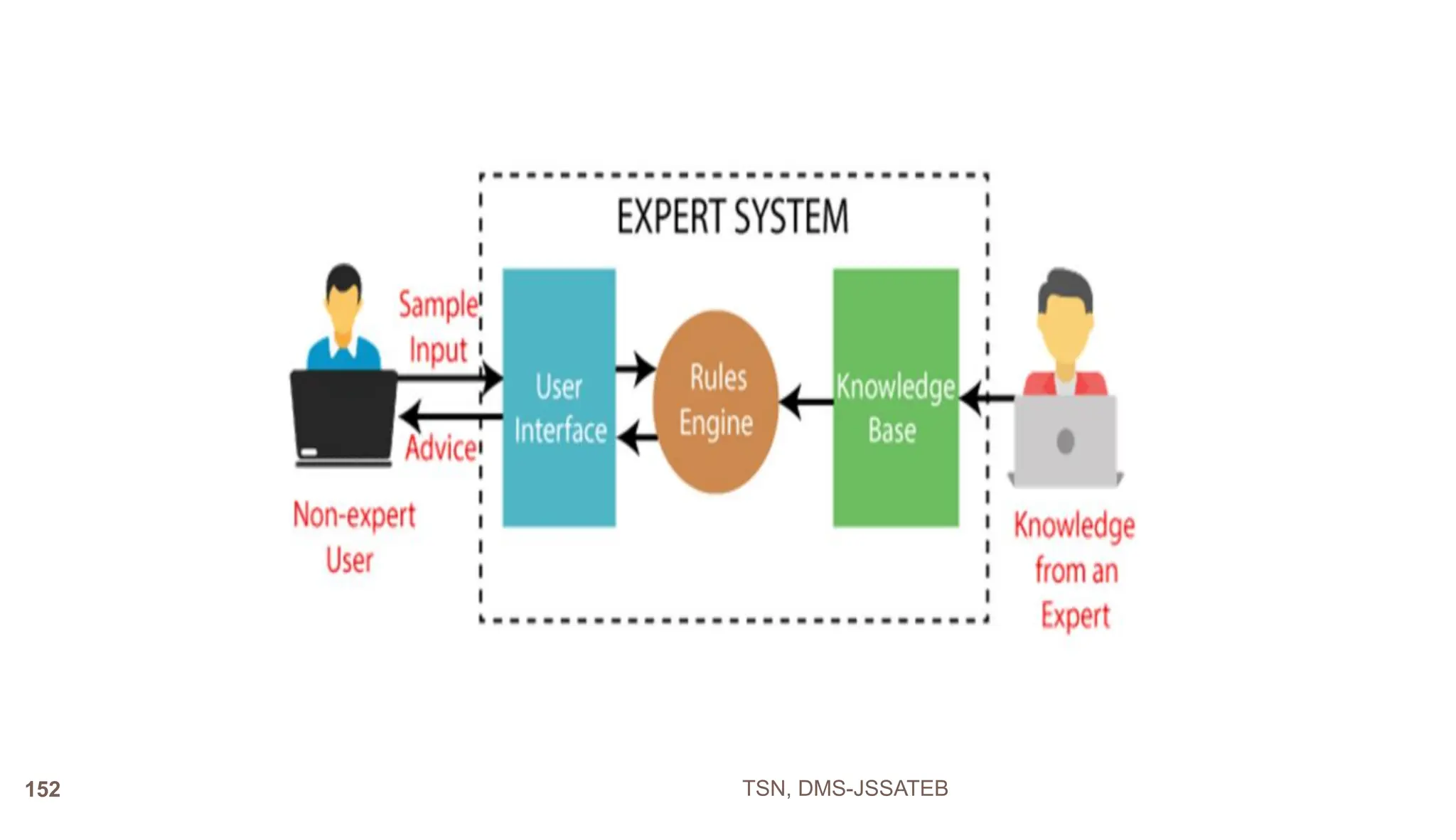
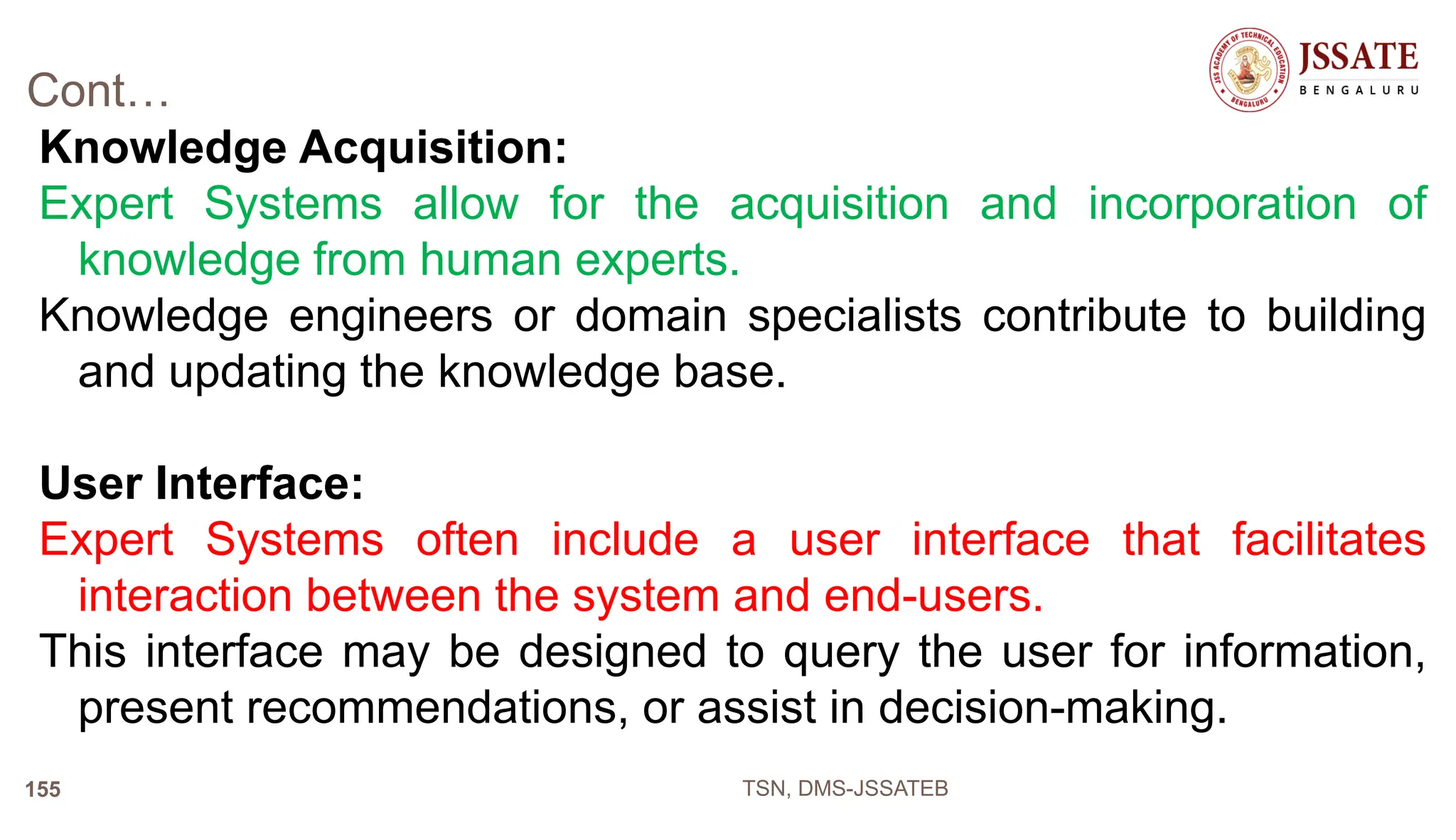
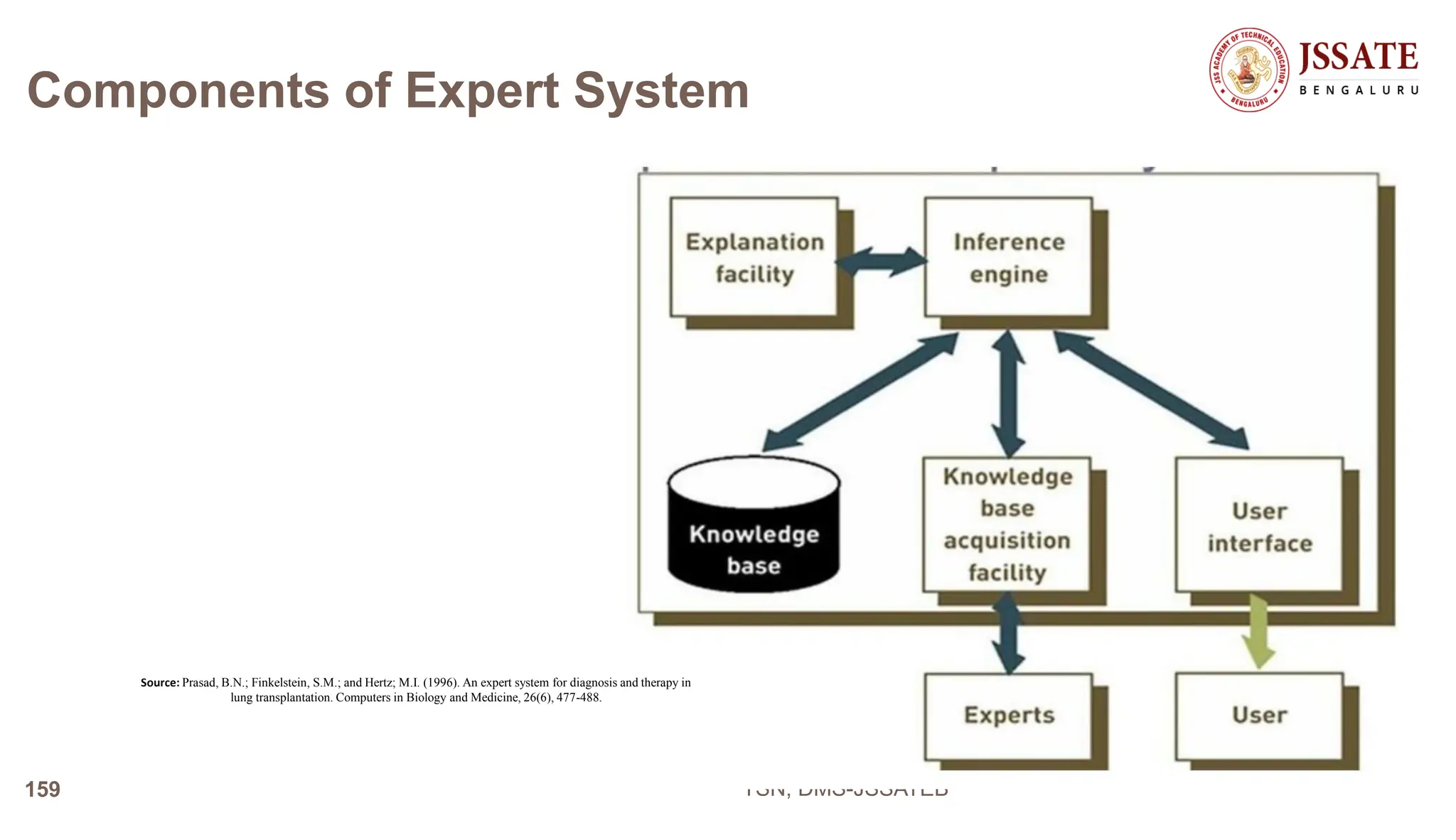
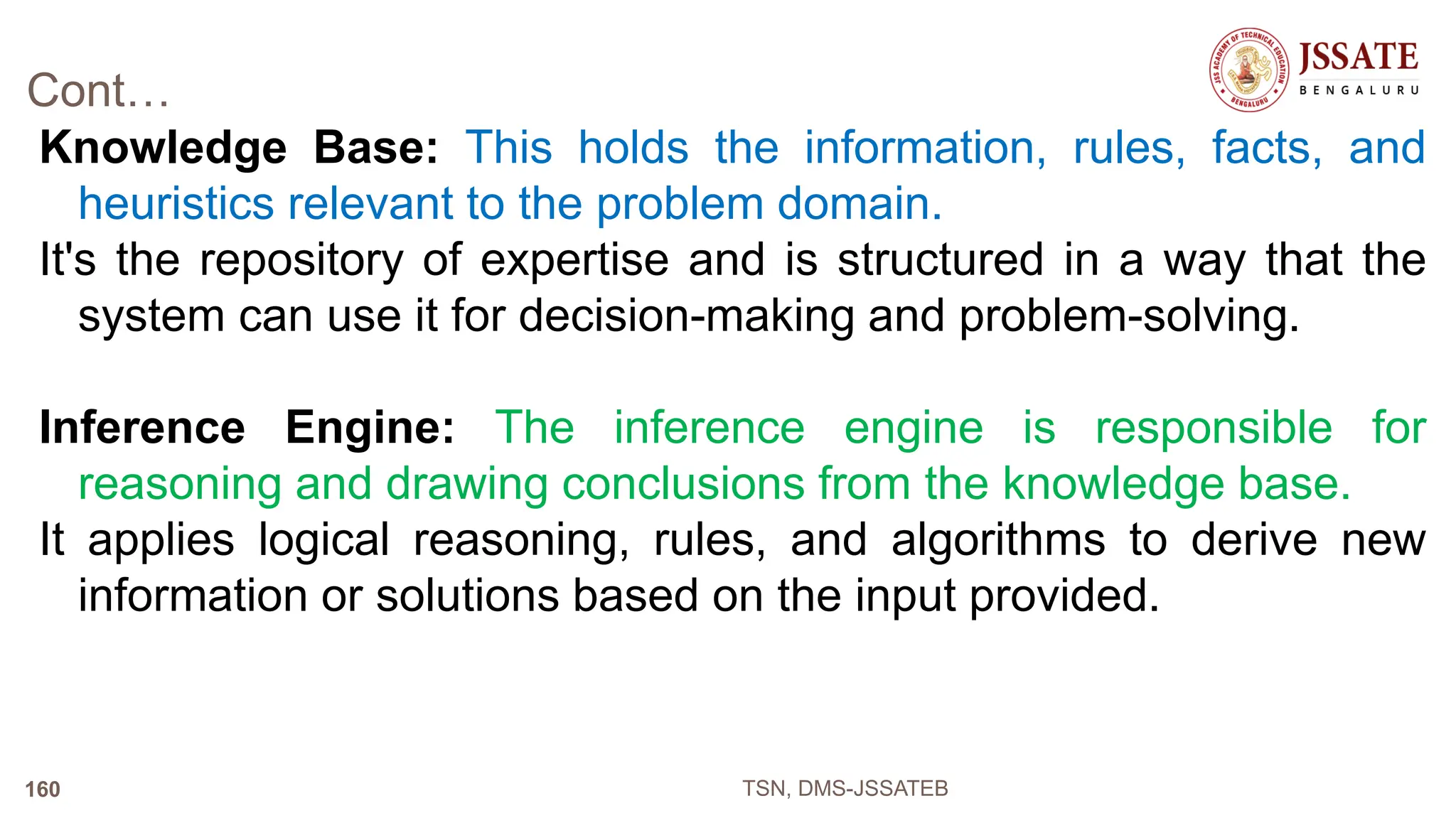
An Office Automation System (OAS) is designed to streamline and automate routine office tasks and processes to improve efficiency and productivity. An OAS integrates various office functions like document management, communication, collaboration, and workflow automation into a unified system. Key characteristics of an OAS include integration of office processes, robust document management tools, automation of routine workflows, platforms for collaborative work, and tools for task management and reporting.